In the fast-paced world of software development, collaboration and efficiency are everything. Imagine a team of five frontend developers working on the same codebase—without a structured system, the risk of overwriting each other’s code or losing progress is high. This is where Version Control comes in, and the two most powerful tools every UI/UX and frontend developer must master are Git and GitHub.
Whether you’re a solo freelancer working on UI/UX projects or part of a larger development team, understanding how Git and GitHub function is a non-negotiable skill in 2025.
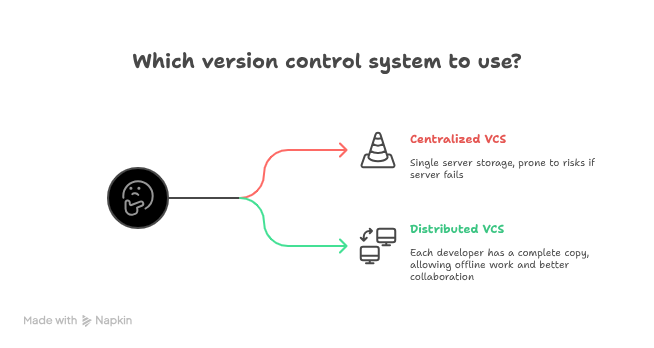
🌐 What is Version Control?
Version control is like a “time machine” for your code. It keeps track of every change you make, allowing you to go back to older versions if needed. This means you can:
- Track every update in your project.
- Work on new features without breaking the main code.
- Collaborate with multiple developers seamlessly.
There are two types of version control systems:
| Type | Description | Examples |
| Centralized VCS | Single server stores all versions; prone to risks if the server fails. | CVS, Subversion (SVN) |
| Distributed VCS | Each developer has a complete copy of the repository, allowing offline work and better collaboration. | Git |
Git belongs to the Distributed Version Control System (DVCS) category, making it one of the most robust tools for modern development.
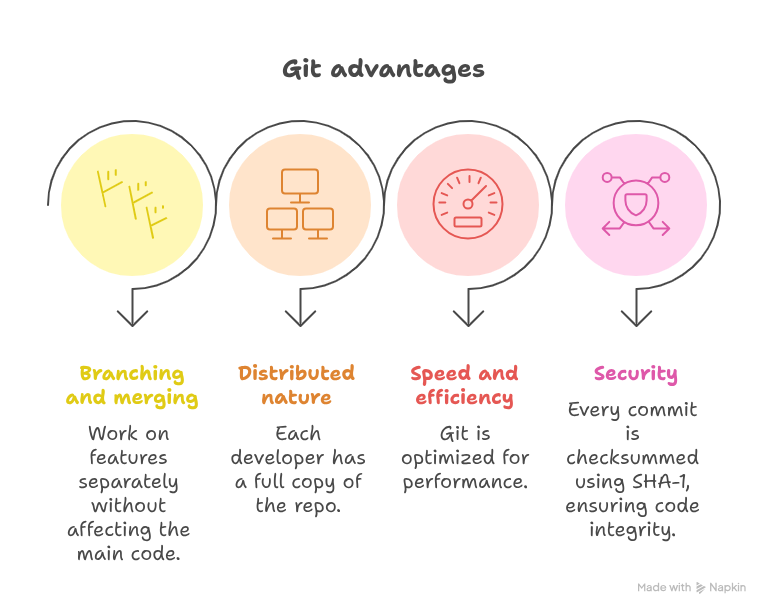
🔑 Why Git is a Developer’s Best Friend
Git is a command-line tool that developers use to manage code history. Some advantages include:
- Branching and merging → Work on features separately without affecting the main code.
- Distributed nature → Each developer has a full copy of the repo.
- Speed and efficiency → Git is optimized for performance.
- Security → Every commit is checksummed using SHA-1, ensuring code integrity.
🚀 Enter GitHub: The Social Network for Developers
While Git manages your code locally, GitHub takes collaboration global. Think of it as a cloud-based hosting service where developers push their Git repositories.
With GitHub, you can:
- Share code with teammates and clients.
- Use Pull Requests for collaborative code review.
- Manage projects with built-in tools like Issues and Projects.
- Showcase your portfolio to recruiters and companies.
At CuriosityTech, when we train fresh developers on frontend technologies, GitHub is introduced as early as week one. It not only helps students practice version control but also builds a professional profile they can proudly share on platforms like LinkedIn or Instagram. Employers often browse through GitHub profiles to gauge real-world coding experience, so your commits and contributions tell your story better than any resume.
🛠️ Git & GitHub Workflow Simplified
Here’s a hierarchical diagram of how Git & GitHub fit into your development process:
Project Start
└── Initialize Repository (git init)
└── Stage Changes (git add .)
└── Commit Changes (git commit -m “message”)
└── Push to GitHub (git push origin main)
└── Collaborate with Team
├── Create Branches
├── Review with Pull Requests
└── Merge Approved Code
This cycle repeats continuously, ensuring your project evolves without chaos.
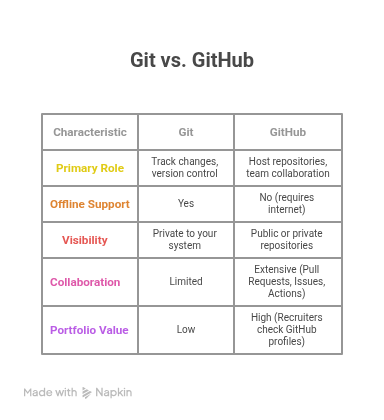
📊 Infographic Breakdown – Git vs GitHub
Git = Local tool for version control
GitHub = Cloud service for collaboration
| Feature | Git (Local) | GitHub (Cloud) |
| Primary Role | Track changes, version control | Host repositories, team collaboration |
| Offline Support | Yes | No (requires internet) |
| Visibility | Private to your system | Public or private repositories |
| Collaboration | Limited | Extensive (Pull Requests, Issues, Actions) |
| Portfolio Value | Low | High (Recruiters check GitHub profiles) |
Practical Example
Imagine you’re designing a responsive landing page for a startup. You create a branch called feature-navbar where you experiment with a new sticky navigation. While you’re testing that, your teammate creates feature-footer. Both of you push your branches to GitHub.
Instead of overwriting each other’s code, GitHub allows you to open a pull request, review the changes, and merge them safely into the main branch. This ensures the production code always remains stable.
At CuriosityTech, we encourage developers to work on multiple features simultaneously using this branch-based workflow, as it mirrors real corporate environments.
🎯 Conclusion
Mastering Git and GitHub is not optional—it’s essential. Whether you are a UI/UX developer polishing micro-interactions or a full-stack engineer deploying APIs, version control ensures your progress is safe, your workflow efficient, and your collaboration seamless.
When you integrate GitHub into your daily routine, you don’t just become a better developer—you build a digital portfolio that speaks volumes about your skills, discipline, and professionalism. Companies like those partnering with CuriosityTech in Nagpur consistently prioritize candidates with solid GitHub activity, because it shows real-world experience, not just textbook knowledge.
So, the next time you start a project, don’t just code—commit, push, and showcase.