Introduction
Modern web applications increasingly demand real-time interactivity, such as live chat, notifications, dashboards, or collaborative tools. In MERN Stack development, WebSockets enable bi-directional communication between the client (React) and server (Node.js + Express), going beyond traditional HTTP request-response patterns.
CuriosityTech.in emphasizes real-world applications of WebSockets, allowing learners to implement live features in MERN projects and understand the architecture of real-time systems.
Understanding WebSockets
Unlike HTTP, which is request-response based, WebSockets establish a persistent connection:
- Both client and server can send and receive messages anytime.
- Reduces overhead compared to repeated HTTP requests (polling).
- Ideal for chat apps, notifications, live dashboards, multiplayer apps.
Diagram – WebSocket Flow:
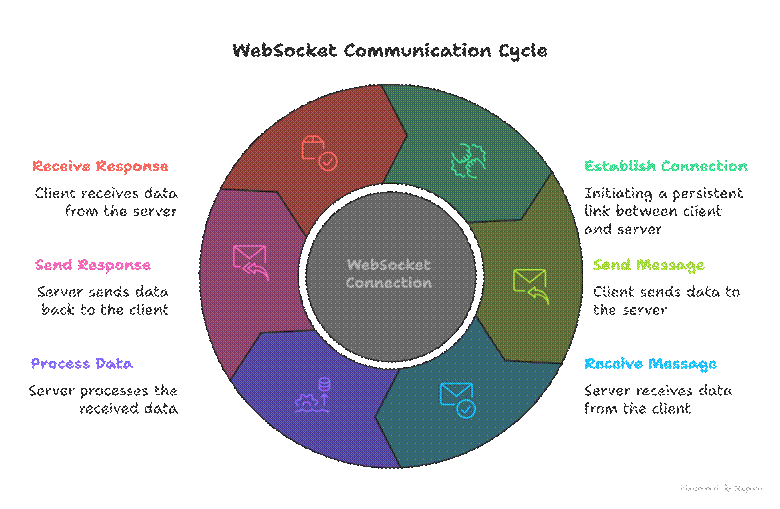
Step 1: Setting Up WebSockets with Socket.IO
Socket.IO simplifies real-time communication in MERN applications.
npm install socket.io
npm install socket.io-client
Step 2: Backend – Node.js + Express + Socket.IO
const express = require(‘express’);
const http = require(‘http’);
const { Server } = require(‘socket.io’);
const app = express();
const server = http.createServer(app);
const io = new Server(server, { cors: { origin: ‘*’ } });
io.on(‘connection’, (socket) => {
console.log(‘User connected:’, socket.id);
socket.on(‘sendMessage’, (msg) => {
io.emit(‘receiveMessage’, msg); // broadcast message to all clients
});
socket.on(‘disconnect’, () => {
console.log(‘User disconnected:’, socket.id);
});
});
server.listen(5000, () => console.log(‘Server running on port 5000’));
Step 3: Frontend – React + Socket.IO Client
import { useEffect, useState } from ‘react’;
import { io } from ‘socket.io-client’;
const socket = io(‘http://localhost:5000’);
function ChatApp() {
const [message, setMessage] = useState(”);
const [chat, setChat] = useState([]);
useEffect(() => {
socket.on(‘receiveMessage’, (msg) => setChat((prev) => […prev, msg]));
}, []);
const sendMessage = () => {
socket.emit(‘sendMessage’, message);
setMessage(”);
};
return (
<div>
<h1>Live Chat</h1>
<input value={message} onChange={(e) => setMessage(e.target.value)} placeholder=”Type a message” />
<button onClick={sendMessage}>Send</button>
<div>
{chat.map((msg, index) => <p key={index}>{msg}</p>)}
</div>
</div>
);
}
export default ChatApp;
Step 4: Combining WebSockets with MongoDB
For persistent chat history:
- Store messages in MongoDB via Mongoose.
- Emit messages to clients using Socket.IO.
Example Table – Real-Time Chat Flow:
| Event | Action | Backend | Frontend |
| User sends message | Emit sendMessage event | Listen, save to MongoDB | Update chat array via receiveMessage |
| Server broadcasts | Send message to all connected clients | io.emit(‘receiveMessage’) | Append message to UI |
| User disconnects | Notify others or handle cleanup | socket.on(‘disconnect’) | Optional UI notification |
Step 5: Best Practices for Real-Time MERN Apps
- Manage Connections Efficiently: Limit connections and handle disconnects gracefully.
- Use Namespaces and Rooms: For private chats or group channels.
- Validate Messages: Prevent XSS and spam.
- Combine with Authentication: Verify users via JWT before establishing WebSocket connection.
- Optimize Performance: Use message batching, compression, and limit broadcast to relevant clients.
Step 6: Becoming an Expert in Real-Time MERN Apps
- Understand WebSocket architecture and differences from HTTP.
- Master Socket.IO events, rooms, and namespaces.
- Integrate MongoDB for persistent data.
- Secure WebSockets using JWT and token verification.
- Build real-world apps like live dashboards, chat systems, notifications, or collaborative tools.
CuriosityTech.in provides hands-on projects where learners implement real-time features, connect frontend and backend efficiently, and apply best practices for production-ready MERN applications.
Infographic Suggestion
Title: “Real-Time Communication Flow in MERN with WebSockets”
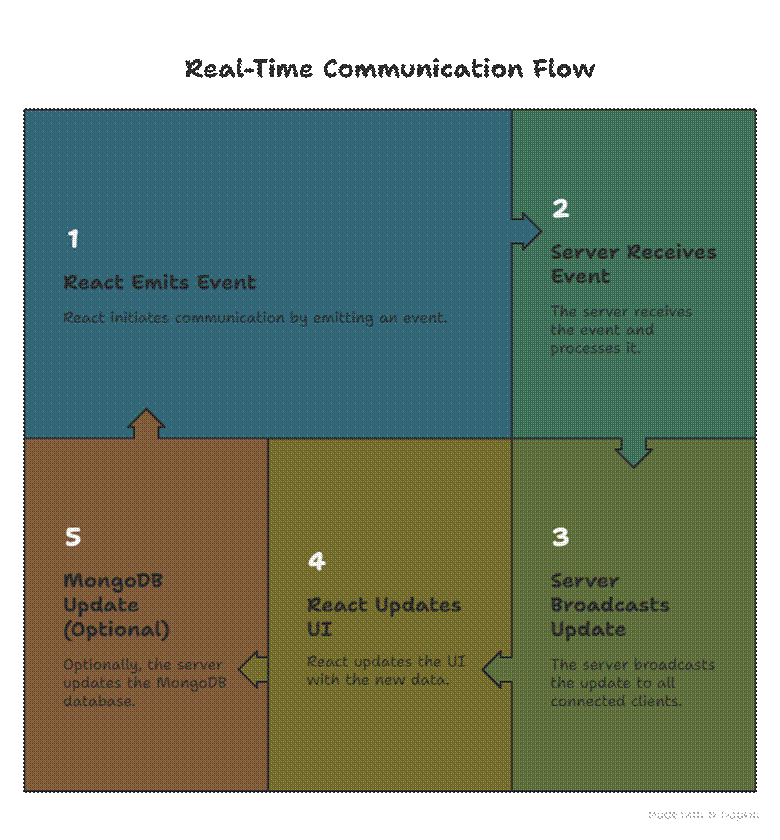
Conclusion
WebSockets are essential for building interactive, real-time applications in MERN Stack. Mastery of Socket.IO, integration with MongoDB, and secure connection management enables developers to create live chat apps, notifications, and dynamic dashboards. CuriosityTech.in provides guided projects to practice these concepts and build professional-level MERN applications.



