Starting your journey as a Python Full Stack Developer is exciting, but before you dive into writing lines of code, the right tools and environment setup can save you countless hours of frustration. Think of it like preparing a workshop: the cleaner and better organized your space, the smoother your projects will flow. With over two decades of experience in software development, I can tell you that a well-structured setup is the foundation for productivity, collaboration, and long-term growth.
Why Environment Setup Matters?
A poorly configured development environment often leads to dependency conflicts, version mismatches, and wasted time debugging simple setup issues. For Python Full Stack developers, where both frontend and backend systems must work in harmony, having a structured environment is essential for building reliable applications.
Step 1: Install Python & Package Managers
- Python Version: Always go for the latest stable version (currently Python 3.x).
- Package Manager: pip is the default, but for full-stack projects, I recommend pipenv or Poetry for dependency management. They keep your projects isolated and conflict-free.
Tip from industry practice: Use virtual environments (venv) to avoid the “dependency hell” problem.
Step 2: Code Editors & IDEs
Your development environment is incomplete without the right IDE.
Here’s a quick comparison:
| Tool | Best For | Why It’s Recommended |
| VS Code | Beginners & Pros | Lightweight, plugin-rich, integrates easily with Python, React, Django. |
| PyCharm | Backend-heavy devs | Superb debugging, intelligent code completion, Django support. |
| Sublime Text | Quick edits | Fast, minimal, but less powerful for large projects. |
At CuriosityTech, we often guide learners toward VS Code in the early stages, as it provides a balance of simplicity and scalability.
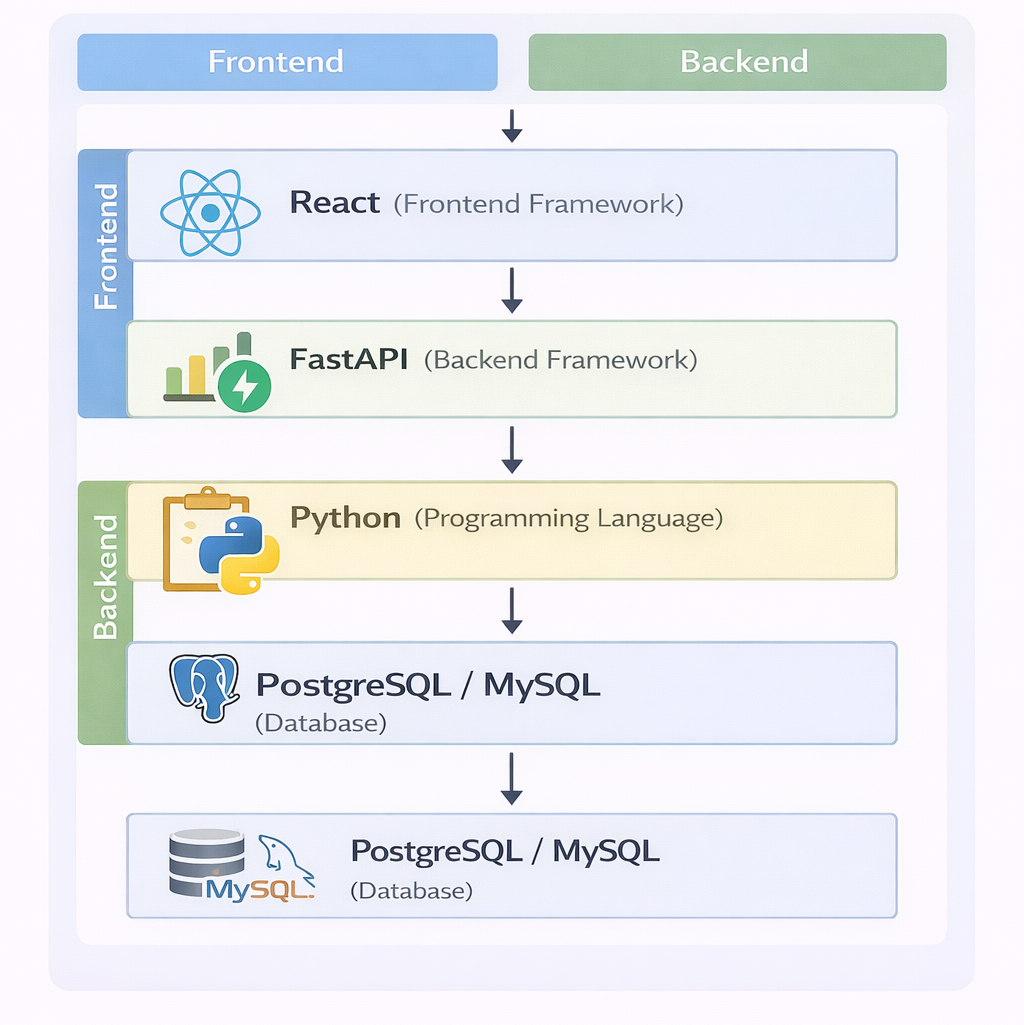
Step 3: Frontend Tools
As a Full Stack Python developer, you’ll need more than Python.
- Node.js & npm/yarn → To manage frontend packages.
- React/Vue (commonly paired with Python backends).
- Chrome DevTools → Debugging frontend interactions.
A good practice is to set up Node.js alongside Python so you can switch between frontend and backend seamlessly.
Step 4: Database Setup
- SQLite → Great for learning and prototyping.
- PostgreSQL/MySQL → Standard for production.
- GUI tools like pgAdmin or DBeaver make database handling easier.
Step 5: Version Control & Collaboration
No developer today can work without Git.
- Install Git and connect to GitHub/GitLab.
- Learn branching strategies (git flow, feature branches) for smooth collaboration.
At CuriosityTech.in, we emphasize Git from day one because it’s not just about coding—it’s about collaborating effectively in real-world projects.
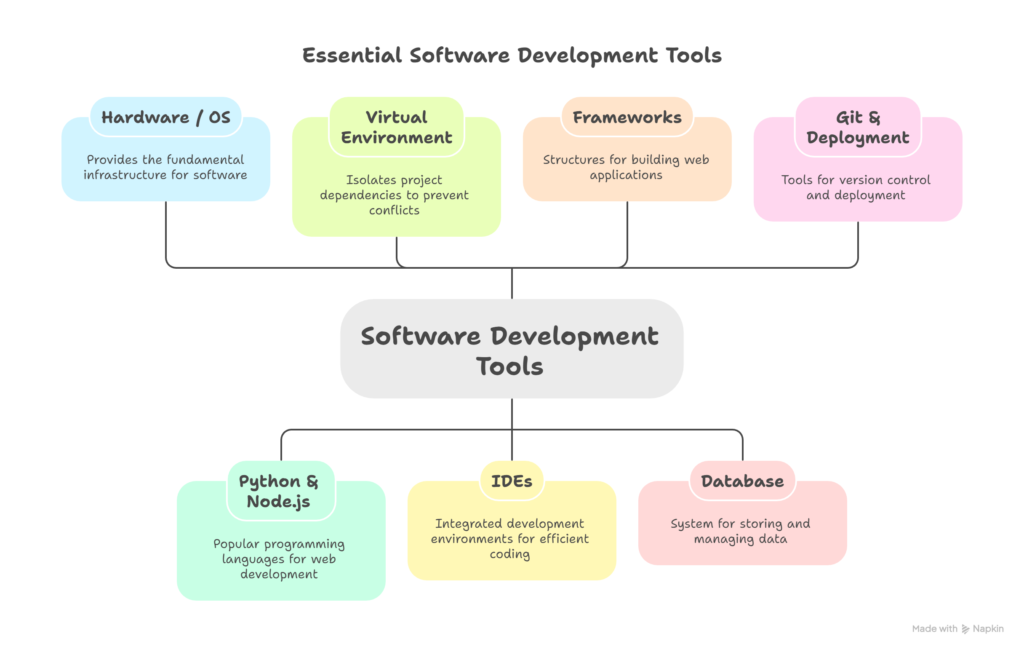
Step 6: Environment Hierarchy
Here’s a simple hierarchy diagram that explains how your tools stack up:
- Hardware / OS :- Foundation for all software tools
- Python & Node.js :- Corre Programming Languages
- Virtual Environment :- Isolated spaces for project dependencies
- IDEs :- Integrated development environment for coding
- Frameworks :- Structure for building web application
- Database :- system for storing and managing data
- Git & Deployment :- Tools for version control and deployment.
Step 7: Extra Utilities
- Docker → For containerized environments (highly recommended for deployment).
- Postman → For API testing.
- Slack/Discord → For team communication.
These aren’t mandatory, but they make your workflow more professional.
Infographic: Ideal Python Full Stack Setup
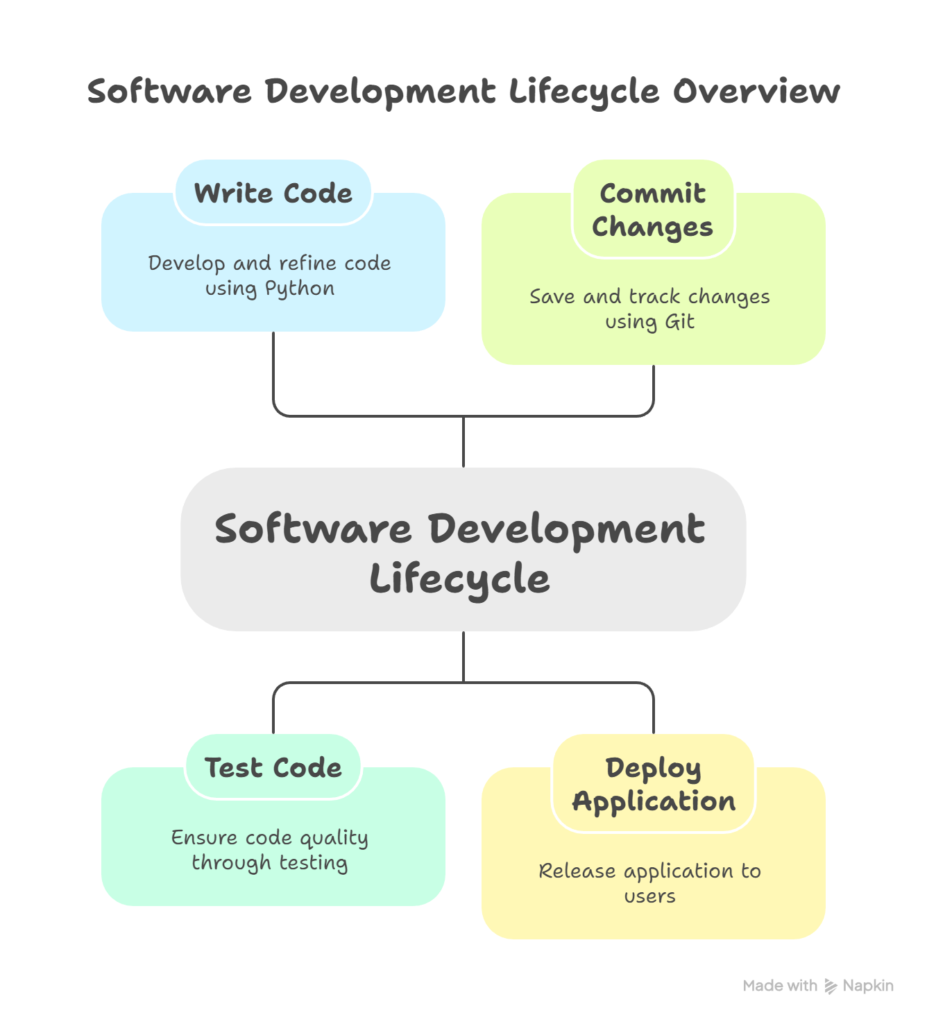
- Write Code :- Develop and refine code using pyhton
- Test Code :- Ensure code quality through testing
- Commit Changes :- Save and track changes using git
- Deploy Application :- Release application to users.
Conclusion
Setting up your environment is not a one-time task—it evolves as your projects grow. The key is starting with the right foundation: Python, Node.js, IDEs, databases, and Git. Over the years, I’ve seen developers waste weeks struggling with poor setups, while others who invested a few hours into proper configuration moved ahead rapidly.
At CuriosityTech, we believe in teaching practical, industry-ready setups from day one. Whether you’re coding in a small project or deploying enterprise-grade applications, a robust environment is your silent partner in success.



