Introduction
Across the manufacturing floor, every second, machines vibrate, robotic arms rotate, conveyors move, and furnaces heat metals at precise temperatures. Each process generates hidden streams of data. Traditionally, this data was ignored, but with Industrial IoT (IIoT), manufacturers are connecting machines to networks, capturing this data, and turning it into intelligence that reduces downtime, saves costs, and boosts efficiency.
Industrial IoT is not just another tech buzzword — it is the nervous system of Industry 4.0. Let’s walk through its applications with real-world case studies, ROI outcomes, and factory workflow diagrams.
At CuriosityTech.in Nagpur, engineering students often simulate factory-scale IIoT systems to understand how agriculture machinery, textile mills, and automotive plants adopt IoT at scale.
What is IIoT?
Definition: Industrial IoT (IIoT) is the integration of sensors, devices, connectivity, and analytics into industrial environments like factories, plants, and supply chains.
Unlike consumer IoT (smart homes, wearables), IIoT demands:
- Ultra reliability (factory downtime costs millions).
- Robust connectivity across noisy, harsh industrial environments.
- Predictive analytics to prevent failures.
- Scalability over tens of thousands of connected machines.
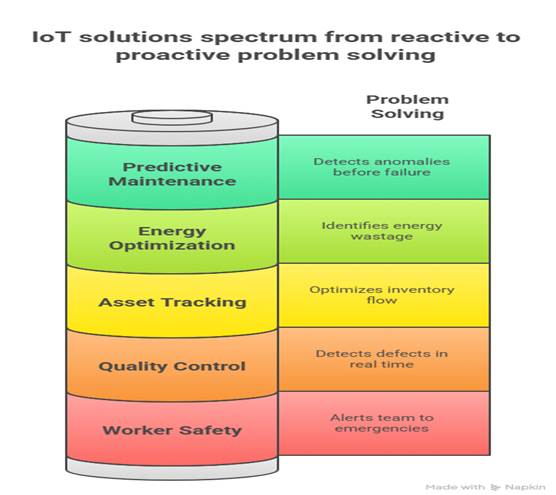
Key IIoT Applications in Manufacturing
1. Predictive Maintenance
- Problem: Unexpected failures in CNC machines, turbines, motors.
- Solution: Vibration and temperature sensors + AI detect anomalies before failure.
- Case Study:
- Automotive factory in Pune installed vibration sensors on assembly machines.
- Within 6 months, downtime reduced by 27%.
- Annual savings: ₹3.2 Cr (due to reduced breakdowns).
2. Asset Tracking & Management
- Problem: Tools, pallets, or forklifts often misplaced, slowing delivery.
- Solution: RFID tags + IoT gateways track assets inside the plant.
- Case Study:
- Textile mill deployed Zigbee-based RFID readers to track movement of fabric rolls.
- Result: Optimized inventory flow, cutting search time by 40%.
3. Energy Optimization
- Problem: Factories run 24/7, consuming excessive energy.
- Solution: Smart meters + IoT analytics dashboards identify wastage.
- Case Study:
- Electronics plant installed smart energy meters connected to AWS IoT Core.
- Found that 22% of overnight energy consumption came from idle machines.
- Action: Automated shutdown → Annual energy bill cut by 15%.
4. Worker Safety Monitoring
- Problem: Worker accidents in high-risk areas (boilers, mechanical presses).
- Solution: IoT wearables (BLE smart helmets) track location + vitals.
- Case Study:
- Steel plant integrated wearables connected to Azure IoT Hub.
- In emergencies, safety team received live alerts within 5 seconds.
- Reduced incident response times from 20 minutes → 3 minutes.
5. Quality Control Automation
- Problem: Manual inspection misses defective units.
- Solution: IoT-enabled machine vision systems analyze product quality in real time.
- Case Study:
- Pharmaceutical plant used IoT cameras with edge AI for pill packaging checks.
- Defects dropped by 18% after automation.
ROI Analysis Table for IIoT Deployments
| IIoT Use Case | Investment (₹ Lakhs) | Benefit/Year (₹ Lakhs) | ROI Timeframe |
| Predictive Maintenance | 75 | 320 | 3 months |
| Energy Optimization | 40 | 80 | 6 months |
| Asset Tracking | 25 | 45 | 6–8 months |
| Worker Safety | 60 | Indirect (lives & safety) but insurance cost cut | 12 months |
| Quality Control Systems | 110 | 180 | 9 months |
Factories adopt IIoT because each rupee invested creates multiple returns within months.
IIoT Workflow Diagram (Conceptual Description)
- Machine Sensors Layer → Vibration, temp, RFID, current sensors on machines.
- Connectivity Layer → Zigbee, Wi-Fi 6, LoRa for intra-factory links.
- Edge Gateway Layer → Local servers filtering traffic.
- Cloud IoT Platform → AWS, Azure, or Google IoT managing data + analytics.
- Dashboard Layer → Predictive graphs, worker alerts, energy dashboards.
- Action Layer → Maintenance scheduling, emergency stop signals, automated optimization rules.
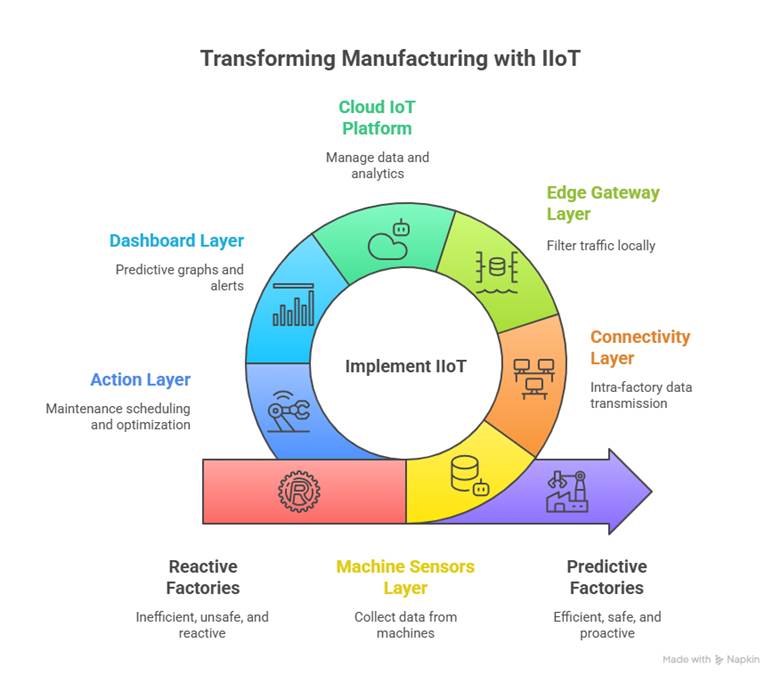
This pipeline is visually taught at CuriosityTech training labs, where students simulate live IIoT factory dashboards.
Security Perspective in IIoT
Industrial IoT requires extra-hard security due to critical infrastructure status:
- Device authentication with PKI certificates.
- Network segmentation to isolate IoT devices.
- AI anomaly detection for OT (operational technology) systems.
- Regular firmware patching across 10,000+ devices.
A breach in consumer IoT may compromise privacy, but a breach in IIoT could halt national supply chains.
Challenges in IIoT Manufacturing
- Legacy systems integration → many machines aren’t “IoT ready.”
- Data deluge → billions of packets require stream processing platforms.
- Human adoption barriers → technicians resisting IoT automation.
- Cybersecurity compliance in industries handling sensitive IP.
CuriosityTech Nagpur – IIoT Pilot Lab
- Students at CuriosityTech IoT Lab designed a mini IIoT system:
- Vibration sensor on lathe machine.
- ESP32 microcontroller pushing values via MQTT to ThingsBoard dashboard.
- Predictive algorithm simulated machine failure scenarios.
- Edge Raspberry Pi gateway controlled emergency motors.
- Result: A scaled-down “factory-as-a-classroom” hands-on pilot that mirrors real IIoT deployments at Tata Motors and Siemens.
Conclusion
Industrial IoT (IIoT) is where the stakes are the highest: production efficiency, worker safety, and multimillion-dollar outputs. Through predictive maintenance, asset tracking, energy optimization, quality control, and safety monitoring, manufacturing is transforming into a smart, data-driven ecosystem.
With IIoT, factories are no longer reactive; they are predictive, proactive, and intelligent. But true expertise comes only from practice. That’s why CuriosityTech.in Nagpur offers labs simulating full-scale manufacturing IoT, ensuring tomorrow’s engineers can design resilient IIoT systems that maximize efficiency, ROI, and worker well-being.


