Introduction
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is rapidly becoming the backbone of modern manufacturing, energy, utilities, and critical infrastructure systems in 2025. However, the interconnectedness that powers advanced IIoT also introduces a vast attack surface for cyber threats. These threats can cause production halts, safety incidents, data breaches, and critical infrastructure failure.
This detailed guide breaks down the layered security best practices necessary to protect IIoT environments, covering device, network, cloud, and operational aspects — informed by the latest expert industry recommendations and standards, while highlighting practical defenses employed by leading organizations.
Unique Security Challenges in IIoT
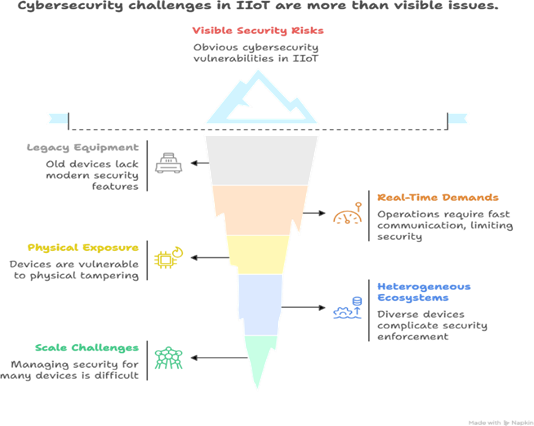
Five Building Blocks of IIoT Security
1. Device Security
- Secure Boot & Hardware Root of Trust: Devices verify firmware authenticity before execution, blocking unauthorized code.
- Unique Certificate-Based Authentication: Each device uses X.509 certificates and private keys for identity verification.
- Firmware Integrity & Secure OTA Updates: Cryptographically signed firmware images, delivered and verified securely, enable patching vulnerabilities.
- Trusted Platform Modules (TPM): Hardware elements securely store keys and verify device integrity, guarding against tampering.
2. Network Security
- Encrypted & Authenticated Communications: Emphasize MQTT over TLS, OPC UA over TLS, and HTTPS to protect data in transit.
- Legacy Protocol Security Upgrades: Replace or encapsulate insecure protocols like Modbus with secure versions or gateways.
- Network Segmentation & Isolation: Purdue model zones and DMZs prevent lateral movement in case of breach.
- Secure IoT Gateways: Act as intermediaries enforcing security policies between OT devices and the cloud.
3. Monitoring and Detection
- Implement specialized OT Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS).
- Real-time aggregation of security events in SIEM platforms, correlating IT & OT telemetry.
- Passive network monitoring to detect anomalies without disrupting operations.
- AI-driven behavioral anomaly detection to identify threats proactively.
4. Operations & Incident Response
- Establish IIoT-tailored Incident Response Plans with rapid containment and recovery strategies.
- Conduct continual security audits, penetration tests focused on OT protocols and firmware.
- Maintain up-to-date device inventories and vulnerability assessments.
- Provide comprehensive security training for OT operators and IT staff.
5. Compliance and Standards
- Adhere to IEC 62443 series standards for industrial control systems security.
- Follow NIST Cybersecurity Frameworks specifically adapted for Critical Infrastructure.
- Implement organizational policies meeting HIPAA, GDPR, ISO 27001 as applicable.
Layered IIoT Security Architecture Overview
| Layer | Primary Security Measures |
| Device | Secure boot, TPMs, signed firmware, unique credentials |
| Network | TLS encryption, segmentation, secure gateways |
| Monitoring | IDS/IPS, SIEM integration, AI anomaly detection |
| Cloud | Role-based access, audit logging, encryption at rest |
| Applications | MFA, API security, secure dashboards |
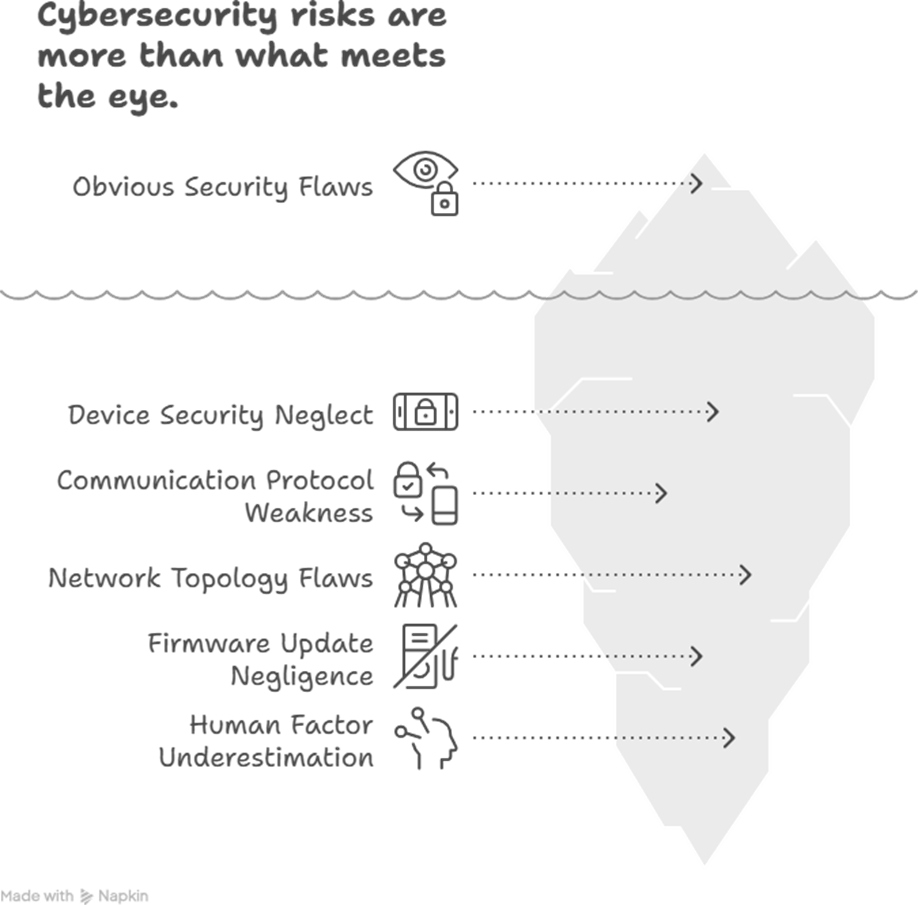
Common IIoT Security Pitfalls to Avoid
Real-World IIoT Security Successes
- Automotive plants successfully block ransomware by network segmentation and behavior-based IDS.
- Oil & gas refineries deploy TPM-backed devices for critical SCADA systems preventing firmware tampering.
- Food production factories leverage SIEM integrated with anomaly detection to quickly identify insider threats.
CuriosityTech Nagpur IIoT Security Labs
Training at CuriosityTech.in emphasizes hands-on practice:
- Configuring MQTT brokers secured with TLS and device certificate management.
- Simulating MQTT flooding and detecting abnormal traffic using SIEM dashboards.
- Architecting Purdue model network segmentation using physical and virtual firewalls.
- Incident response drills focused on threat containment in factory environments.
Conclusion
In 2025, secure Industrial IoT demands a defense-in-depth, multi-layered approach addressing device authenticity, encrypted communication, stringent network segmentation, active monitoring, and prepared incident response. The stakes are high—production line interruptions, safety hazards, and exposure of proprietary data—making cybersecurity a strategic imperative.
Educating and equipping IIoT engineers through continuous hands-on training, as done at CuriosityTech.in Nagpur, is critical to building resilient, safe industrial ecosystems prepared for evolving cyber threats.
