Introduction
Securing a robotics engineering role requires not only technical skills but also the ability to articulate your knowledge during interviews. Whether applying for industrial automation, healthcare robotics, or AI-integrated systems, understanding commonly asked questions, practical scenarios, and how to respond effectively is essential.
At CuriosityTech.in, aspiring robotics engineers access mock interviews, project demonstrations, and career guidance to prepare thoroughly for real-world interviews.
1. Technical Questions and Answers
Q1: What are the different types of robots, and where are they commonly used?
Answer: Robots can be classified as:
- Industrial Robots: Used in manufacturing, assembly, and welding (e.g., ABB, KUKA robots).
- Service Robots: Used in healthcare, hospitality, and education (e.g., telepresence robots).
- Autonomous Robots: Drones, AGVs, and self-driving cars using sensors and AI.
- Collaborative Robots (Cobots): Work alongside humans in factories or labs.
Tip: Provide examples of real-world applications to demonstrate practical knowledge.
Q2: Explain forward and inverse kinematics.
Answer:
- Forward Kinematics: Determines the end-effector position from given joint angles.
- Inverse Kinematics: Determines joint angles required to reach a desired end-effector position.
Example: In a robotic arm for assembly, forward kinematics predicts where the arm moves based on servo angles, while inverse kinematics calculates the angles needed to pick and place components accurately.
Diagram Idea: Robotic arm showing joint angles and end-effector coordinates.
Q3: What is ROS, and why is it important?
Answer: ROS (Robot Operating System) is a middleware framework for robotics. It provides tools, libraries, and communication protocols to:
- Integrate sensors, actuators, and control algorithms.
- Simulate and visualize robots in Gazebo or RViz.
- Enable modular, scalable development for multi-robot systems.
Tip: Mention experience with simulation, sensor integration, or ROS nodes in your answer.
Q4: How do you implement obstacle avoidance in mobile robots?
Answer:
- Sensors: Use LiDAR, ultrasonic, or IR sensors.
- Algorithms: Implement A*, Dijkstra, or RRT path-planning algorithms.
- Control: Adjust robot trajectory in real-time using feedback from sensors.
Scenario Example: A warehouse robot detecting an unexpected obstacle and rerouting dynamically using ROS navigation stack.
Q5: Explain the difference between open-loop and closed-loop control systems.
Answer:
- Open-loop: Executes commands without feedback. Example: Stepper motor moving a fixed number of steps.
- Closed-loop: Uses sensor feedback to adjust actions. Example: PID-controlled motor maintaining precise speed or position.
Tip: Highlight situations where closed-loop control is necessary for precision.
2. Scenario-Based Questions
Q6: How would you design a robot for a hospital to assist nurses?
Answer:
- Objective: Reduce nurse workload and ensure timely delivery of medications.
- Design Steps:
- Hardware : Mobile base, manipulator arm, storage compartment.
- Sensor : LiDAR for navigation, cameras for obstacle detection.
- Software : ROS for navigation, scheduling algorithm for task assignment.
- Safety : Emergency stop, Collision detection, Smooth movement.
Tip: Use structured approaches to demonstrate problem-solving skills.
Q7: You need to integrate AI into a robotic system. How would you proceed?
Answer:
- Identify problem scope (e.g., object recognition, path optimization).
- Select AI framework (TensorFlow, PyTorch) compatible with ROS.
- Collect data for training models (images, sensor logs).
- Deploy AI model in simulation first, then on hardware with safety constraints.
- Monitor performance and refine algorithms continuously.
Diagram Idea: Flowchart showing data collection → AI model training → simulation → deployment.
3. Behavioral Questions
Q8: Describe a challenging robotics project you worked on.
Answer:
- Explain the objective clearly.
- Mention technical challenges (sensor noise, algorithm efficiency, hardware limitations).
- Describe solution approach (simulation, iterative testing, collaboration).
- Highlight outcome and learning.
Tip: Use the STAR method: Situation, Task, Action, Result.
Q9: How do you ensure safety when testing a new robot?
Answer:
- Conduct simulations before physical testing.
- Use emergency stop mechanisms and protective barriers.
- Test incrementally, verifying each component separately.
- Follow ISO safety standards for collaborative robots.
4. Practical Advice for Robotics Interviews
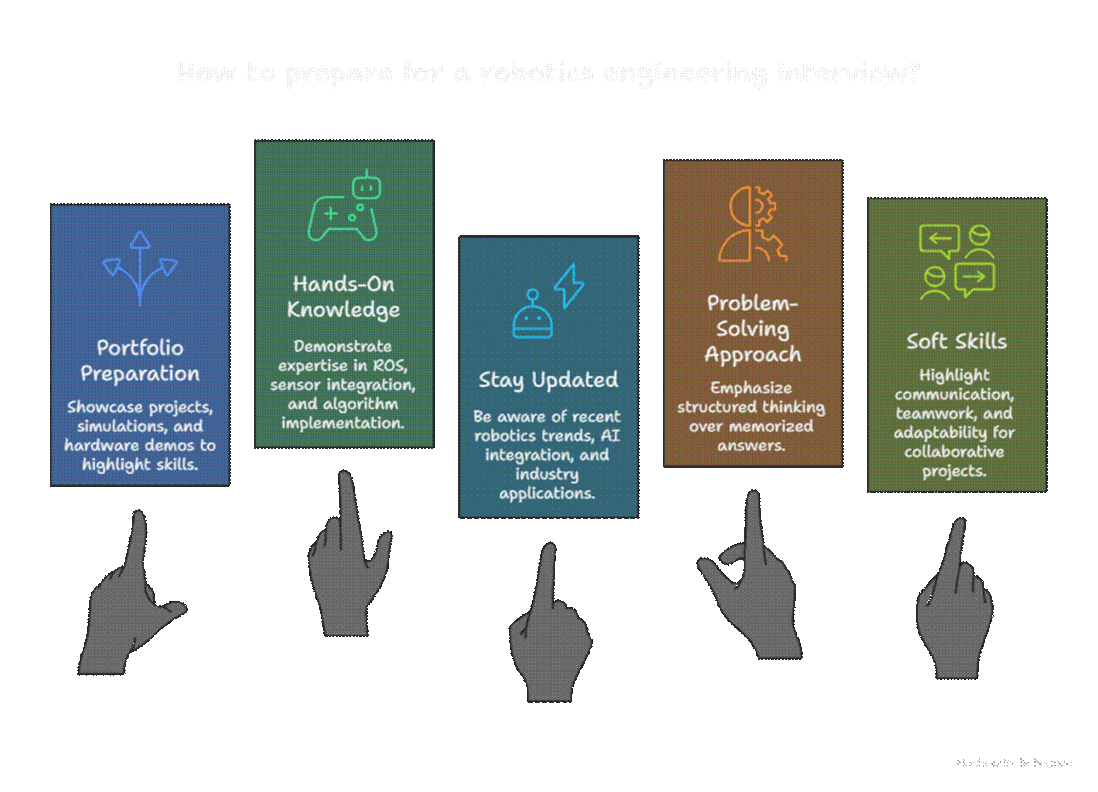
CuriosityTech.in provides mock interviews, scenario-based exercises, and practical tutorials to help learners confidently answer technical and behavioral questions.
5. Additional Tips for Technical Mastery
- Practice coding and algorithm implementation in Python/C++.
- Experiment with simulation tools like Gazebo, Webots, and V-REP.
- Work on integrated robotics projects combining hardware, sensors, and AI.
- Document experiments and share GitHub repositories with interviewers.
Conclusion
Preparing for robotics engineering interviews requires a mix of technical knowledge, practical experience, problem-solving ability, and communication skills. By reviewing commonly asked questions, scenario-based problems, and hands-on project experience, candidates can confidently demonstrate their expertise. Platforms like CuriosityTech.in provide structured guidance, mock interviews, and project tutorials to help learners excel in robotics interviews and secure professional roles.