Introduction
Industrial IoT (IIoT) security is among the most critical concerns in the rapidly evolving connected manufacturing and infrastructure landscape of 2025. IIoT integrates sensors, devices, and industrial equipment with cloud and edge platforms, creating powerful automation but also expansive attack surfaces. The repercussions of IIoT security breaches are severe, including production downtime, safety hazards, data theft, and regulatory non-compliance.
This article presents detailed, mandatory best practices for securing IIoT deployments, backed by the latest industry research, regulatory frameworks, and real-world incident lessons. I’ve structured it differently than the last post: instead of a roadmap, here you’ll find challenges, best practices, real-world case studies, emerging trends and Curiosity Tech insights.
Top Challenges in IIoT Security
- Legacy Devices: Older industrial equipment often lacks modern security features.
- Performance vs Security: Real-time industrial processes require security solutions with minimal latency.
- Physical Accessibility: Devices deployed in unprotected areas face tampering risks.
- Protocol Diversity: Variety of communication protocols including some insecure by design.
- Scale and Management: Tens of thousands of devices spread across geographies demand orchestrated security management.
Core Best Practices for IIoT Security in 2025
1. Device Identity and Trust
- Provision unique cryptographic identities for every IIoT device using X.509 certificates or hardware-backed keys (TPMs or secure elements).
- Implement Secure Boot along with cryptographic firmware signatures to ensure only authenticated firmware runs.
- Enable firmware over-the-air (OTA) updates with signed images to patch security flaws promptly and securely.
2. Network Security
- Enforce encrypted communication protocols such as MQTT over TLS 1.3, OPC UA over TLS, and HTTPS.
- Implement network segmentation using the Purdue model, creating isolated zones with demilitarized zones (DMZs) for secure data flow and breach containment.
- Replace or encapsulate legacy and insecure protocols like Modbus with secure tunneled versions.
- Deploy industrial firewalls and intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDS/IPS) specialized for operational technology (OT) environments.
3. Security Monitoring and Analytics
- Use a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) platform that integrates OT telemetry and IT security logs for centralized visibility.
- Implement continuous network traffic monitoring including passive monitoring tools that do not disrupt critical industrial operations.
- Employ AI-driven behavioral anomaly detection to identify deviations from baseline device and network behavior in real time.
4. Operational Security
- Prepare and regularly test incident response plans tailored for industrial environments including procedures for emergency shutdowns and device isolation.
- Conduct frequent penetration testing and security audits focusing on vulnerabilities in protocols, devices, and cloud interfaces.
- Maintain comprehensive asset inventories that track device firmware versions, network configurations, and lifecycle status.
- Invest in rigorous employee security awareness and training programs covering IIoT specific risks and mitigation strategies.
Compliance and Regulatory Standards
- IEC 62443 series — the foundational security standard for industrial automation and control systems.
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework — adapted guidelines for critical infrastructure and industrial control systems.
- Data privacy standards including GDPR, HIPAA where applicable for personally identifiable information or healthcare devices.
- ISO/IEC 27001 for information security management across industrial IT and cloud systems.
Real-World Case Studies
- Several automotive manufacturing plants blocked ransomware intrusions by implementing network segmentation and device certificate controls.
- Oil and gas refineries employed TPM-secured IoT devices and AI-powered anomaly detection combined with cloud SIEM for early compromise detection.
- Pharmaceutical companies strengthened compliance with HIPAA and FDA standards by enforcing encrypted telemetry and controlled device lifecycle management.
Emerging Trends in IIoT Security for 2025
- Zero Trust Architectures: Continuous authentication and least-privilege access policies across devices and networks.
- Blockchain for Firmware and Identity Management: Immutable audit trail of device firmware versions and lifecycle events.
- Edge Security Enhancements: Deploy security analysis and threat detection algorithms on IoT gateways and edge nodes rather than in centralized cloud only.
- Automated Orchestration and Patch Management: AI-driven upgrade scheduling minimizing downtime and ensuring security patch compliance at scale.
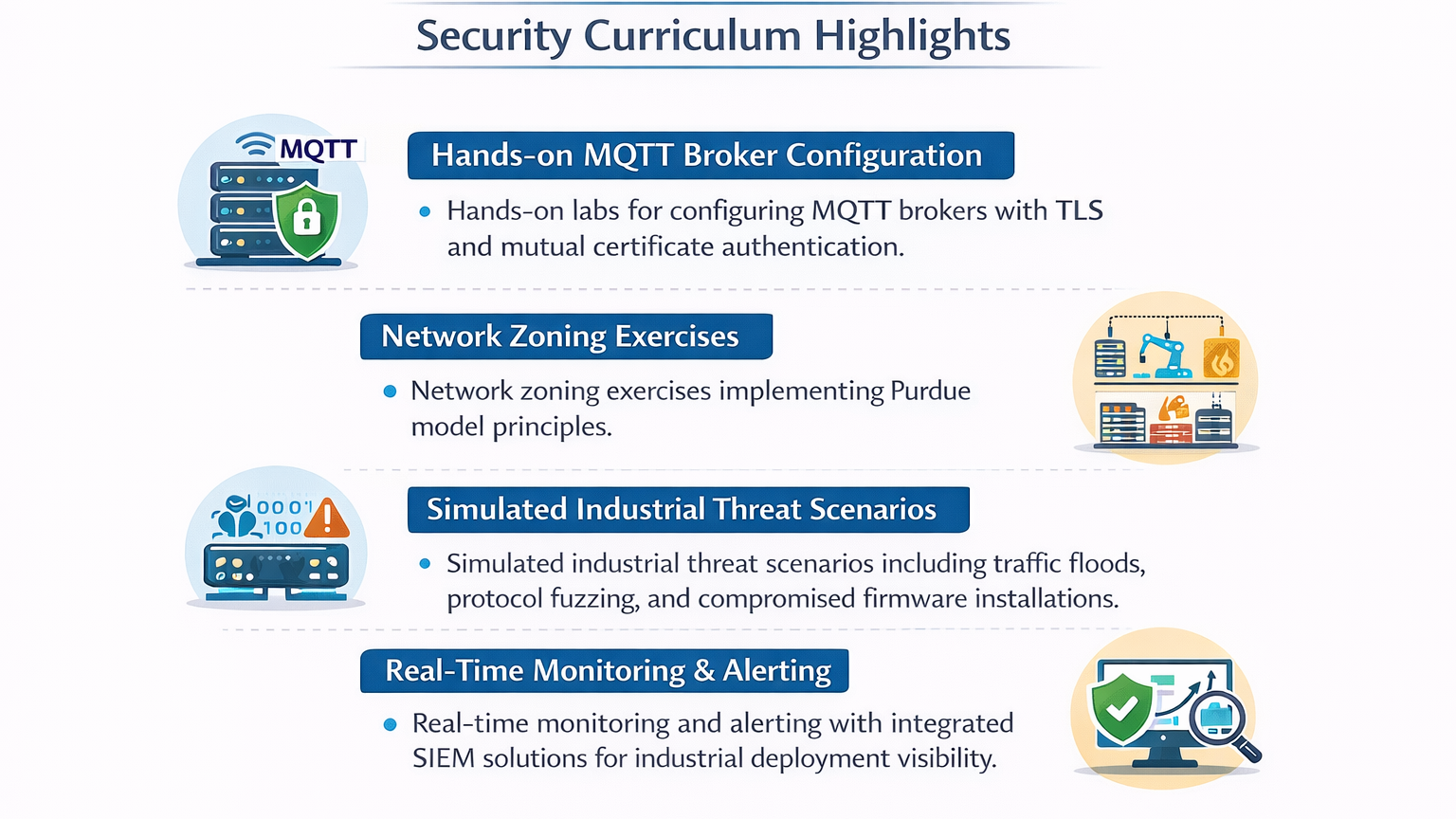
Curiosity Tech Nagpur Security Curriculum Highlights
Conclusion
Securing IIoT in 2025 requires a holistic, layered defense approach combining hardware-rooted trust, robust encrypted communications, segmented OT network architectures, continuous monitoring, and rapid incident response plans. Amid the growing complexity of IIoT environments, proactive security management backed by ongoing training is critical.
Training platforms like Curiosity Tech Nagpur empower engineers with the knowledge and practical skills to build, deploy, and defend resilient IIoT systems, ensuring business continuity, safety, and regulatory compliance.