Introduction
Unit testing and Test-Driven Development (TDD) are essential for building reliable, maintainable, and bug-free FullStack .NET applications. By writing tests before or alongside code, developers ensure application correctness, scalability, and long-term maintainability.
At CuriosityTech.in, learners gain hands-on experience implementing unit tests, mocks, and TDD workflows for ASP.NET Core, EF Core, and frontend-backend integrated projects.
1. Understanding Unit Testing and TDD
| Concept | Description | Benefits |
| Unit Testing | Test individual methods or components | Detect bugs early, ensures code correctness |
| TDD | Write tests before code | Produces cleaner, modular, maintainable code |
| Integration Testing | Test interaction between components | Ensures system behaves as expected |
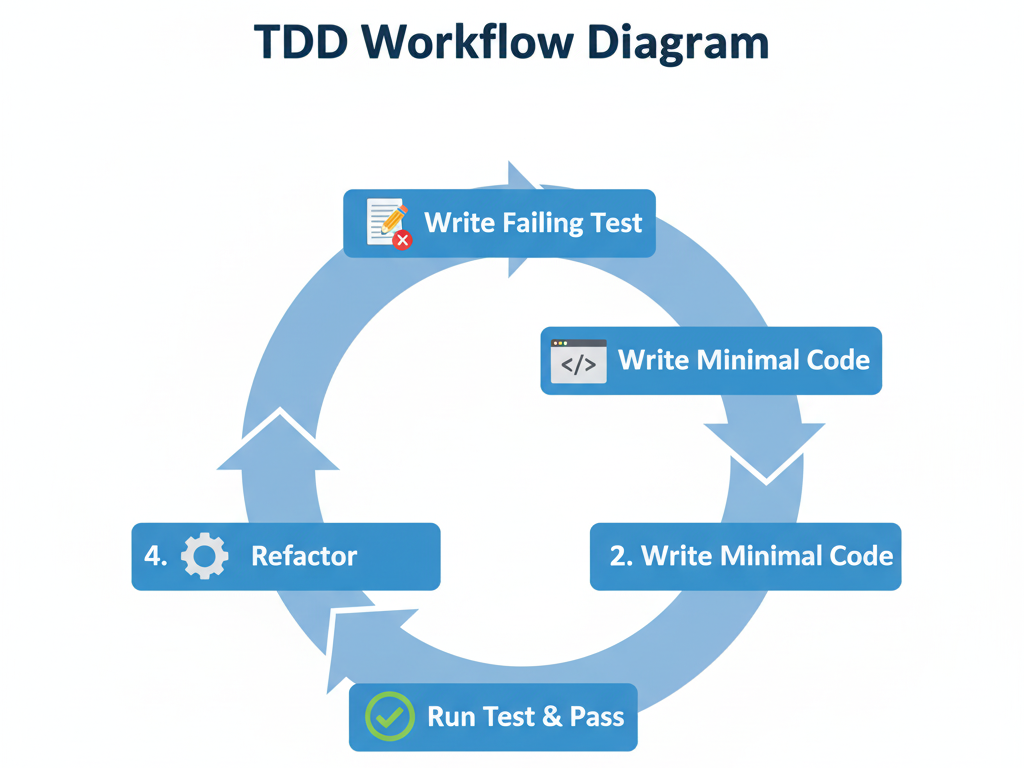
TDD Workflow Diagram:
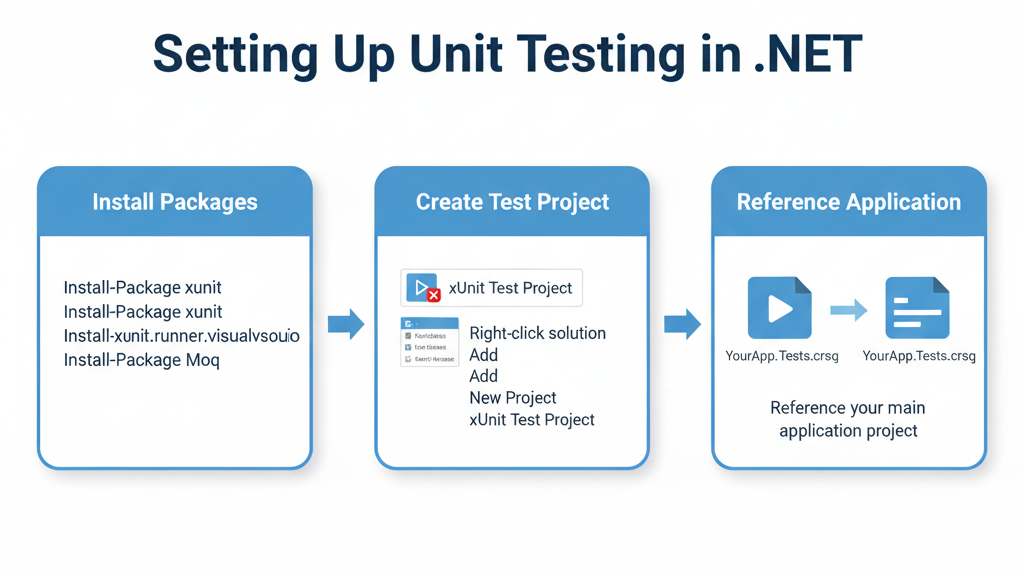
2. Setting Up Unit Testing in .NET
Install xUnit Package:
Install-Package xunit
Install-Package xunit.runner.visualstudio
Install-Package Moq
Create Test Project:
- Right-click solution → Add → New Project → xUnit Test Project
- Reference your main application project
3. Writing Unit Tests
Service Example – JobService:
public class JobService
{
public List<Job> GetJobs() => new List<Job> { new Job { Id = 1, Title = “Developer” } };
}
Unit Test Example:
public class JobServiceTests
{
[Fact]
public void GetJobs_ReturnsListOfJobs()
{
// Arrange
var service = new JobService();
// Act
var result = service.GetJobs();
// Assert
Assert.NotNull(result);
Assert.Single(result);
Assert.Equal(“Developer”, result[0].Title);
}
}
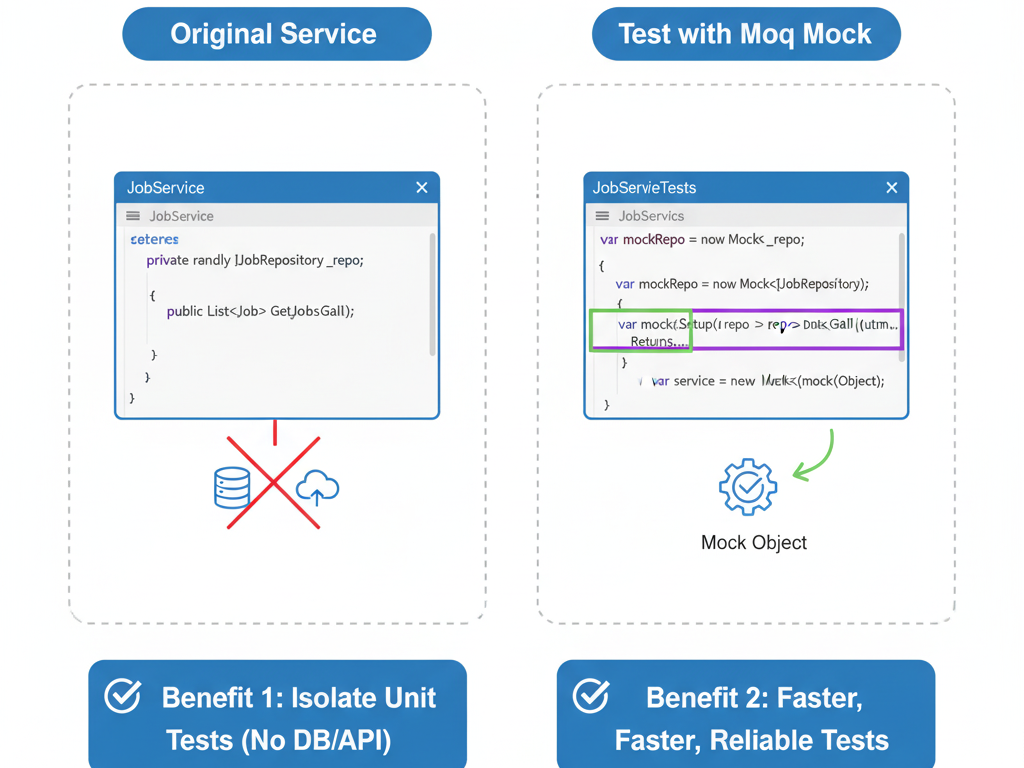
4. Mocking Dependencies
For services with dependencies, use Moq:
var mockRepo = new Mock<IJobRepository>();
mockRepo.Setup(repo => repo.GetAll()).Returns(new List<Job> { new Job { Id = 1, Title = “Tester” } });
var service = new JobService(mockRepo.Object);
var jobs = service.GetJobs();
Assert.Single(jobs);
Assert.Equal(“Tester”, jobs[0].Title);
Benefits:
- Isolate unit tests
- Test logic without database or external API calls
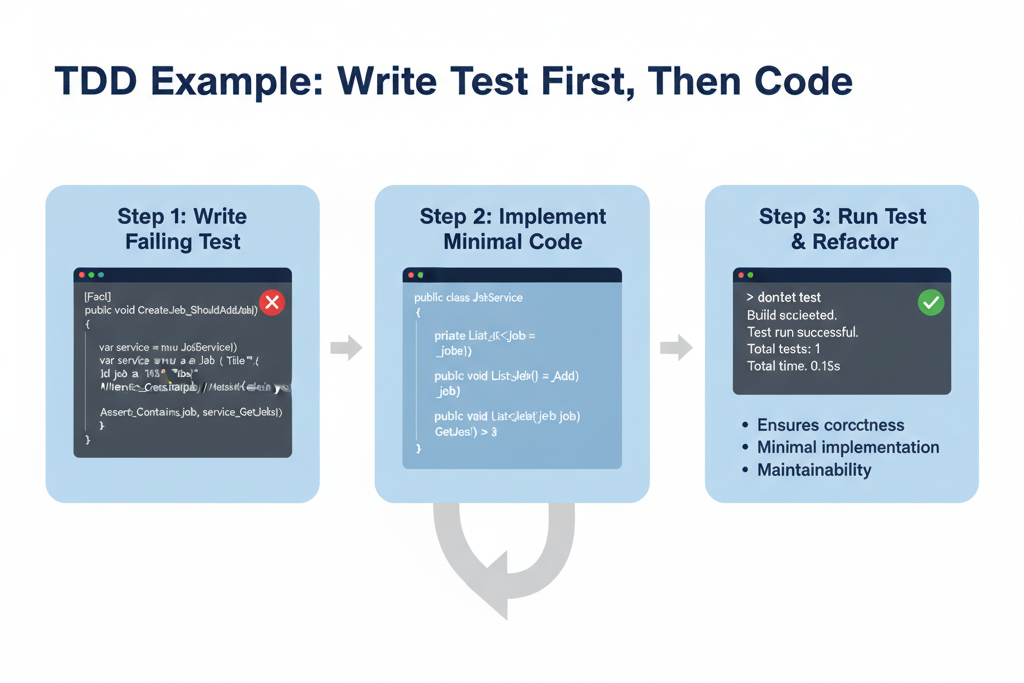
5. TDD Example
Step 1 – Write Test First:
[Fact]
public void CreateJob_ShouldAddJob()
{
var service = new JobService();
var job = new Job { Id = 1, Title = “Developer” };
service.CreateJob(job);
Assert.Contains(job, service.GetJobs());
}
Step 2 – Implement Minimal Code:
public void CreateJob(Job job)
{
_jobs.Add(job);
}
Step 3 – Run Test & Refactor
- TDD ensures code correctness, minimal implementation, and maintainability
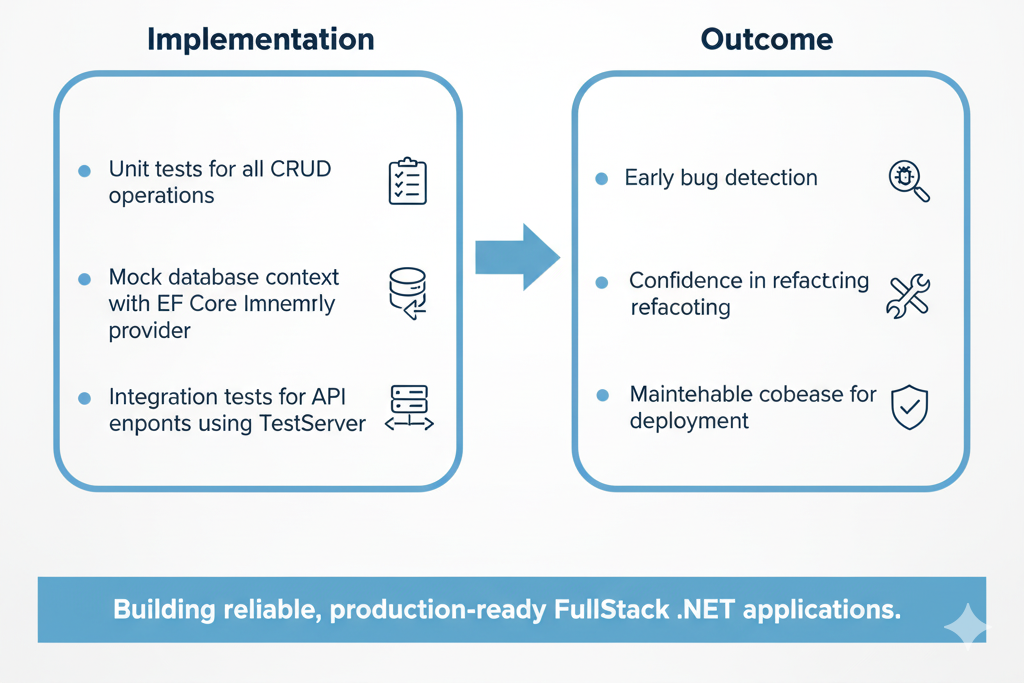
6. Real-World Project: CuriosityTech Job Portal
- Scenario: Apply TDD for JobService, UserService, and ApplicationService
- Implementation:
- Unit tests for all CRUD operations
- Mock database context with EF Core InMemory provider
- Integration tests for API endpoints using TestServer
- Outcome:
- Early bug detection
- Confidence in refactoring
- Maintainable codebase for production deployment
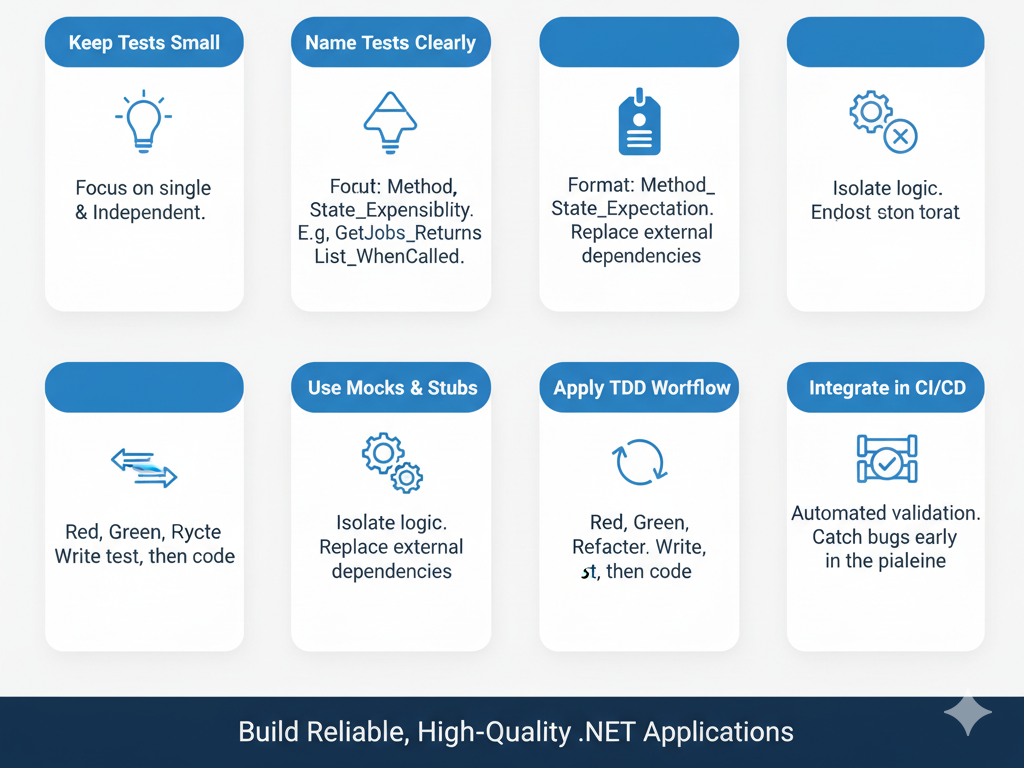
7. Best Practices
- Keep tests small and independent
- Name tests clearly: MethodName_StateUnderTest_ExpectedBehavior
- Use mocks and stubs to isolate tests
- Apply TDD workflow consistently
- Integrate tests in CI/CD pipelines for automated validation
8. CuriosityTech.in Mentorship Insights
- Hands-on TDD and unit testing for FullStack .NET projects
- Real-world exercises with mocking, dependency injection, and API testing
- Prepares learners for enterprise-grade testing and quality assurance
Conclusion
Unit testing and TDD are cornerstones of professional .NET development. They improve code quality, reduce bugs, and simplify maintenance. At CuriosityTech.in, learners practice writing robust tests and following TDD principles in real-world FullStack projects, preparing them for high-quality, production-ready applications.
The next step is Day 23 – Git & GitHub for .NET Developers, focusing on version control best practices, branching, and collaborative development.