React has become the go-to library for building dynamic and interactive web applications. One of the core strengths of React is its ability to seamlessly fetch and integrate data from external sources using APIs. Today, we’ll explore how UI/UX developers and frontend engineers can effectively work with APIs, manage asynchronous data, and build robust React applications. At CuriosityTech.in, we often emphasize real-world projects where fetching data dynamically is essential for creating interactive dashboards, modern user interfaces, and responsive applications.
What is an API and Why React Needs It ?
An API (Application Programming Interface) allows your application to communicate with external services or back-end systems. Whether it’s fetching weather information, social media feeds, or product listings, APIs enable your frontend to stay dynamic and up-to-date without hardcoding static content.
React relies heavily on APIs because it allows developers to:
- Render dynamic content seamlessly
- Keep the UI responsive while fetching data asynchronously
- Build scalable applications with reusable components
Step-by-Step Guide to Fetching Data in React
Fetching data in React is usually done using fetch, axios, or other HTTP clients. Let’s break down the steps:
1. Setting Up Your React Component
import React, { useState, useEffect } from “react”;
const DataFetcher = () => {
const [data, setData] = useState([]);
const [loading, setLoading] = useState(true);
useEffect(() => {
fetch(“https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts”)
.then((response) => response.json())
.then((data) => {
setData(data);
setLoading(false);
})
.catch((error) => console.error(“Error fetching data:”, error));
}, []);
if (loading) return <p>Loading data…</p>;
return (
<div>
{data.map((item) => (
<div key={item.id}>
<h3>{item.title}</h3>
<p>{item.body}</p>
</div>
))}
</div>
);
};
export default DataFetcher;
Explanation:
- useState manages the data and loading state
- useEffect fetches the data once the component mounts
- The UI updates automatically once the data is retrieved
2. Using Axios for Better HTTP Requests
Axios is a popular library for making HTTP requests with more functionality:
import axios from “axios”;
import React, { useState, useEffect } from “react”;
const AxiosDataFetcher = () => {
const [data, setData] = useState([]);
const [loading, setLoading] = useState(true);
useEffect(() => {
axios
.get(“https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts”)
.then((response) => {
setData(response.data);
setLoading(false);
})
.catch((error) => console.error(“Error fetching data:”, error));
}, []);
if (loading) return <p>Loading posts…</p>;
return (
<div>
{data.map((item) => (
<div key={item.id}>
<h3>{item.title}</h3>
<p>{item.body}</p>
</div>
))}
</div>
);
};
export default AxiosDataFetcher;
Key Benefits of Axios:
- Automatic JSON parsing
- Handles errors and request cancellations efficiently
- Cleaner syntax for POST requests
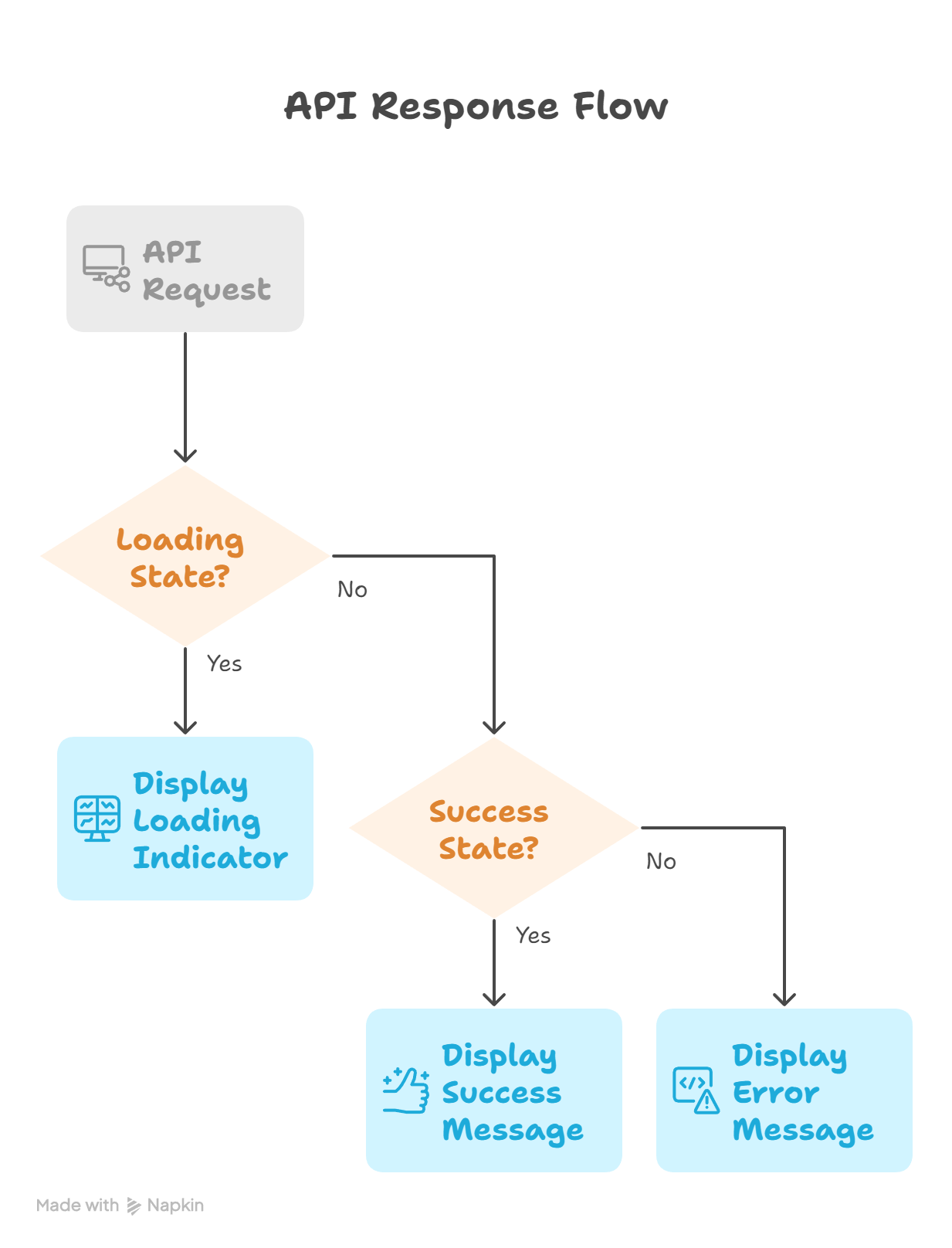
3. Handling API Response States
To make a robust React application, you must handle loading, success, and error states effectively. Here’s a visual hierarchy of API response handling:
4. Best Practices for API Integration in React
- Use Environment Variables: Keep API keys secure in .env files.
- Debounce Requests: Avoid sending API calls on every keystroke; use lodash.debounce for efficiency.
- Error Handling: Always catch errors to prevent UI crashes.
- Caching: Implement caching for frequently accessed data using libraries like React Query.
- Loading Feedback: Always show loaders or skeleton screens to enhance UX.
5. Infographic: API Integration in React
Real-World Example
Imagine building a blog dashboard where all posts are fetched from an API:
- Users can filter posts dynamically
- Data updates in real-time without page reloads
- Loading indicators and error messages enhance trust and usability
This approach reflects modern UI/UX standards followed in professional projects at CuriosityTech.in, where dynamic and responsive designs are key to engaging users.
Conclusion
Fetching data in React is more than just making HTTP requests—it’s about creating dynamic, responsive, and user-friendly interfaces. By understanding API integration, handling response states, and following best practices, developers can create applications that are both functional and delightful to use. Incorporating these techniques, as practiced by teams at CuriosityTech.in, can significantly elevate your frontend projects and UX quality.



