In the complex world of software development, business analysis, and project management, requirements gathering is the cornerstone of project success. Without a clear understanding of what a client or end-user needs, even the most advanced technology can fall short. Day 4 of our learning journey focuses on unraveling the nuances of requirements gathering, exploring techniques, and understanding best practices that turn project visions into reality.
At CuriosityTech.in, we emphasize that requirements gathering is not just a checklist task; it is a strategic approach that can make or break project outcomes. Whether you are a budding analyst, developer, or project manager, mastering this skill will accelerate your ability to deliver high-quality results.
What is Requirements Gathering?
Requirements gathering is the process of collecting, analyzing, and documenting the needs of stakeholders to ensure that the final product meets expectations. It serves as a bridge between business objectives and technical implementation. Essentially, it is about asking the right questions, listening actively, and translating user needs into actionable project specifications.
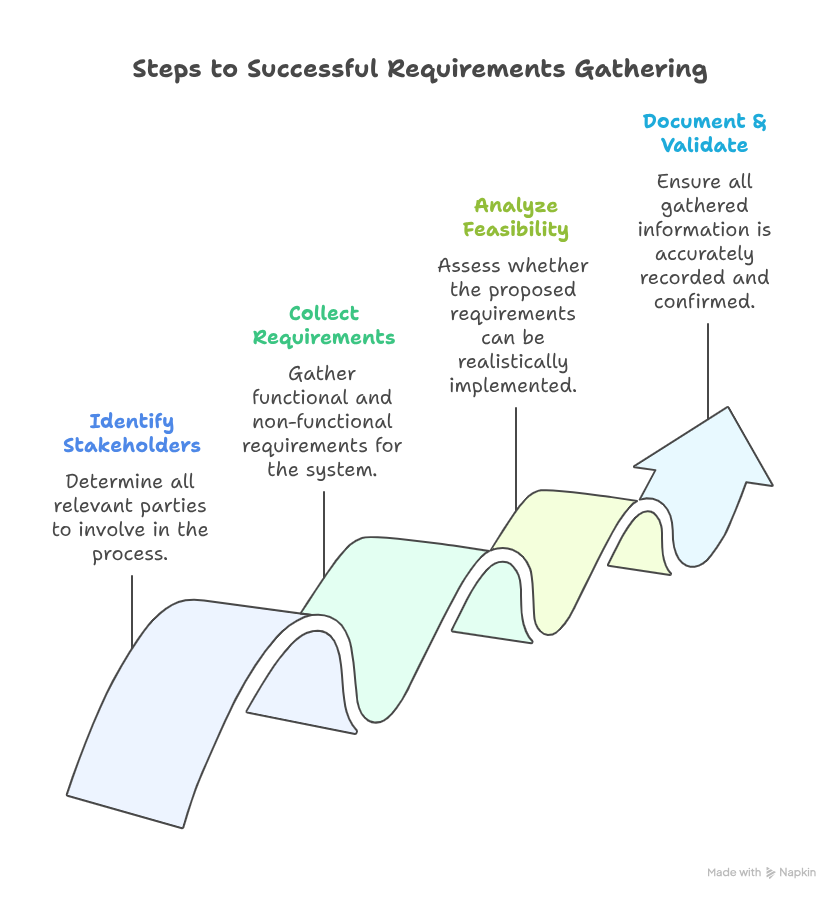
A typical requirements-gathering workflow includes:
- Identifying stakeholders
- Collecting functional and non-functional requirements
- Analyzing requirements for feasibility
- Documenting and validating requirements
Without proper requirements gathering, projects are prone to scope creep, budget overruns, and missed deadlines.
Key Techniques for Effective Requirements Gathering
To gather precise and actionable requirements, multiple techniques are employed. Here are the most effective:
1. Interviews
Interviews are direct, one-on-one conversations with stakeholders. They allow for deep exploration of expectations and pain points. At CuriosityTech.in, we train our teams to ask open-ended questions to elicit comprehensive insights rather than simple yes/no answers.
Tips for Successful Interviews:
- Prepare a structured questionnaire
- Encourage storytelling from stakeholders
- Document responses meticulously
2. Workshops
Workshops bring together stakeholders from different departments. These sessions foster collaboration and help identify conflicting requirements early. They are particularly effective in agile environments where feedback loops are short.
Workshop Best Practices:
- Facilitate group discussions effectively
- Use visual aids like whiteboards or digital boards
- Summarize findings immediately after sessions
3. Surveys and Questionnaires
Surveys are suitable for reaching a large audience. They help collect quantitative data quickly but need to be carefully structured to avoid biased responses.
Pro Tip: Combine surveys with interviews to balance quantity and quality of data.
4. Observation
Observing users in their natural environment uncovers unspoken requirements. This technique is highly valuable for user-centric projects where behavior drives functionality.
5. Document Analysis
Reviewing existing documents such as reports, manuals, or system logs helps understand current processes and gaps. At CuriosityTech, our experts often combine document analysis with stakeholder interviews for a comprehensive understanding.
Requirements Types: Understanding What to Gather
Requirements can be broadly classified into:
| Requirement Type | Description | Example |
| Functional | Describes what the system should do | User login, data entry, reporting |
| Non-Functional | Quality attributes of the system | Performance, security, scalability |
| Technical | Technical constraints | Database choice, APIs, integration |
| Business | Business objectives | Cost reduction, customer satisfaction |
Best Practices in Requirements Gathering
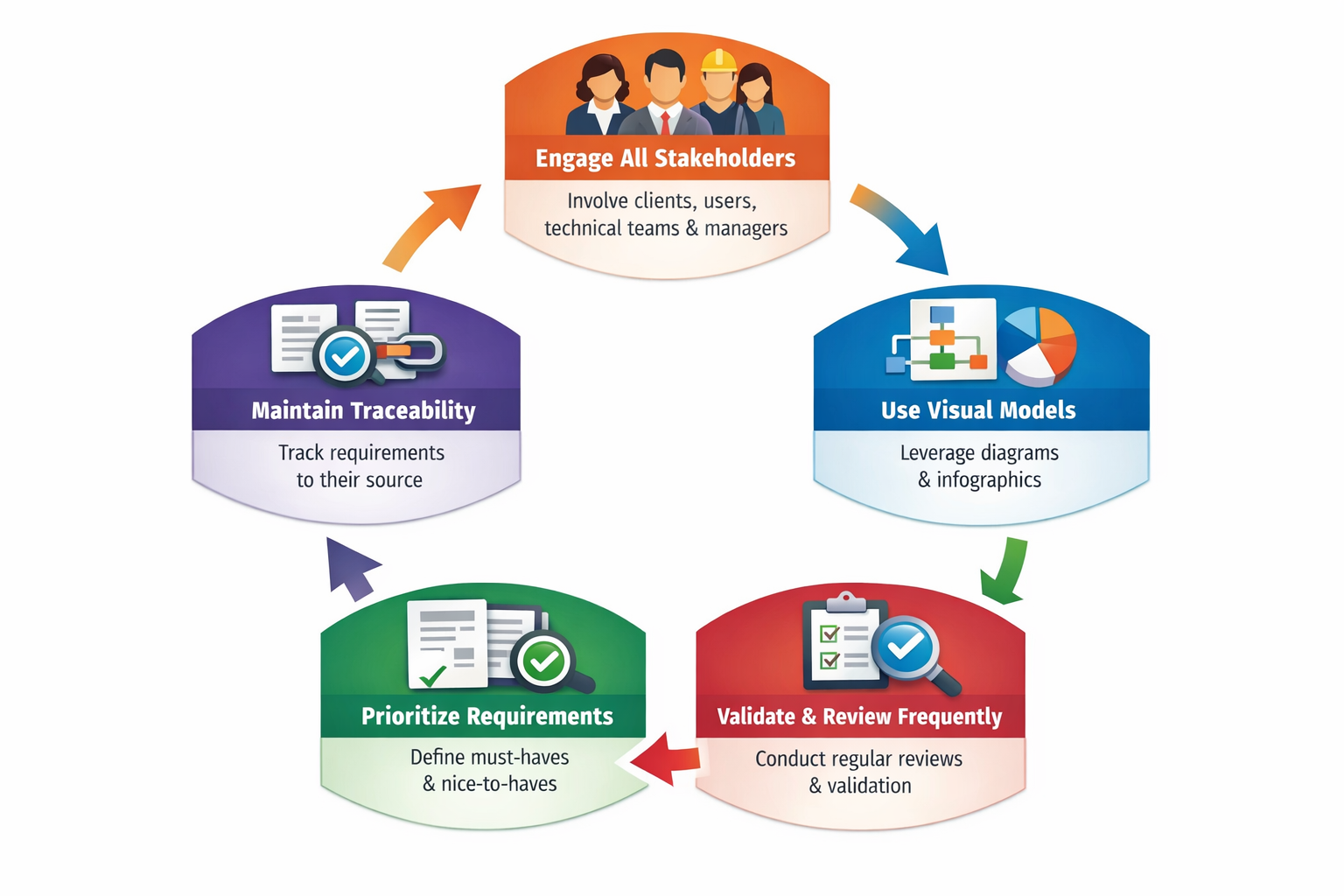
Following best practices ensures the gathered requirements are accurate, actionable, and aligned with business goals:
- Engage All Stakeholders – Include clients, end-users, technical teams, and managers.
- Use Visual Models – Diagrams, flowcharts, and infographics clarify complex processes.
- Prioritize Requirements – Distinguish between must-have and nice-to-have features.
- Validate and Review Frequently – Continuous validation reduces rework and misunderstandings.
- Maintain Traceability – Link each requirement to its source and ensure accountability.
Hierarchical Diagram of Requirements Gathering
Here’s a conceptual hierarchy of requirements gathering techniques:
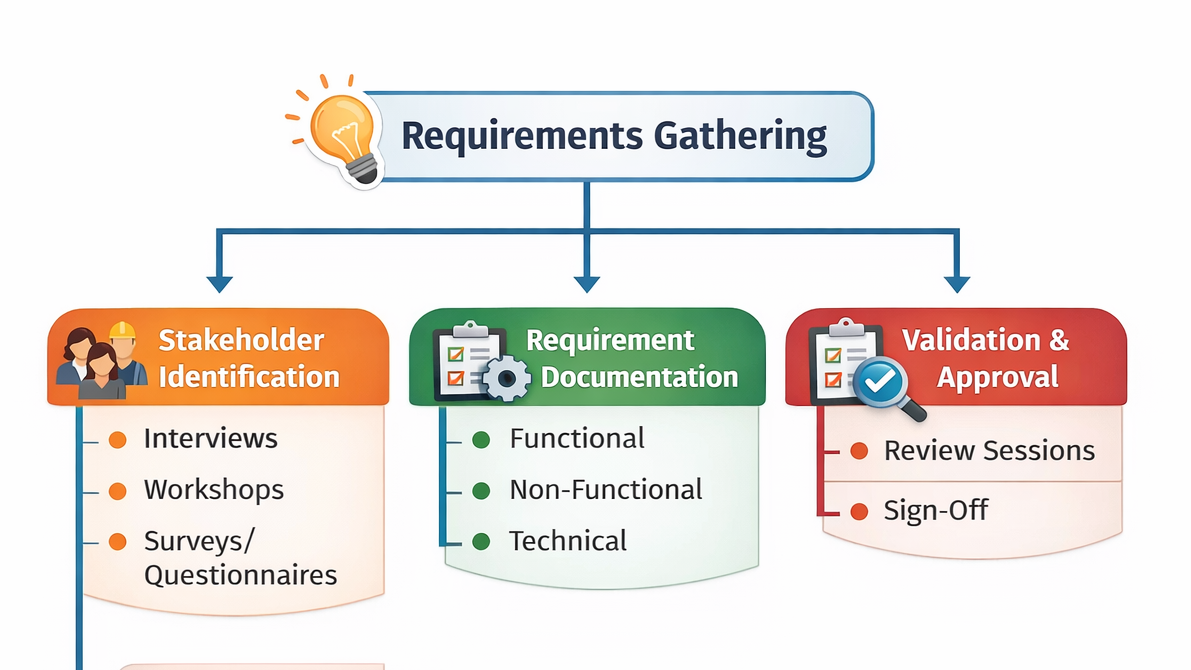
This hierarchy helps teams visualize the flow of activities from stakeholder engagement to formal sign-off.
Infographic Suggestion
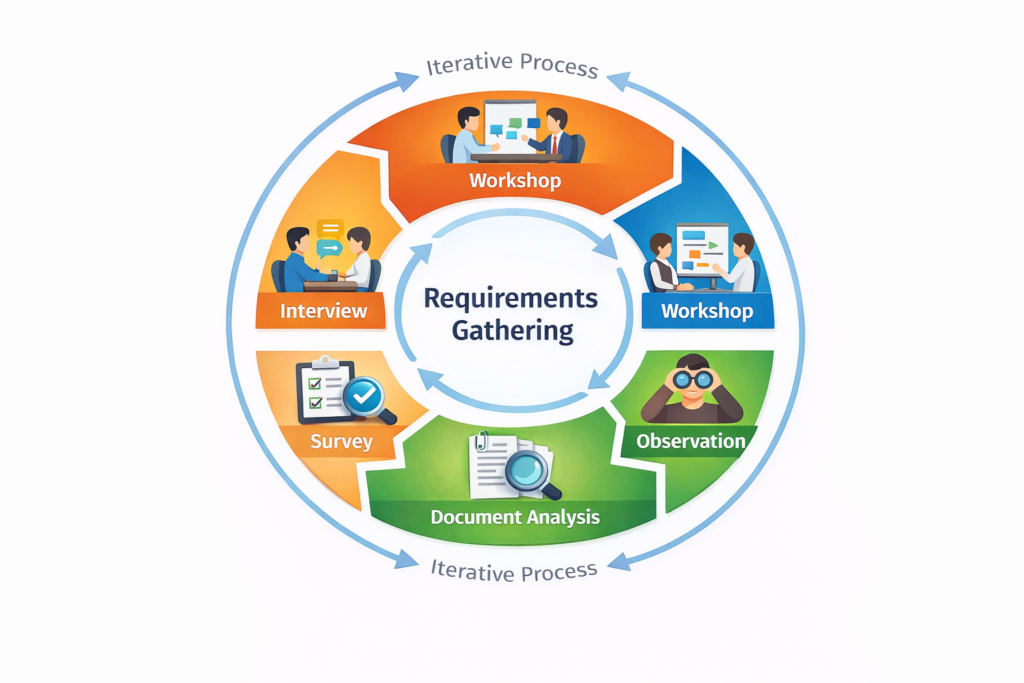
A simple infographic could illustrate the 5 techniques of requirements gathering (Interview, Workshop, Observation, Survey, Document Analysis) in a circular flow, emphasizing that the process is iterative, not linear.
Humanized Insights: Why CuriosityTech.in Stands Out
At CuriosityTech.in, we believe that technology is only as effective as the insights driving it. Our approach to requirements gathering is human-centric, ensuring we truly understand the problems before offering solutions. By blending classic techniques with modern agile practices, we help organizations transform ideas into reality efficiently. This methodology has empowered our clients to reduce project risks, enhance usability, and achieve measurable outcomes.
Conclusion
Requirements gathering is both an art and a science. By employing diverse techniques, engaging stakeholders effectively, and adhering to best practices, businesses can ensure project success from the outset. Remember, gathering requirements is not just a step in a project—it’s the foundation for delivering value, building trust, and fostering innovation.
Mastering this skill today will pay dividends in every project you undertake tomorrow.



