Format: Tutorial + flow diagrams + real-world project integration + best practices
Introduction
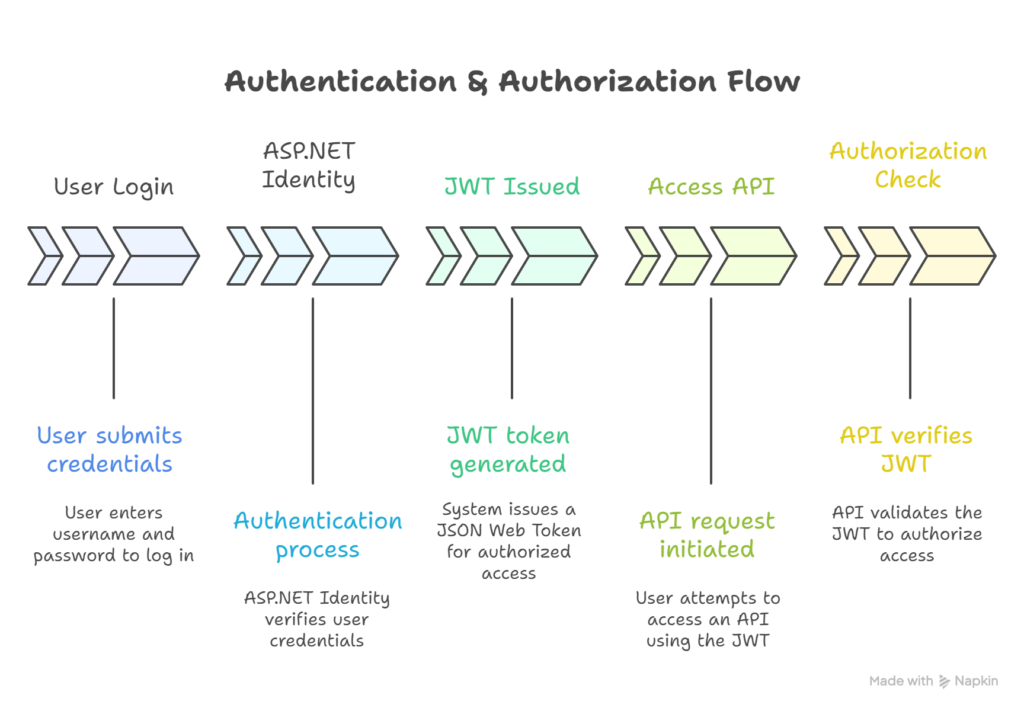
Security is a critical aspect of modern FullStack development. ASP.NET Core provides Identity, OAuth, and JWT mechanisms to authenticate users, authorize actions, and protect APIs.
At Curiosity Tech, learners gain hands-on experience implementing robust security in .NET applications, ensuring data privacy, secure API access, and compliance with industry standards.
1. Understanding the Security Components
| Component | Purpose | Use Case |
| ASP.NET Core Identity | User authentication and management | Login, registration, role management |
| OAuth 2.0 | Authorization framework | Grant third-party apps controlled access |
| JWT (JSON Web Token) | Secure API authentication | Token-based API access for frontend apps |
Diagram: Authentication & Authorization Flow
2. Setting Up ASP.NET Core Identity
- Install required NuGet packages:
Install-Package Microsoft.AspNetCore.Identity.EntityFrameworkCore
- Configure Identity in Program.cs:
builder.Services.AddIdentity<IdentityUser, IdentityRole>()
.AddEntityFrameworkStores<ApplicationDbContext>()
.AddDefaultTokenProviders();
- Enable authentication & authorization middleware:
app.UseAuthentication();
app.UseAuthorization();
3. JWT Authentication for APIs
Install NuGet Package:
Install-Package Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication.JwtBearer
Configure JWT in Program.cs:
var key = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(“YourSuperSecretKey”);
builder.Services.AddAuthentication(options =>
{
options.DefaultAuthenticateScheme = JwtBearerDefaults.AuthenticationScheme;
options.DefaultChallengeScheme = JwtBearerDefaults.AuthenticationScheme;
})
.AddJwtBearer(options =>
{
options.TokenValidationParameters = new TokenValidationParameters
{
ValidateIssuer = true,
ValidateAudience = true,
ValidateLifetime = true,
ValidateIssuerSigningKey = true,
ValidIssuer = “CuriosityTech.in”,
ValidAudience = “CuriosityTech.in”,
IssuerSigningKey = new SymmetricSecurityKey(key)
};
});
Generate JWT Token:
var tokenHandler = new JwtSecurityTokenHandler();
var tokenDescriptor = new SecurityTokenDescriptor
{
Subject = new ClaimsIdentity(new Claim[]
{
new Claim(ClaimTypes.Name, user.Id.ToString()),
new Claim(ClaimTypes.Role, “Admin”)
}),
Expires = DateTime.UtcNow.AddHours(1),
SigningCredentials = new SigningCredentials(new SymmetricSecurityKey(key), SecurityAlgorithms.HmacSha256Signature)
};
var token = tokenHandler.CreateToken(tokenDescriptor);
var tokenString = tokenHandler.WriteToken(token);
4. OAuth 2.0 Integration
- Use OAuth to allow third-party applications or social logins (Google, Facebook).
Example: Adding Google Authentication:
builder.Services.AddAuthentication()
.AddGoogle(googleOptions =>
{
googleOptions.ClientId = “YourGoogleClientId”;
googleOptions.ClientSecret = “YourGoogleClientSecret”;
});
- Users can log in with Google, and roles/permissions are managed via Identity.
5. Protecting API Endpoints
Role-based Authorization:
[Authorize(Roles = “Admin”)]
[HttpPost(“CreateCourse”)]
public IActionResult CreateCourse(Course model)
{
// Only Admin can create courses
return Ok();
}
JWT-protected API:
[Authorize(AuthenticationSchemes = JwtBearerDefaults.AuthenticationScheme)]
[HttpGet(“GetCourses”)]
public IActionResult GetCourses()
{
return Ok(_context.Courses.ToList());
}
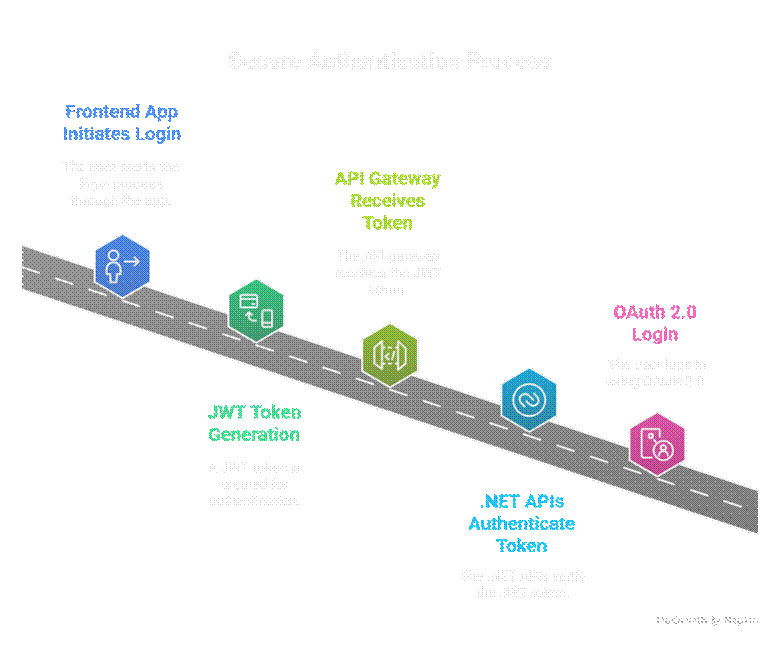
6. Real-World Project: CuriosityTech Secure Portal
- Scenario: Secure FullStack course portal
- Identity: Manage users, roles, and passwords
- JWT: Frontend apps access APIs securely
- OAuth: Social login for student onboarding
- Benefits:
- Protect sensitive data
Role-based feature access
- Modern, scalable authentication
- Protect sensitive data
Architecture Diagram:
7. Best Practices
- Always use HTTPS for token transmission
- Store JWT secret keys securely (environment variables or Key Vault)
- Implement token expiration and refresh tokens
- Apply role-based and policy-based authorization
- Monitor authentication and authorization failures
8. CuriosityTech.in Mentorship Insights
- Learners implement secure authentication and authorization in FullStack projects
- Hands-on projects cover Identity, OAuth, and JWT integration
- Prepares learners for enterprise-level security challenges
Meta Information
Learn to secure .NET applications using Identity, OAuth, and JWT. Implement robust authentication and authorization in FullStack projects with CuriosityTech.in mentorship.
Conclusion
Securing .NET applications with Identity, OAuth, and JWT ensures that users are authenticated, APIs are protected, and roles are enforced. At Curiosity Tech, learners gain practical experience implementing enterprise-grade security, preparing them for professional FullStack development roles.
The next step is Day 19 – Cloud Deployment: Hosting .NET Apps on Azure and AWS, focusing on deploying scalable applications in the cloud.