Modern iOS apps rarely operate in isolation. Most applications—from social media to e-commerce—rely heavily on network communication to fetch data, sync content, and interact with backend servers. Understanding networking fundamentals is therefore crucial for every iOS developer, and mastering URLSession, Swift’s primary API for HTTP networking, is a key milestone. At CuriosityTech.in, we emphasize learning networking not just as code syntax but as architectural thinking, integrating robust networking patterns for real-world app reliability and performance.
Why Networking Matters in iOS Development
Networking allows iOS apps to:
- Fetch data from APIs (REST, GraphQL)
- Send user-generated content (forms, posts, uploads)
- Synchronize data between devices
- Integrate with third-party services (payment gateways, analytics, social login)
Failing to properly manage network calls can result in poor performance, slow apps, or crashes. That’s why understanding URLSession, request handling, and asynchronous programming is fundamental for professional iOS developers.
Understanding URLSession
URLSession is the backbone of networking in Swift. It allows developers to perform HTTP requests asynchronously, handle responses, and manage background downloads/uploads efficiently.
Core Components of URLSession:
- URLSession – The central object managing tasks and sessions.
- URLSessionTask – Represents a single network request (data, upload, or download).
- URLRequest – Encapsulates the details of the HTTP request (method, headers, body).
- URLResponse & HTTPURLResponse – Represent server responses, including status codes.
- Error Handling – Handles network failures, timeouts, and invalid responses.
Diagram of URLSession Workflow:
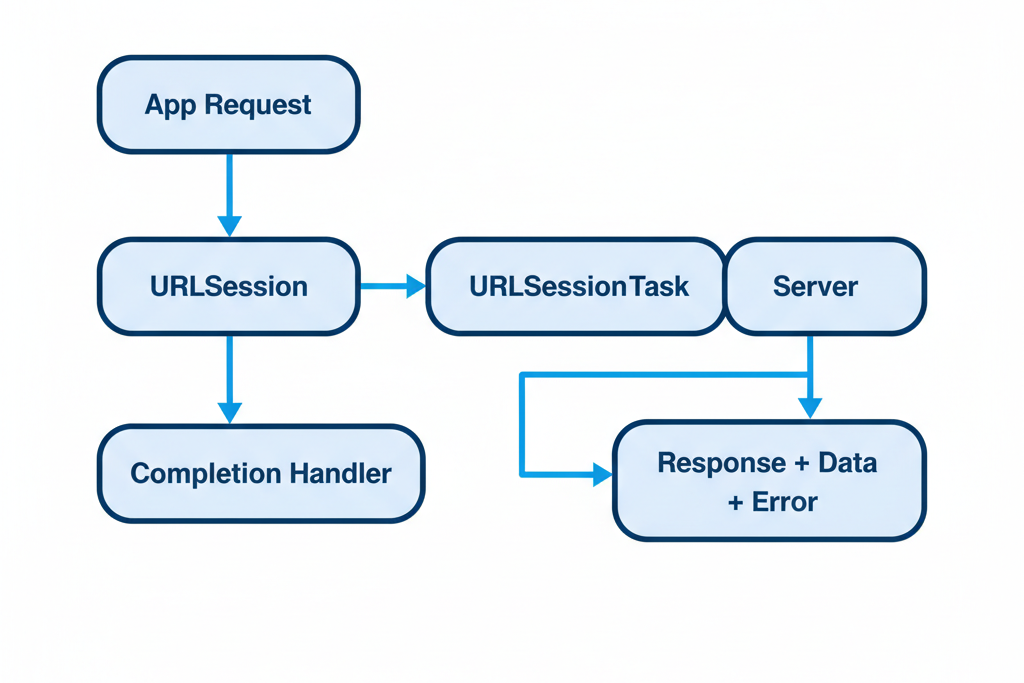
At CuriosityTech.in, learners visualize this flow before implementing network calls, which ensures clean architecture and maintainable code.
Making a Simple API Request
Step 1: Define the URL
guard let url = URL(string: “https://api.curiositytech.in/posts”) else { return }
Step 2: Create a URLSessionTask
let task = URLSession.shared.dataTask(with: url) { data, response, error in
guard let data = data, error == nil else { return }
// Process data
}
task.resume()
Step 3: Handle Response
- Convert data to Swift objects using JSONDecoder
- Check status codes via HTTPURLResponse
- Handle errors appropriately
Practical Tip: Always perform UI updates on the main thread after fetching data:
DispatchQueue.main.async {
self.tableView.reloadData()
}
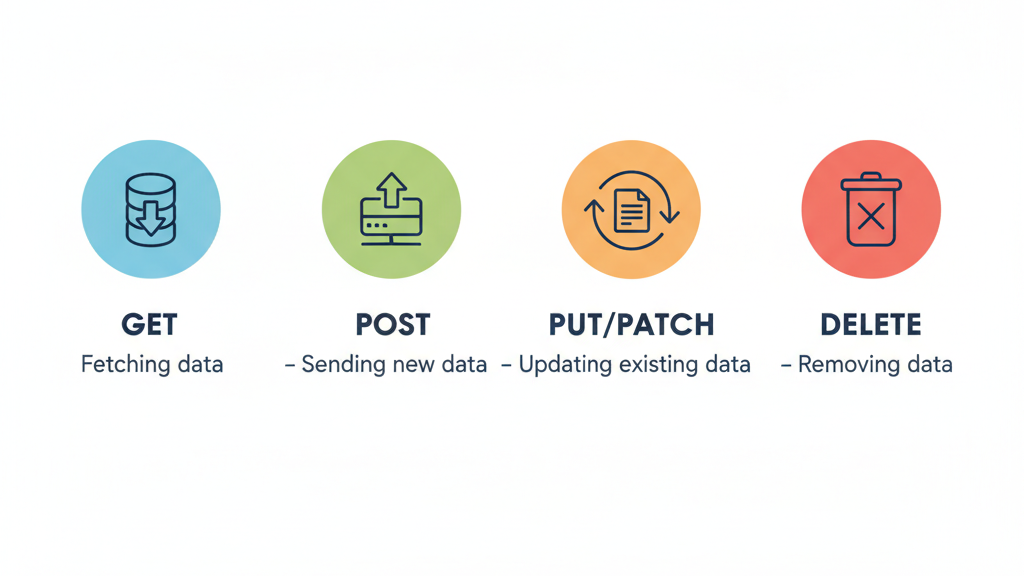
Working with HTTP Methods
- GET – Fetching data
- POST – Sending new data
- PUT/PATCH – Updating existing data
- DELETE – Removing data
Example: Sending POST Request with JSON Body:
var request = URLRequest(url: url)
request.httpMethod = “POST”
request.setValue(“application/json”, forHTTPHeaderField: “Content-Type”)
request.httpBody = try? JSONEncoder().encode(newPost)
Proper HTTP handling ensures data integrity, API compliance, and security.
Networking Best Practices
- Use Codable Models: Swift’s Codable protocol simplifies JSON parsing and reduces boilerplate code.
- Handle Errors Gracefully: Network failures, timeouts, and invalid responses must be anticipated.
- Use Background Sessions: For long downloads/uploads, URLSession background configuration keeps tasks alive even when the app is closed.
- Caching: Reduce repeated API calls by caching responses using URLCache.
- Security: Always use HTTPS, validate SSL certificates, and consider token-based authentication.
CuriosityTech.in Approach: Students build apps that interact with live APIs, implement caching, handle errors, and observe network performance metrics, teaching them industry-grade practices.
Asynchronous Networking
Modern networking relies heavily on asynchronous operations. URLSession uses completion handlers, but Swift also supports async/await for cleaner, readable code.
Async/Await Example:
func fetchPosts() async throws -> [Post] {
let (data, _) = try await URLSession.shared.data(from: url)
let posts = try JSONDecoder().decode([Post].self, from: data)
return posts
}
Async/await reduces callback hell and makes complex networking flows easier to maintain, a skill emphasized in advanced CuriosityTech.in modules.
Testing and Debugging Network Calls
- Use Postman or similar tools to verify API endpoints.
- Simulate Slow Networks: Xcode’s Network Link Conditioner allows testing app behavior under latency or loss.
- Log Requests & Responses: Helps in debugging unexpected API behavior.
- Unit Test Networking Code: Mock URLSession responses to test parsing and error handling without hitting real servers.

Becoming an Expert
- Understand API Contracts: Know request/response formats, headers, and status codes.
- Master Async Patterns: Combine completion handlers, async/await, and Combine for reactive networking.
- Optimize Performance: Use background sessions, batching, and caching for scalability.
- Secure APIs: Implement OAuth, JWT, and SSL pinning.
- Integrate Third-Party Libraries: Alamofire or Moya can simplify complex networking tasks while maintaining control.
At CuriosityTech.in, learners practice end-to-end networking, building apps that fetch, display, update, and delete data from real APIs while maintaining performance and security.
Conclusion
Networking is the lifeline of modern iOS apps. By mastering URLSession, HTTP methods, async operations, error handling, and performance optimization, developers can create apps that are responsive, reliable, and professional. Combining these skills with Core Data, Swift fundamentals, and UI mastery ensures your iOS applications are robust, scalable, and user-friendly, giving you a competitive edge in app development.



