Security is the foundation of cloud computing. On Day 13, we explore AWS security essentials, focusing on encryption, key management, compliance frameworks, and security best practices.
At Curiosity Tech, learners understand that security isn’t just configuration—it’s designing systems that are secure by default, resilient, and compliant with industry standards.
1. AWS Shared Responsibility Model
AWS uses a shared responsibility model:
| Responsibility | AWS | Customer |
| Infrastructure Security | Physical servers, networking, and facilities | N/A |
| Platform Security | Hypervisors, storage, and virtualization | N/A |
| Data Protection | Encryption, key management | Encrypt data, manage access, compliance |
| Configuration | N/A | Configure security groups, IAM policies, monitoring |
Expert Tip: Beginners often assume AWS handles all security. Understanding the shared responsibility model is crucial for avoiding misconfigurations and ensuring compliance.
2. Encryption Essentials in AWS
Encryption protects data at rest and in transit.
a) Data at Rest
- AWS Services Supporting Encryption: S3, EBS, RDS, DynamoDB, Redshift
- Encryption Options:
- Server-Side Encryption(SSE-S3/SSE-KMS) : Managed by AWS
- Customer-Managed Keys (CMK) in KMS : Full control keys
- Transparent Data Encryption (TDE) for RDS/Aurora
b) Data in Transit
- Protocols: TLS/SSL for HTTP/S, VPN for private connectivity
- Services: CloudFront, ELB, API Gateway
CuriosityTech.in Insight: Learners implement S3 bucket encryption and HTTPS for CloudFront, ensuring end-to-end security for web applications.
3. AWS Key Management Service (KMS)
AWS KMS is a centralized service for creating, managing, and auditing cryptographic keys.
| Feature | Description | Example |
| CMK | Customer Master Key | CuriosityTechCMK |
| Key Policies | Permissions for who can use keys | Allow Lambda function to decrypt S3 objects |
| Automatic Rotation | Rotate keys every 1 year | Ensures key security best practices |
| Audit via CloudTrail | Track key usage | Detect unauthorized access |
Expert Tip: Use least privilege access for keys to minimize security risks.
4. Identity & Access Management (IAM) for Security
IAM controls who can do what in AWS.
Best Practices:
- Use least privilege: Grant only necessary permissions
- Enable MFA (Multi-Factor Authentication) for all users
- Avoid using root account for daily operations
- Use IAM roles for services instead of access keys
Example Workflow:
- EC2 instance needs S3 access → assign IAM role with S3 read/write policy
- Lambda function processes data → assign execution role with KMS decrypt permissions
5. Compliance and Regulatory Standards
AWS provides services compliant with global standards:
| Standard | Description |
| ISO 27001 | Information security management system |
| SOC 1/2/3 | Service Organization Controls reporting |
| HIPAA | Health data protection |
| PCI DSS | Payment card data security |
| GDPR | Data protection and privacy for EU citizens |
Curiosity Tech Insight: Beginners simulate compliance audits using CloudTrail logs, Config rules, and Security Hub, learning how to meet enterprise-level security standards.
6. Security Architecture Diagram:
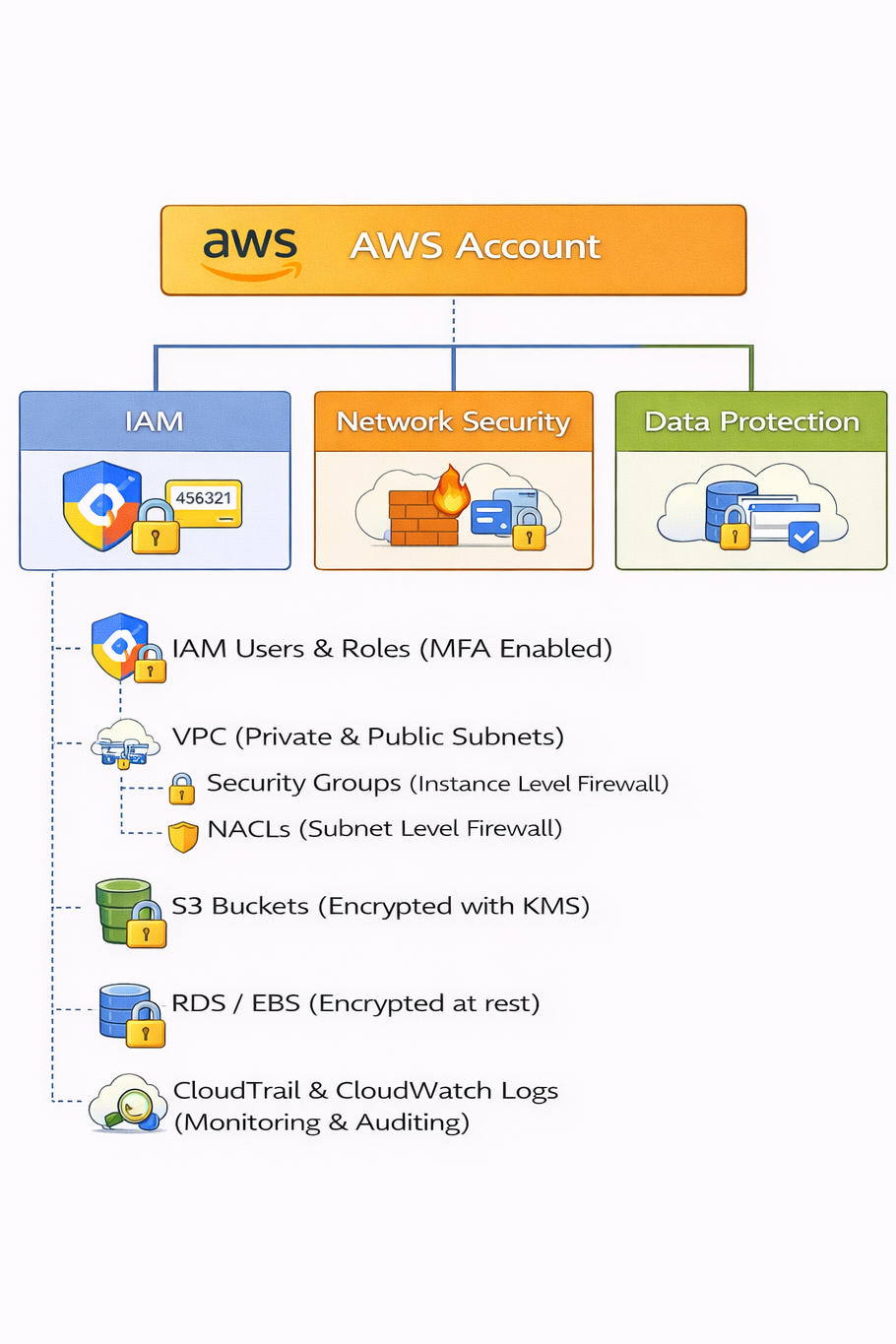
Explanation:
- IAM controls access
- Security Groups & NACLs control network traffic
- KMS ensures encryption at rest
- CloudTrail & CloudWatch provide auditing and monitoring
7. Step-by-Step Lab: Encrypt S3 and Enable CloudTrail
1 – Create an S3 Bucket
- Navigate to S3 → Create Bucket
- Enable SSE-KMS encryption
- Assign bucket policy restricting access to IAM role
2 – Configure CloudTrail
- Navigate to CloudTrail → Trails → Create Trail
- Enable Management and Data Events
- Deliver logs to encrypted S3 bucket
- Enable CloudWatch log integration for monitoring
3 – Test Access
- Use IAM user/role to upload/download files
- Confirm access denied for unauthorized users
- Verify logs in CloudTrail and CloudWatch
8. Best Practices
| Practice | Reason |
| Enable encryption at rest and in transit | Protect sensitive data |
| Use IAM roles with least privilege | Minimize attack surface |
| Enable MFA for all users | Prevent unauthorized access |
| Regularly rotate keys | Security best practice |
| Enable CloudTrail & Security Hub | Detect anomalies and maintain compliance |
9. Common Beginner Mistakes
- Using root account for daily tasks → high risk
- Ignoring encryption for S3, EBS, RDS → data exposure
- Misconfiguring IAM policies → over-permission
- Not enabling CloudTrail → missed audit trails
- Skipping multi-region logging → incomplete monitoring
10. Path to Expertise
- Start with IAM, MFA, and basic encryption
- Implement S3, EBS, and RDS encryption with KMS
- Enable CloudTrail and CloudWatch logs
- Learn security auditing, AWS Config rules, and Security Hub
- Integrate compliance frameworks and multi-region monitoring
At CuriosityTech.in, learners advance from basic security concepts to designing enterprise-grade, compliant, and secure cloud architectures.
Conclusion
Security is non-negotiable in cloud computing. Mastering encryption, IAM, and compliance ensures data is protected, applications remain secure, and organizations meet industry standards.
Practical labs and mentorship at Curiosity Tech equip learners to implement, monitor, and audit security effectively, transforming beginners into confident, security-conscious AWS cloud engineers.