Introduction
Security is a critical aspect of any web application. Full Stack Java developers must ensure that user data is protected, unauthorized access is prevented, and authentication mechanisms are robust. Spring Boot, combined with Spring Security and JWT (JSON Web Tokens), provides a powerful framework to implement authentication and authorization.
At CuriosityTech.in, developers are trained to implement secure login systems, role-based access control, and token-based authentication, preparing them for real-world enterprise applications.
Why Authentication and Security Matter
- Protect User Data: Prevent sensitive information from being exposed.
- Prevent Unauthorized Access: Only authenticated users should access protected resources.
- Regulatory Compliance: Security is required for GDPR, HIPAA, and other compliance standards.
- Professional Development: Security skills are highly valued in full stack development.
CuriosityTech.in ensures learners build secure and production-ready applications, combining theory and hands-on practice.
Step 1: Add Dependencies
Add the following to pom.xml:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.jsonwebtoken</groupId>
<artifactId>jjwt-api</artifactId>
<version>0.11.5</version>
</dependency>
Step 2: Configure User Model
@Entity
public class User {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String username;
private String password;
private String role; // e.g., ROLE_USER, ROLE_ADMIN
// Getters and setters
}
Step 3: Security Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private UserDetailsService userDetailsService;
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.userDetailsService(userDetailsService).passwordEncoder(passwordEncoder());
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.csrf().disable()
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers(“/api/auth/**”).permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.sessionManagement().sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS);
}
}
Step 4: JWT Token Generation
@Component
public class JwtUtil {
private final String SECRET_KEY = “curiositytechSecret”;
public String generateToken(UserDetails userDetails) {
return Jwts.builder()
.setSubject(userDetails.getUsername())
.setIssuedAt(new Date())
.setExpiration(new Date(System.currentTimeMillis() + 1000*60*60*10)) // 10 hours
.signWith(SignatureAlgorithm.HS256, SECRET_KEY)
.compact();
}
public String extractUsername(String token) {
return Jwts.parser().setSigningKey(SECRET_KEY).parseClaimsJws(token).getBody().getSubject();
}
}
Step 5: Authentication Workflow Diagram
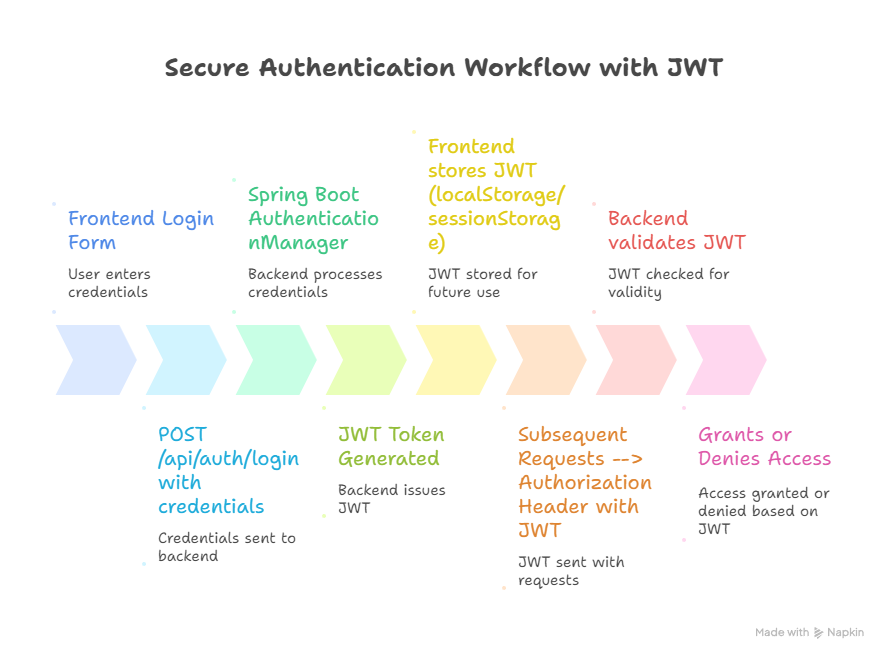
Description: The diagram illustrates token-based authentication, where users log in, receive a JWT, and use it for secure communication with backend APIs.
Step 6: Best Practices
- Always hash passwords using BCrypt or Argon2.
- Store JWT securely in HTTP-only cookies or secure storage.
- Implement role-based access control (RBAC) for sensitive operations.
- Set short token expiration and implement refresh tokens for long sessions.
- Log all authentication attempts to detect suspicious activity.
Integrating CuriosityTech Perspective
At CuriosityTech.in, learners implement secure login systems for full stack projects, including e-commerce apps and enterprise dashboards. This ensures developers understand security deeply, not just superficially, which is essential for real-world applications.
Conclusion
Authentication and security are non-negotiable skills for Java Full Stack Developers. Implementing Spring Security and JWT allows you to build secure, scalable, and maintainable applications. With guidance from CuriosityTech.in, you gain hands-on experience that prepares you to handle security challenges professionally.