Introduction
Testing REST APIs is a crucial skill for Java Full Stack Developers. Even if you’ve built robust APIs using Spring Boot, you need to validate that they work correctly before integrating them with the frontend. Postman is one of the most popular tools for testing APIs, offering automation, debugging, and collaboration features.
At CuriosityTech.in, developers are trained to test APIs thoroughly, ensuring that applications behave as expected in real-world scenarios.
Why API Testing Matters
- Ensures Correct Functionality: Confirms that endpoints return expected data and status codes.
- Catches Bugs Early: Detects issues before integrating with the frontend.
- Validates Security: Ensures authentication, authorization, and data validation work properly.
- Supports Automation: Enables CI/CD pipelines with automated API tests.
CuriosityTech.in emphasizes hands-on testing, teaching developers how to test CRUD APIs, handle errors, and optimize performance.
Step 1: Setting Up Postman
- Download and install Postman from Postman Official Website.
- Launch Postman and create a new workspace for your Java project.
- Organize API requests into collections for easy management.
Step 2: Testing CRUD APIs
1. GET Request
- URL: http://localhost:8080/api/products
- Method: GET
- Purpose: Retrieve all products from the backend.
Expected Response:
[
{ “id”: 1, “name”: “Laptop”, “price”: 850.00 },
{ “id”: 2, “name”: “Smartphone”, “price”: 500.00 }
]
2. POST Request
- URL: http://localhost:8080/api/products
- Method: POST
- Body (JSON):
{
“name”: “Headphones”,
“price”: 75.00
}
- Purpose: Add a new product.
- Expected Response: Newly created product object with id.
3. PUT Request
- URL: http://localhost:8080/api/products/1
- Method: PUT
- Body (JSON):
{
“name”: “Gaming Laptop”,
“price”: 950.00
}
- Purpose: Update product details.
4. DELETE Request
- URL: http://localhost:8080/api/products/2
- Method: DELETE
- Purpose: Remove a product from the database.
Step 3: Using Postman Features
| Feature | Description |
| Collections | Group API requests for organized testing |
| Environment | Store variables like baseUrl or authentication tokens |
| Pre-request Scripts | Run scripts before requests for dynamic setup |
| Tests Scripts | Validate responses with JavaScript assertions |
| Mock Servers | Simulate API endpoints during frontend development |
Step 4: Automating API Tests
Postman allows writing test scripts to automatically verify API responses. Example:
pm.test(“Status code is 200”, function () {
pm.response.to.have.status(200);
});
pm.test(“Response has product name”, function () {
var jsonData = pm.response.json();
pm.expect(jsonData[0]).to.have.property(“name”);
});
- Run these tests manually or integrate into CI/CD pipelines using Postman CLI (Newman).
Step 5: REST API Testing Workflow Diagram
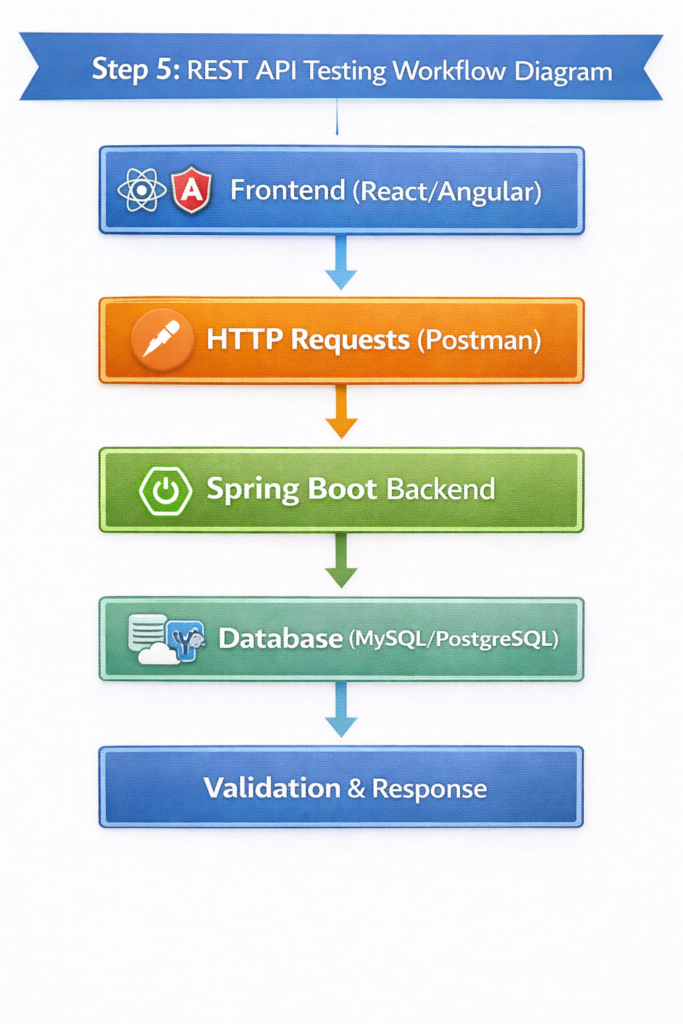
Description: This workflow demonstrates how Postman interacts with the backend to validate API responses before connecting the frontend, ensuring reliability and functionality.
Step 6: Best Practices
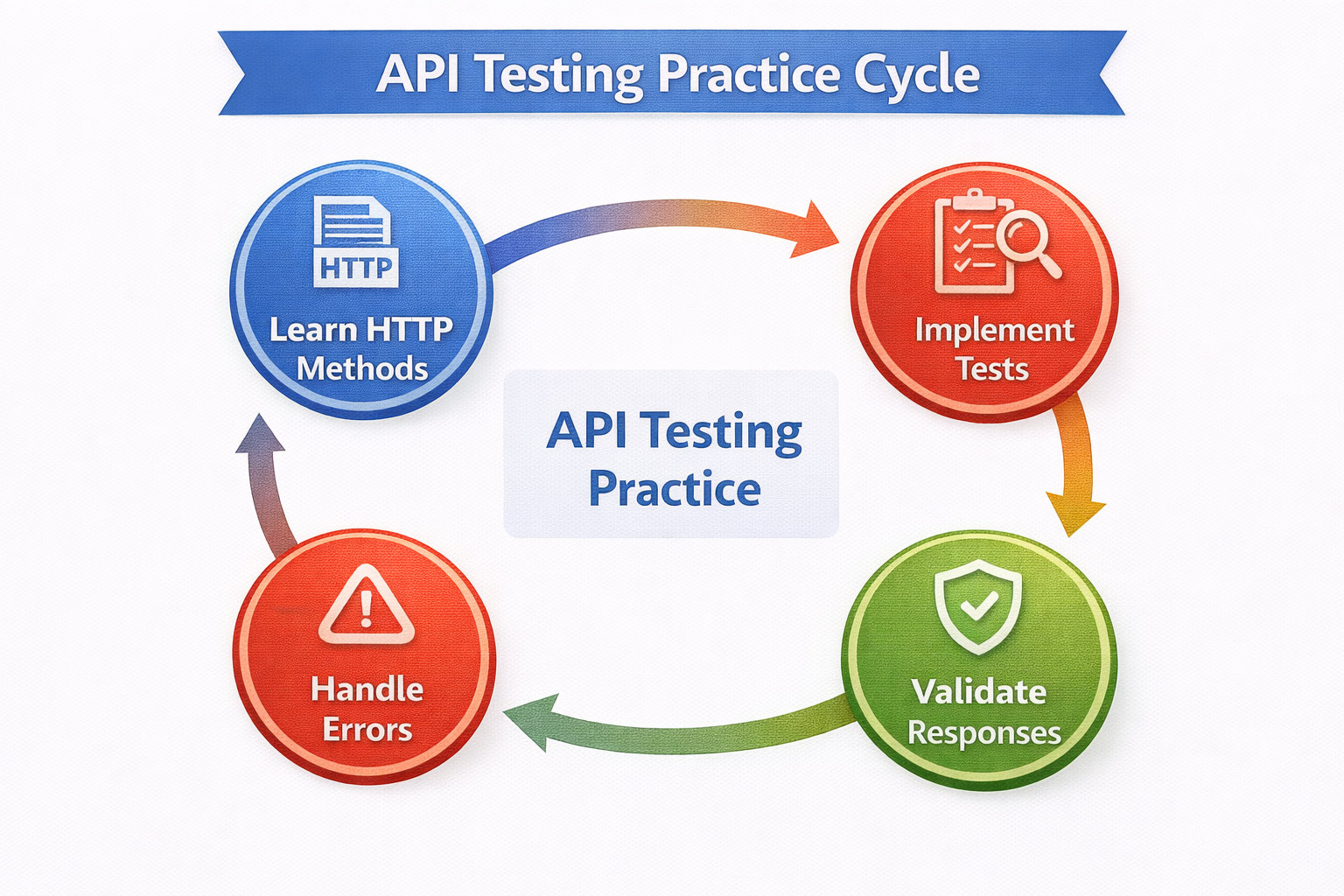
Integrating CuriosityTech Perspective
At CuriosityTech.in, learners practice real-world API testing, including error handling, authentication, and integration with frontend apps. This ensures developers not only build APIs but also deliver reliable, production-ready systems.
Conclusion
REST API testing with Postman is an essential skill for Java Full Stack Developers. It ensures that backend services function correctly, are secure, and integrate seamlessly with frontend components. With guidance from CuriosityTech.in, developers gain practical experience in testing, automation, and debugging, preparing them for real-world full stack projects.



