Introduction
In today’s connected world, mobile apps rarely function in isolation. Whether it’s fetching weather data, displaying social feeds, or handling e-commerce inventories, apps often rely on external servers. This is where APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) come into play, acting as bridges between your app and remote data sources.
In Android development, Retrofit is one of the most popular libraries for consuming APIs efficiently. At CuriosityTech.in, our Android courses emphasize integrating APIs using Retrofit in real-world apps, ensuring learners understand both the theory and hands-on implementation.
Main Content
Understanding APIs in Android
- API Basics: An API allows apps to communicate with servers over the network using HTTP requests.
- RESTful APIs: Most Android apps interact with REST APIs that use standard HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE) and JSON for data exchange.
- Use Case Example: Fetching a list of users from https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users.
Why Retrofit?
- Retrofit simplifies network requests and response parsing.
- Supports Kotlin coroutines, RxJava, and OkHttp for advanced networking.
- Reduces boilerplate compared to HttpUrlConnection or Volley.
Setting Up Retrofit
- Add dependencies in build.gradle:
implementation ‘com.squareup.retrofit2:retrofit:2.9.0’
implementation ‘com.squareup.retrofit2:converter-gson:2.9.0’
- Create API Interface:
interface ApiService {
@GET(“users”)
suspend fun getUsers(): List<User>
}
- Initialize Retrofit:
val retrofit = Retrofit.Builder()
.baseUrl(“https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/”)
.addConverterFactory(GsonConverterFactory.create())
.build()
val apiService = retrofit.create(ApiService::class.java)
- Fetch Data in Coroutine:
lifecycleScope.launch {
try {
val users = apiService.getUsers()
users.forEach { Log.d(“API”, it.name) }
} catch (e: Exception) {
Log.e(“API”, “Error fetching users”, e)
}
}
Best Practices for API Integration
- Error Handling: Handle timeouts, 4xx/5xx errors, and null responses gracefully.
- Threading: Always make network requests off the main thread using coroutines or RxJava.
- Caching: Use OkHttp interceptors to cache responses and improve performance.
- Security: Never hardcode API keys; use encrypted storage or build configs.
Practical Example
Imagine you’re building a news app. Using Retrofit, your app can fetch the latest articles from a remote API, parse the JSON response, and display headlines dynamically. You can combine RecyclerView to present the data, offering users a seamless experience without blocking the UI.
At CuriosityTech.in, learners build real-world projects like chat apps, weather apps, and e-commerce dashboards, all powered by API integration. Our mentors guide students to understand networking nuances, JSON parsing, and error handling, bridging the gap between theory and professional development.
How to Become an Expert
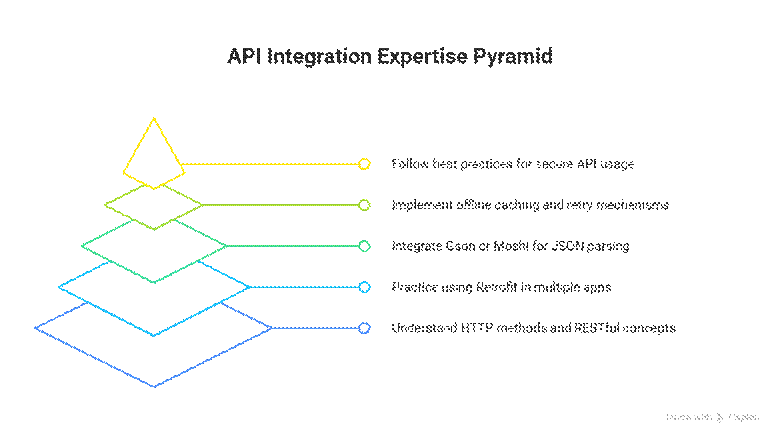
Conclusion
API integration is a cornerstone of modern Android apps. Retrofit, combined with Kotlin coroutines, allows developers to fetch, parse, and display data efficiently while keeping the UI responsive. Mastering APIs not only makes your apps dynamic but also opens doors to more complex functionalities like real-time chat, push notifications, and cloud synchronization.
Platforms likeCuriosity Tech provide hands-on exercises, guided projects, and mentorship to help you become proficient in API integration and modern Android development techniques.



