On Day 16, we explore AWS DevOps services, specifically CodePipeline and CodeDeploy, which allow engineers to implement continuous integration (CI) and continuous deployment (CD).
At CuriosityTech.in, learners understand that DevOps is not just automation—it’s about reliability, repeatability, and collaboration. Mastery of CI/CD pipelines is essential for scalable, error-free cloud application deployment.
1. What is AWS CodePipeline?
AWS CodePipeline is a fully managed CI/CD service that automates the build, test, and deployment phases of your release process every time there’s a code change.
Key Features:
- Automates end-to-end deployment workflow
- Integrates with GitHub, CodeCommit, Jenkins, S3
- Supports multi-environment deployments
- Enables manual approvals at any stage
Analogy: Think of CodePipeline as a production line in a factory—code goes in, gets tested, built, and deployed automatically without manual intervention.
2. What is AWS CodeDeploy?
AWS CodeDeploy automates application deployment to EC2 instances, Lambda functions, and on-premises servers.
Key Features:
- Supports rolling updates and blue/green deployments
- Automates rollback on failures
- Integrates with CodePipeline for end-to-end automation
- Tracks deployment health and success metrics
Analogy: CodeDeploy is the robotic arm in the production line that ensures each unit (application version) is deployed safely and consistently.
3. CI/CD Workflow Diagram
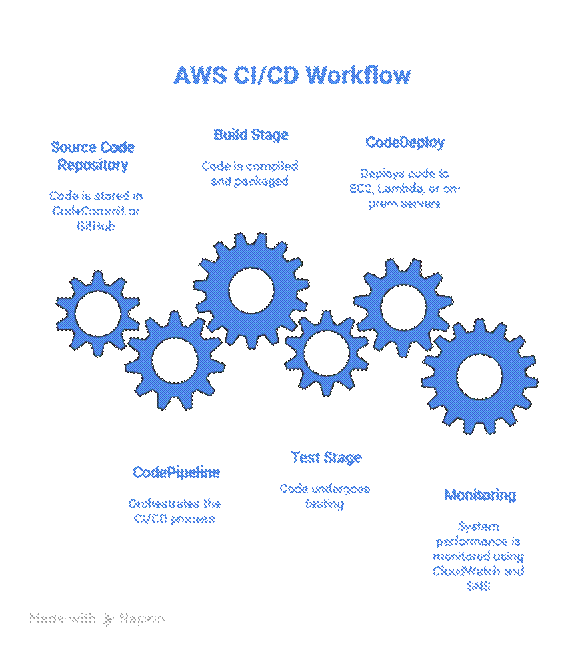
Explanation:
- Code changes trigger CodePipeline automatically
- Build and test stages ensure code quality
- CodeDeploy handles deployment safely and efficiently
- Monitoring tracks success/failure of deployments
4. Core Concepts & Components
| Service | Component | Description | Example |
| CodePipeline | Pipeline | End-to-end CI/CD process | CuriosityTech-Pipeline |
| CodePipeline | Stage | Build, Test, Deploy phases | Build → Unit Test → Deploy |
| CodePipeline | Action | Specific task in a stage | CodeBuild build, CodeDeploy deploy |
| CodeDeploy | Application | Logical representation of deployable app | CuriosityTech-WebApp |
| CodeDeploy | Deployment Group | Collection of instances for deployment | EC2 Auto Scaling Group |
| CodeDeploy | Deployment Config | Strategy for deployment | Rolling, Blue/Green |
5. Step-by-Step Lab: Deploying a Web Application
Step 1 – Prepare Source Code
- Example: Simple Node.js app
const express = require(‘express’);
const app = express();
app.get(‘/’, (req, res) => res.send(‘Hello from CuriosityTech CI/CD!’));
app.listen(3000, () => console.log(‘Server running on port 3000’));
- Push to AWS CodeCommit repository
Step 2 – Create CodePipeline
- Navigate to CodePipeline → Create Pipeline
- Pipeline Name: CuriosityTech-Pipeline
- Source: CodeCommit repository
- Build Provider: CodeBuild (specify buildspec.yml)
- Deploy Provider: CodeDeploy
Step 3 – Configure CodeDeploy
- Create CodeDeploy Application → CuriosityTech-WebApp
- Create Deployment Group → select EC2 instances or Auto Scaling group
- Deployment type: Rolling update or Blue/Green
- IAM role for CodeDeploy with S3, EC2, and CloudWatch permissions
Step 4 – Build & Deploy
- CodePipeline automatically triggers on code push
- CodeBuild runs build scripts and tests
- CodeDeploy deploys application to EC2 instances
- Check deployment status in console and CloudWatch logs
6. Deployment Strategies
| Strategy | Description | Use Case |
| In-Place / Rolling | Deploys version gradually on existing instances | Minor updates, low traffic |
| Blue/Green | Creates new environment, switches traffic | Zero downtime, high-availability production |
| Canary | Gradual rollout to subset of instances | Test new features with controlled risk |
CuriosityTech.in Insight: Blue/Green deployments are preferred for production because they eliminate downtime and enable quick rollback.
7. Monitoring & Best Practices
- CloudWatch Metrics: Track deployment duration, failures
- SNS Notifications: Alerts on deployment success/failure
- IAM Roles: Use least privilege for pipeline and deployment
- Automated Testing: Integrate unit/integration tests in pipeline
- Rollback Triggers: Enable automatic rollback on errors
8. Common Beginner Mistakes
- Misconfiguring IAM roles → pipeline fails to access resources
- Ignoring test stages → errors reach production
- Deploying to single instance without rollback strategy → risk of downtime
- Not monitoring pipeline logs → hard to troubleshoot failures
- Overcomplicating pipeline initially → beginners should start simple
9. Path to Expertise
- Start with simple Node.js or Python app deployment using CodePipeline + CodeDeploy
- Integrate unit and integration tests in pipeline
- Use CloudWatch metrics and SNS alerts to monitor deployments
- Experiment with blue/green and rolling deployments for production readiness
- Build end-to-end automated pipelines with multi-environment support
At CuriosityTech.in, learners practice full CI/CD workflows, learning automation, monitoring, and deployment strategies for professional cloud applications.
10. Conclusion
AWS DevOps tools like CodePipeline and CodeDeploy are essential for automating the software release process, ensuring reliability, speed, and quality. By mastering these tools, cloud engineers can reduce manual intervention, prevent errors, and deploy confidently.
Hands-on labs at CuriosityTech.in help learners implement, monitor, and optimize pipelines, transforming them into expert cloud DevOps engineers ready for real-world projects.



