On Day 18, we explore high availability (HA) and disaster recovery (DR) strategies in AWS, which are essential for business continuity, fault tolerance, and minimizing downtime.
At AWS EC2 tutorial, learners understand that designing HA and DR systems is not just about redundancy—it’s about planning, automation, and risk management.
1. Understanding High Availability (HA)
High Availability ensures that your application remains accessible and functional even when some components fail.
Key Principles:
- Redundancy: Duplicate critical components (EC2 instances, databases)
- Load Balancing: Distribute traffic across healthy instance
- Auto Scaling: Add or remove instances automatically based on demand
- Fault Isolation: Deploy resources across multiple Availability Zones (AZs)
HA Example in AWS:
- Web Servers: EC2 instances in multiple AZs
- Load Balancer: Elastic Load Balancer (ALB/ELB) distributes traffic
- Database: Multi-AZ RDS deployment for automatic failover
2. Understanding Disaster Recovery (DR)
Disaster Recovery focuses on restoring operations after a catastrophic event, such as data center failure, cyberattack, or natural disaster.
DR Strategies in AWS:
- Backup & Restore – Basic strategy: backup data to S3/Glacier, restore as needed
- Pilot Light – Minimal infrastructure running, can scale quickly in disaster
- Warm Standby – Smaller version of the environment always running, scales up when needed
- Multi-Site Active-Active – Full production environment in multiple regions, automatic failover
3. HA & DR Architecture Diagram
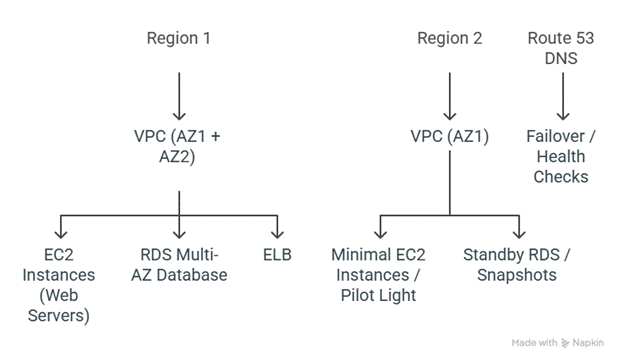
Explanation:
- Primary region handles live traffic
- Secondary region acts as DR site (can be Pilot Light or Warm Standby)
- Route 53 DNS health checks redirect traffic automatically if primary fails
4. AWS Services Supporting HA & DR
| Service | Role in HA/DR | Description |
| EC2 Auto Scaling | HA | Automatically adjusts compute capacity |
| Elastic Load Balancer | HA | Distributes traffic across healthy instances |
| RDS Multi-AZ | HA | Automatic failover for databases |
| S3 & Glacier | DR | Durable storage for backups |
| Route 53 | DR | DNS-based failover and routing |
| CloudFormation | DR | Infrastructure as Code to rebuild environments quickly |
| AWS Backup | DR | Centralized backup management |
| CloudWatch & CloudTrail | HA/DR | Monitor system health, alert on failures |
CuriosityTech.in Insight: Learners simulate failure scenarios using EC2 termination, AZ disruption, and RDS failover to experience HA and DR in real-time.
5. Step-by-Step HA Implementation Lab
1 – Multi-AZ Deployment
- Launch RDS database with Multi-AZ → automatic standby in another AZ
- Deploy EC2 instances in two AZs
- Attach Elastic Load Balancer → routes traffic only to healthy instances
2 – Auto Scaling
- Configure launch template for EC2
- Set scaling policies based on CPU/memory
- Test by terminating instances → Auto Scaling launches new instances automatically
3 – Monitoring & Alerts
- Enable CloudWatch Alarms for CPU, memory, disk usage
- Configure SNS notifications for automated alerts
- Use Route 53 health checks for failover routing
6. Step-by-Step DR Implementation Lab
1 – Backup & Restore
- Backup RDS snapshots → store in another region
- Backup EC2 AMIs → can restore in DR region
- Test restore by launching a new instance from AMI
2 – Pilot Light Deployment
- Minimal EC2 in secondary region → deploy only core services
- Use CloudFormation templates to quickly launch full environment in case of failure
3 – Warm Standby Deployment
- Run smaller version of full production environment in DR region
- Scale up resources using Auto Scaling when primary fails
4 – Multi-Site Active-Active
- Deploy full production environment in two regions
- Use Route 53 weighted routing for load distribution
- Ensure databases are replicated across region
7. Cost Considerations
| Strategy | Cost | Pros | Cons |
| Backup & Restore | Low | Minimal cost | Longer recovery time |
| Pilot Light | Medium | Quick recovery | Some maintenance needed |
| Warm Standby | High | Faster recovery | Higher cost |
| Multi-Site Active-Active | Very High | Zero downtime | Expensive, complex |
Expert Tip: Beginners often assume HA & DR is free. Planning cost-effective strategies is key to real-world deployment success.
8. Common Beginner Mistakes
- Deploying single AZ resources → no fault tolerance
- Ignoring backup automation → recovery delays
- Not testing failover scenarios → surprises during actual disaster
- Over-provisioning secondary resources → unnecessary cost
- Skipping monitoring → failures go undetected
CuriosityTech.in Insight: Hands-on labs teach learners to balance availability, recovery time objectives (RTO), and cost, which is critical for enterprise-ready cloud architectures.
9. Path to Expertise
- Start with Multi-AZ deployments for EC2 & RDS
- Enable Auto Scaling and Load Balancers for HA
- Implement backup and restore strategies for DR
- Explore Pilot Light, Warm Standby, and Active-Active DR patterns
- Test failover, recovery, and monitoring in simulated scenarios
At CuriosityTech.in, learners practice building fault-tolerant architectures, ensuring high availability, disaster resilience, and minimal downtime for cloud applications.
Conclusion
High Availability and Disaster Recovery are critical components of cloud architecture. Understanding multi-AZ deployment, failover strategies, and backup mechanisms ensures systems remain resilient, reliable, and cost-effective.
With CuriosityTech.in’s hands-on labs, learners gain real-world HA and DR experience, preparing them to design enterprise-grade, resilient cloud systems.