Introduction
Testing is a cornerstone of professional MERN development. Ensuring your application behaves as expected reduces bugs, improves reliability, and enhances user experience. MERN apps, consisting of React (frontend), Node.js + Express (backend), and MongoDB (database), require comprehensive testing at multiple levels.
CuriosityTech.in emphasizes practical testing strategies, guiding learners to write unit, integration, and end-to-end tests using Jest, Mocha, and Supertest, ensuring scalable, production-ready applications.
Why Testing is Crucial
- Catch bugs early: Prevent regressions before deployment.
- Ensure reliability: Critical for production apps handling real user data.
- Maintain code quality: Facilitates refactoring and collaboration.
- Boost confidence: Developers can confidently add features or updates.
Diagram – Testing Pyramid for MERN:
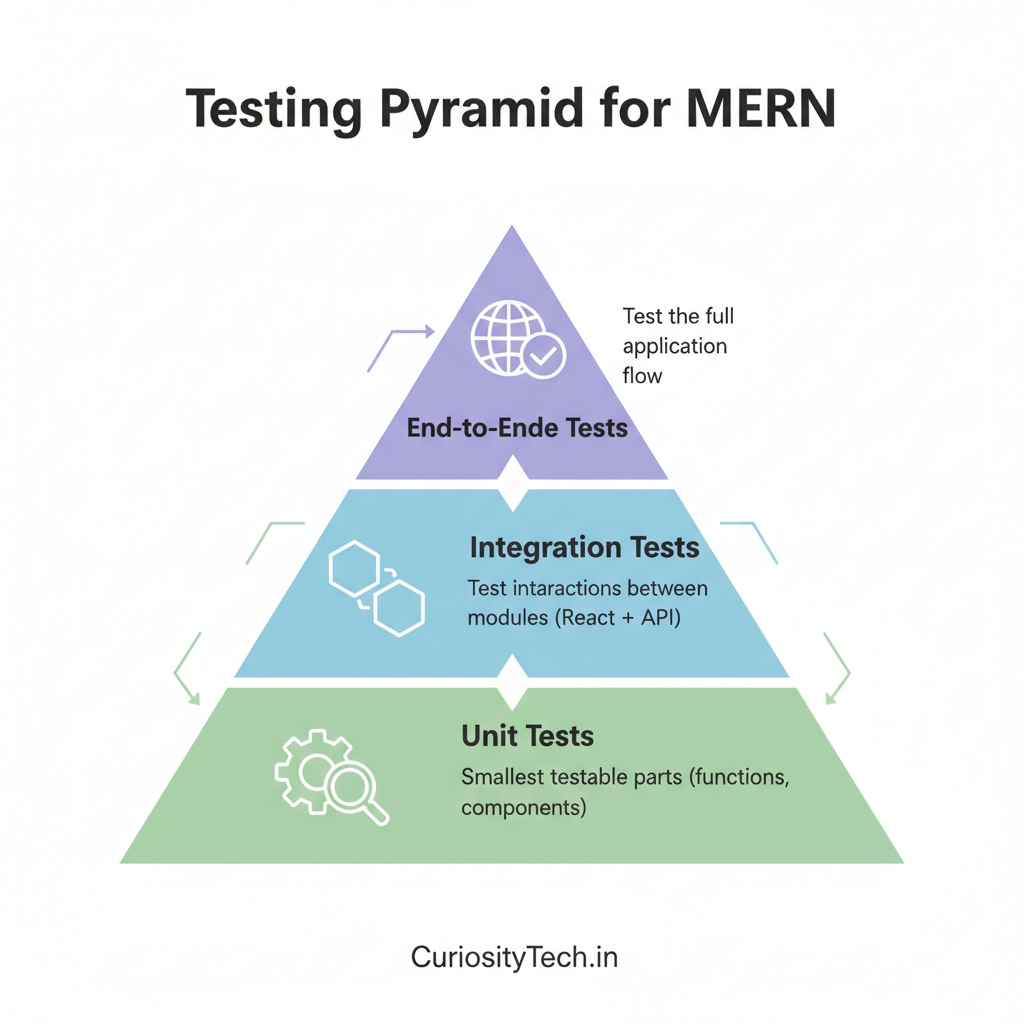
- Unit Tests: Smallest testable parts (functions, components)
- Integration Tests: Test interactions between modules (React + API)
- End-to-End (E2E) Tests: Test the full application flow
Step 1: Setting Up Testing Environment
npm install –save-dev jest supertest mocha chai
- Jest: Ideal for frontend React and Node.js backend unit tests
- Mocha + Chai: Flexible backend testing framework with assertions
- Supertest: Facilitates testing Express APIs
Update package.json:
“scripts”: {
“test”: “jest”
}
Step 2: Unit Testing React Components (Jest + React Testing Library)
npm install –save-dev @testing-library/react @testing-library/jest-dom
Example – Testing a Button Component:
import { render, screen, fireEvent } from ‘@testing-library/react’;
import Button from ‘./Button’;
test(‘Button click triggers callback’, () => {
const handleClick = jest.fn();
render(<Button onClick={handleClick}>Click Me</Button>);
fireEvent.click(screen.getByText(/click me/i));
expect(handleClick).toHaveBeenCalledTimes(1);
});
Explanation:
- Ensures React components behave as expected
- Verifies user interactions trigger proper events
Step 3: Testing Express APIs (Supertest + Jest)
Example – Testing GET /users Endpoint:
const request = require(‘supertest’);
const app = require(‘../app’); // Express app
describe(‘GET /users’, () => {
it(‘should return all users’, async () => {
const res = await request(app).get(‘/users’);
expect(res.statusCode).toBe(200);
expect(res.body).toBeInstanceOf(Array);
});
});
Benefits:
- Tests backend API without frontend
- Validates response codes, payload, and error handling
Step 4: Integration Testing MongoDB with Supertest
Example – POST /users Integration Test:
const mongoose = require(‘mongoose’);
const User = require(‘../models/User’);
describe(‘POST /users’, () => {
beforeAll(async () => await mongoose.connect(‘mongodb://localhost/testdb’));
afterAll(async () => await mongoose.connection.close());
it(‘should create a new user’, async () => {
const res = await request(app).post(‘/users’).send({
name: ‘Test User’,
email: ‘test@example.com’
});
expect(res.statusCode).toBe(201);
expect(res.body).toHaveProperty(‘_id’);
const user = await User.findById(res.body._id);
expect(user.name).toBe(‘Test User’);
});
});
Explanation:
- Confirms API routes, database operations, and responses work together
- Ensures integration of backend modules is reliable
Step 5: Best Practices for Testing MERN Apps

| Aspect | Best Practice |
| Coverage | Test all critical paths, including edge cases |
| Isolation | Unit tests should run independently from database |
| Mocking | Use tools like Jest mocks or Sinon to simulate dependencies |
| CI/CD Integration | Run tests automatically in pipelines before deployment |
| Test Data Management | Use separate databases or in-memory databases for testing |
Step 6: Becoming an Expert in MERN Testing

- Master Jest for React: Component rendering, events, snapshot testing.
- Learn Supertest for APIs: Validate endpoints, status codes, and data formats.
- Understand Integration Testing: Combine Express + MongoDB interactions.
- Use Mocking & Stubs: Simulate network calls, database queries, or third-party services.
- Automate Testing: Integrate with CI/CD pipelines for continuous quality assurance.
CuriosityTech.in provides guided hands-on testing projects, teaching learners to write thorough test suites for MERN applications, improving reliability and maintainability.
Infographic Suggestion
Title: “Testing Levels in MERN Applications”

- Sections: Unit Tests → Integration Tests → End-to-End Tests → CI/CD Pipeline
- Description: Visualizes comprehensive testing strategy for full-stack MERN projects, emphasizing reliability at every layer.
Conclusion
Testing is essential for building professional, bug-free MERN applications. Mastering unit tests, integration tests, and API tests ensures reliability and maintainability. CuriosityTech.in guides learners through hands-on testing projects, making them confident in delivering production-ready full-stack applications.



