Introduction
In modern DevOps and cloud-native environments, managing secrets securely is critical.
Secrets include API keys, database credentials, certificates, and encryption keys, which, if exposed, can compromise entire systems. At Curiosity Tech, we train DevOps engineers to implement robust secrets management solutions using HashiCorp Vault, AWS Key Management Service(KMS), and other industry-standard tools.
What is Secrets Management?
Secrets management is the process of storing, accessing, and controlling sensitive information in a secure, centralized manner.
Key objectives:
- Confidentiality: Ensure only authorized services and users can access secrets.
- Integrity: Protect secrets from unauthorized changes.
- Auditability: Track secret usage for compliance and governance.
- Dynamic Secrets: Generate secrets on-demand to minimize risk exposure.
Secrets management is foundational to secure CI/CD pipelines, cloud automation, and microservices architectures.
Why Use HashiCorp Vault & AWS KMS?
| Tool | Purpose | Strengths |
| HashiCorp Vault | Centralized secrets management platform | Dynamic secrets, leasing, revocation, audit logs, multi-cloud support |
| AWS KMS | Managed encryption and key management service | Key rotation, encryption for S3, RDS, EBS, integrated IAM access control |
| Use Together | Vault for secret lifecycle management, KMS for key encryption | End-to-end security, compliance, automation-ready |
Architecture Diagram: Secrets Management Workflow
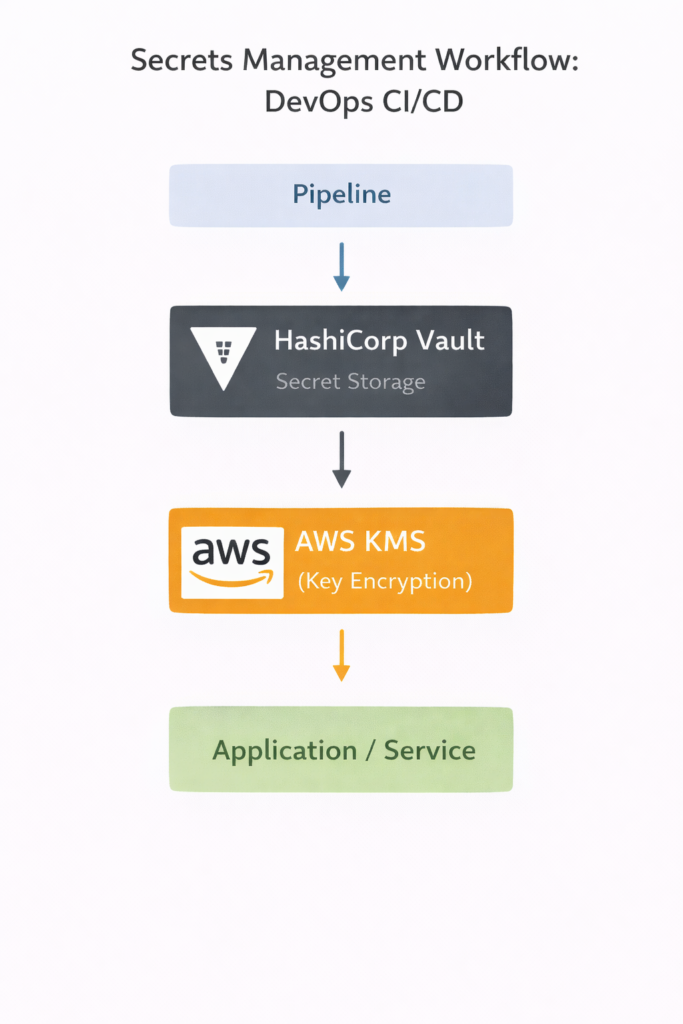
Description: CI/CD pipelines pull secrets dynamically from Vault, encrypted via AWS KMS, ensuring end-to-end secure secret usage without hardcoding credentials.
HashiCorp Vault Key Features
- Dynamic Secrets: Generate database credentials or API keys on-demand.
- Leasing & Revocation: Automatically revoke secrets after a lease period.
- Secret Engines: Supports databases, cloud providers, SSH, PKI, and more.
- Policies & ACLs: Fine-grained access control for teams and apps.
- Audit Logging: Full visibility into secret access for compliance.
AWS KMS Key Features
- Centralized Key Management: Manage encryption keys centrally across AWS services.
- Automatic Key Rotation: Rotate keys automatically to reduce exposure risk.
- IAM Integration: Fine-grained permissions on key usage.
- Envelope Encryption: Encrypt large datasets securely using data keys protected by KMS.
- Cross-Region Replication: Encrypt data across multiple AWS regions for HA/DR compliance.
Step-by-Step Secrets Management in DevOps
Step 1: Vault Setup
- Install Vault on a secure server or use Vault Enterprise in cloud mode.
- Configure a storage backend (Consul, AWS S3, or integrated storage).
- Enable authentication methods (AppRole, LDAP, GitHub).
- Create policies for team-specific secret access.
Step 2: Define Secrets
- Database credentials (PostgreSQL, MySQL)
- API keys (Stripe, Twilio, third-party services)
- Certificates and tokens
Example Policy:
path "database/creds/myapp" {
capabilities = ["read"]
}
Step 3: Integrate with CI/CD
- Jenkins, GitLab CI, or GitHub Actions authenticate with Vault via AppRole or OIDC.
- Pull dynamic secrets at runtime instead of hardcoding.
- Inject secrets into containers using environment variables or config files.
Step 4: Encryption via AWS KMS
- Vault stores secrets encrypted using AWS KMS keys.
- Services fetch encrypted secrets and decrypt via KMS.
- Enable key rotation policies and auditing.
Best Practices for Secrets Management
| Best Practice | Implementation |
| Avoid Hardcoding Secrets | Use Vault or environment variables injected at runtime |
| Use Dynamic Secrets | Generate short-lived database credentials |
| Centralize Secrets | Single source of truth with Vault or KMS |
| Enable Audit Logs | Track who accessed secrets and when |
| Rotate Keys Regularly | Configure automatic rotation in Vault & KMS |
| Limit Access Scope | Apply least privilege via IAM & Vault policies |
| Encrypt at Rest & In Transit | TLS for communication; KMS for storage encryption |
Practical Use Case: CI/CD Pipeline with Vault & KMS
- Developer commits code to GitLab.
- GitLab CI authenticates with Vault using AppRole.
- Vault generates PostgreSQL credentials with a 5-minute lease.
- Jenkins deploys Docker containers with secrets as environment variables.
- AWS KMS encrypts all stored secrets for auditability and secure key management.
- Vault revokes expired credentials automatically after deployment.
This workflow ensures zero hardcoded credentials, automated rotation, and compliance-ready secret management.
Challenges & Solutions:-
| Challenge | Solution |
| Secret Sprawl | Use centralized Vault instead of local files |
| Credential Expiration | Implement dynamic secrets with auto-renewal |
| Unauthorized Access | Enforce strict ACLs, AppRole authentication, and IAM policies |
| Key Management Complexity | Automate AWS KMS key rotation and integrate with Vault |
Conclusion
Effective secrets management is critical for secure DevOps pipelines and cloud-native applications. Tools like HashiCorp Vault and AWS KMS provide automation, encryption, auditing, and fine-grained access control, ensuring that sensitive data is never exposed.
At Curiosity Tech, learners practice end-to-end secrets management, integrating Vault, AWS KMS, and CI/CD pipelines to build secure, scalable, and compliant DevOps environments.