Swift is the heart of iOS development. For beginners and even intermediate developers, understanding Swift at a deep level is essential to writing clean, maintainable, and scalable iOS applications. At CuriosityTech.in, our philosophy revolves around combining conceptual mastery with hands-on experience, guiding learners from syntax to complex problem-solving in iOS development.
Why Swift is Essential for iOS Development ?
Swift, introduced by Apple in 2014, is a modern programming language designed for safety, speed, and ease of use. Unlike Objective-C, Swift emphasizes readability and concise syntax, making it ideal for beginners while still being powerful for experienced developers. Apple’s ecosystem—iPhones, iPads, Apple Watch, and Mac—relies on Swift to leverage high-performance frameworks like UIKit, SwiftUI, CoreData, and ARKit.
Learning Swift is not just about writing code; it’s about understanding programming paradigms, memory management, error handling, and performance optimization. At CuriosityTech.in, we encourage learners to internalize Swift fundamentals through interactive exercises, mini-projects, and abstraction-based learning.
Core Concepts of Swift Every iOS Developer Must Know
1. Variables and Constants
Variables are containers for storing values that can change, while constants hold values that remain the same throughout the program. Swift emphasizes type safety, so understanding type inference and explicit typing is essential.
| Concept | Example | Notes |
| Variable | var name = “Curiosity” | Can be changed later |
| Constant | let maxUsers = 100 | Immutable once assigned |
Pro Tip: Using constants wherever possible improves code safety and prevents unintended side-effects in iOS apps, which is crucial when managing multiple UI states or background processes.
2. Data Types and Collections
Swift provides robust primitive types (Int, Double, Bool, String) and collection types like Arrays, Dictionaries, and Sets. Mastery of collections is critical for managing lists, tables, and app data efficiently.
- Arrays: Ordered collections, ideal for lists such as contacts or app notifications.
- Dictionaries: Key-value storage, perfect for user settings or API responses.
- Sets: Unique item collections, used in situations like tags or filters.
At CuriosityTech.in, students practice designing real-world data models using these types before diving into complex frameworks like CoreData.
3. Control Flow: Conditional & Looping
Swift’s control flow enables logic execution:
- If-else statements: Decision-making for UI changes, notifications, or validation.
- Switch statements: Efficient for multiple condition checking.
- Loops (for, while, repeat-while): Useful in animations, data parsing, and batch processing.
Hierarchical Example of Control Flow in Swift for App Logic:
Check if user is logged in
if yes: display home screen
if no: show login
switch user type:
case admin: show admin panel
case guest: show guest dashboard
This hierarchical approach ensures app logic is clear and maintainable.
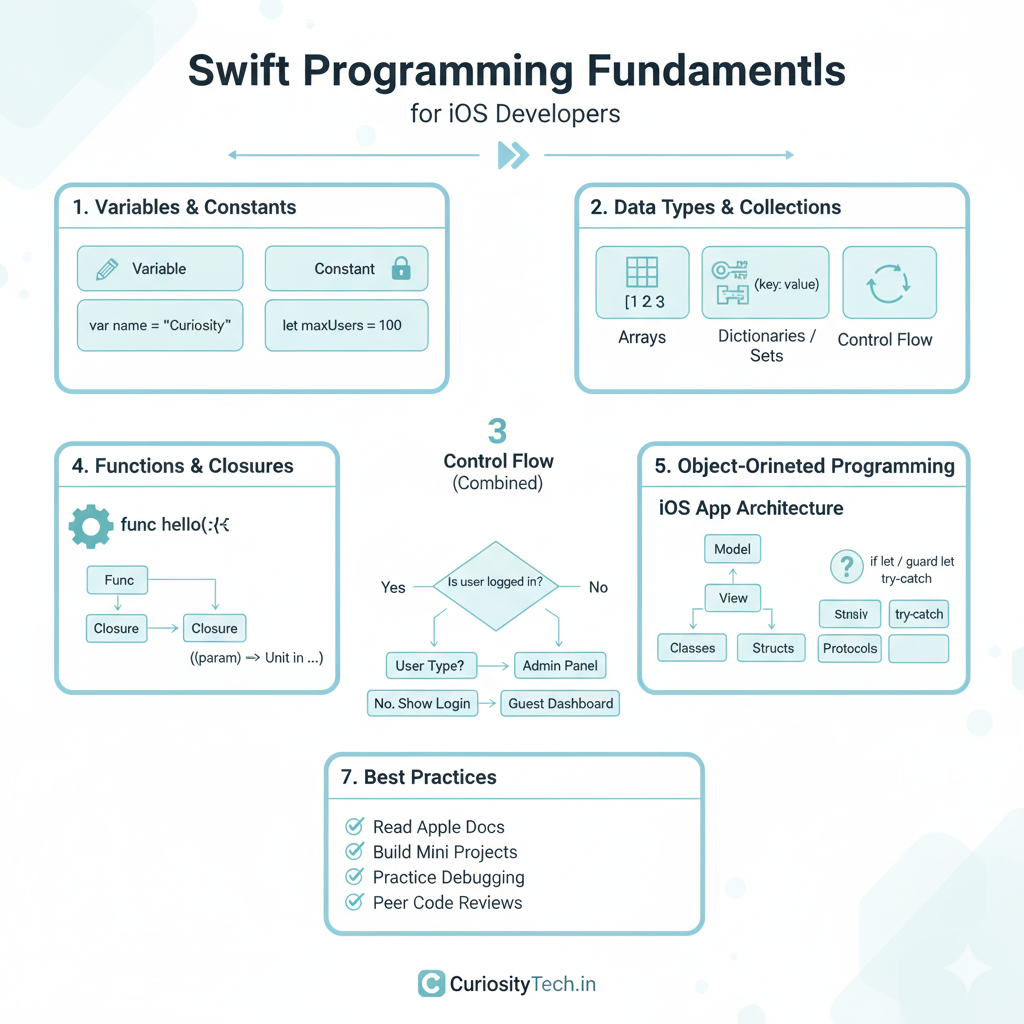
4. Functions and Closures
Functions allow modular, reusable code. Closures are self-contained blocks of functionality. Mastering closures is crucial for asynchronous tasks like API calls, animations, and event handling.
Example Insight: At CuriosityTech.in, we emphasize understanding capturing values in closures, which helps in memory management and avoids retain cycles—a common challenge for beginner iOS developers.
5. Object-Oriented Programming in Swift
Swift supports OOP principles: Classes, Structs, Inheritance, and Protocols.
- Classes: Reference types, useful for complex UI elements or shared data models.
- Structs: Value types, safer for immutable data like app configurations or theme settings.
- Protocols: Define interfaces for delegation patterns, essential in iOS architecture.
Visual Representation:
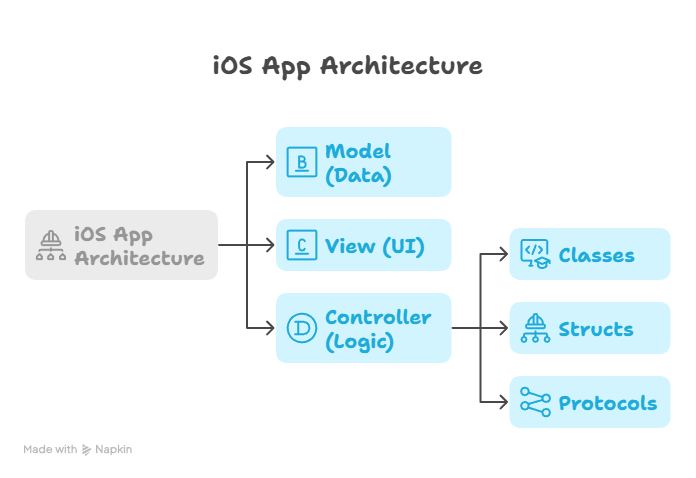
At CuriosityTech.in, we teach learners to combine these principles to create modular, scalable iOS apps.
6. Error Handling & Optionals
Swift introduces optionals to handle the absence of values safely. Proper understanding avoids runtime crashes, especially when dealing with APIs, databases, or user input.
- if let / guard let for safe unwrapping
- try-catch for error handling in networking or file operations
This combination makes Swift both safe and expressive, a major advantage over older languages.
7. Best Practices to Become an Expert
- Read Apple’s Documentation daily to understand new frameworks and updates.
- Build Mini Projects integrating multiple Swift concepts together, such as a task manager app or a simple game.
- Refactor Code Regularly to improve readability and efficiency.
- Practice Debugging and Profiling using Xcode instruments to track memory leaks, CPU usage, and app performance.
- Participate in Peer Code Reviews to understand different approaches and avoid common beginner mistakes.
At CuriosityTech.in, learners are guided through hands-on exercises and real-world project scenarios, accelerating the path from beginner to professional iOS developer.
Conclusion
Swift is the foundation of iOS app development, and mastering its fundamentals is critical for building reliable, high-performance apps. By internalizing concepts like variables, data types, control flow, functions, OOP principles, and error handling, you can progress confidently into advanced topics such as SwiftUI, CoreData, and API integration. Structured learning, practical projects, and guidance from experienced platforms like CuriosityTech.in transform beginners into professional iOS developers ready to tackle complex applications.



