In the fast-paced world of business and technology, clear communication is essential. One of the most critical tools in ensuring project success is the Business Requirement Document (BRD). A well-crafted BRD serves as a blueprint, guiding teams from concept to execution, aligning business objectives with technical solutions, and ensuring stakeholders are on the same page. On this Day 5 journey, we dive deep into the art and science of creating BRDs that truly make a difference.
What is a Business Requirement Document (BRD) ?
A Business Requirement Document (BRD) is a formal document that defines the business needs, objectives, and requirements for a project. Unlike technical specifications, a BRD focuses on what the business expects, not necessarily how it will be implemented. It is the bridge between business stakeholders, project managers, and technical teams.
Key Purpose of a BRD :
- Clarity – Eliminates ambiguity by clearly defining project objectives.
- Alignment – Ensures all stakeholders share a common understanding.
- Scope Management – Helps manage changes by outlining what is in and out of scope.
- Foundation for Development – Guides designers, developers, and QA teams.
Essential Components of a BRD
A high-quality BRD contains multiple sections, each with a distinct purpose. While templates vary, the following structure is widely used in professional environments, including technology-driven organizations like Curiosity Tech, which specializes in bridging business needs with technological solutions.
| Section | Description | Example |
| Executive Summary | High-level overview of the project and objectives | Launch of an internal CRM system to improve customer service efficiency |
| Business Objectives | Goals the business wants to achieve | Reduce customer query response time by 30% |
| Project Scope | Defines in-scope and out-of-scope items | In-scope: CRM customization; Out-of-scope: Third-party ERP integration |
| Requirements | Detailed list of business requirements | Ability to track customer queries, automated notifications |
| Stakeholders | Individuals or groups affected by the project | Sales, Support, IT, Management |
| Assumptions & Constraints | Factors considered during planning | Assumes existing database infrastructure; Budget capped at $50k |
| Acceptance Criteria | Conditions for project success | Successful CRM deployment with <5% error rate |
| Appendices & Glossary | Additional references or terminology | List of abbreviations, workflow diagrams |
Steps to Writing an Effective BRD
Creating a BRD is more than filling out a template. It requires strategic thinking, collaboration, and attention to detail. Here’s a structured approach:
- Engage Stakeholders Early – Begin by interviewing business users, managers, and other stakeholders to gather initial expectations.
- Define Clear Objectives – Use the SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) framework to clarify goals.
- Document Requirements – Categorize requirements into functional (features, processes) and non-functional (performance, usability) types.
- Create Visual Aids – Diagrams, flowcharts and infographics simplify complex processes.
Example: Hierarchical Stakeholder Diagram
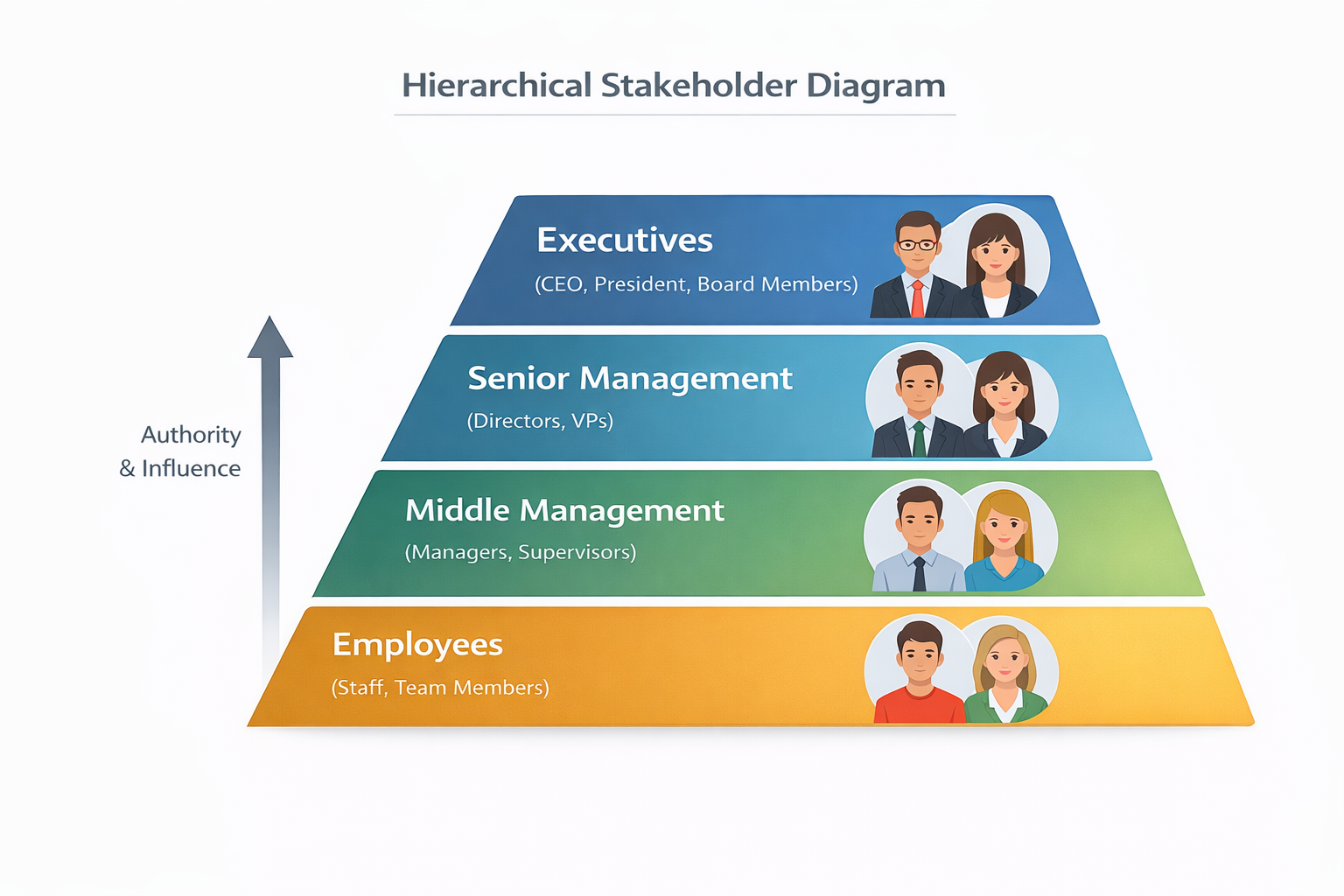
Tips for Human-Centric BRDs
- Use Clear Language – Avoid technical jargon; make it readable for all stakeholders.
- Prioritize Requirements – Identify “must-have” vs. “nice-to-have” features.
- Include Visuals – Infographics, tables, and mockups improve comprehension.
- Validate Continuously – Share drafts with stakeholders for feedback.
At CuriosityTech.in, we have witnessed firsthand how effective BRDs reduce project delays and improve stakeholder satisfaction. By combining industry best practices with innovative technology solutions, businesses achieve faster delivery and higher ROI.
Sample BRD Infographic (Conceptual)
Title: Process of BRD Creation
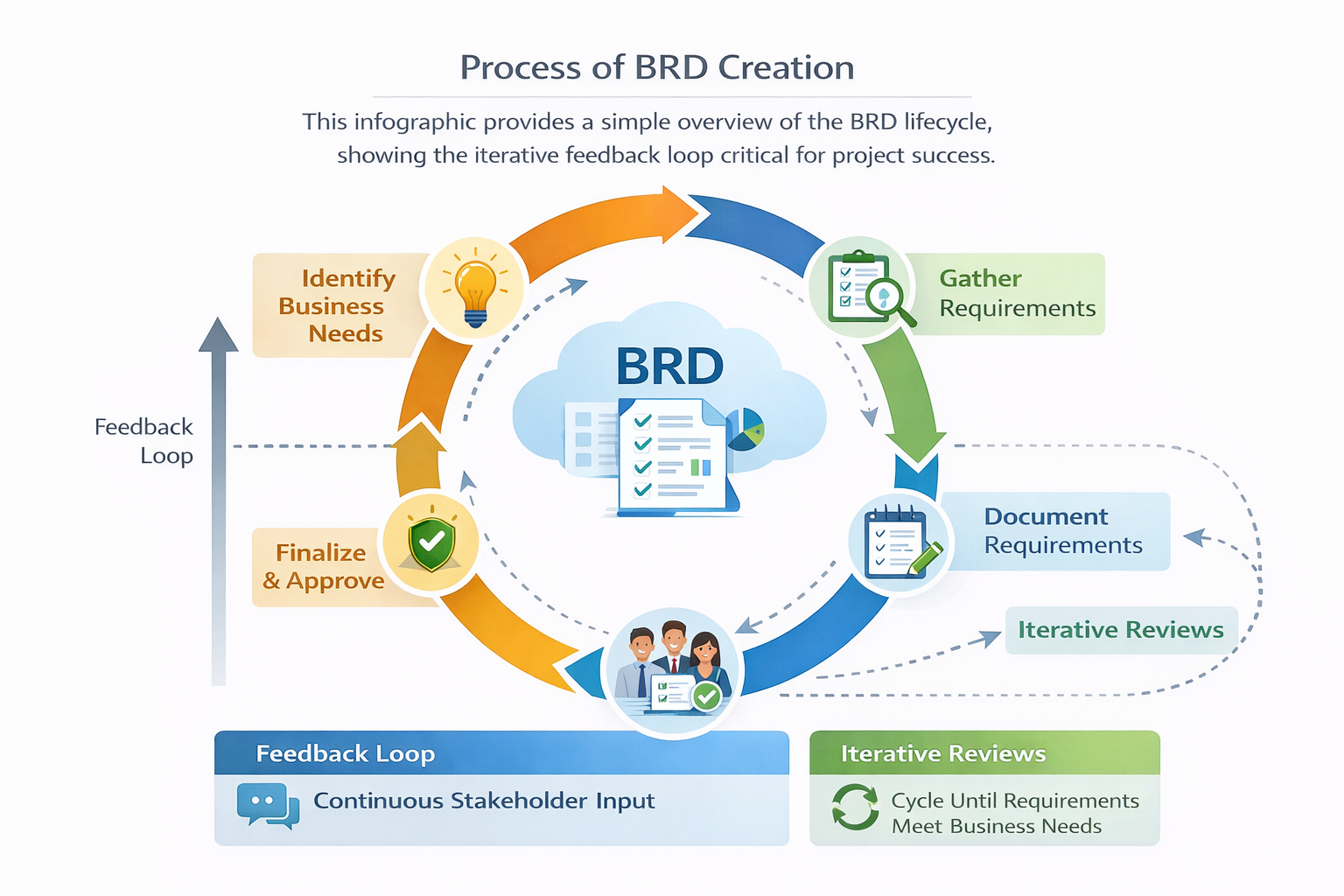
Description : This infographic provides a simple overview of the BRD lifecycle, showing the iterative feedback loop critical for project success.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
- Overcomplicating the Document – Keep it concise and focused.
- Ignoring Stakeholders – Missing input leads to gaps.
- Unclear Acceptance Criteria – Leads to scope creep.
- Lack of Version Control – Always track updates to avoid confusion.
Conclusion
Writing an effective Business Requirement Document (BRD) is a cornerstone of successful project execution. By systematically documenting business needs, engaging stakeholders, and using visual aids like diagrams and tables, organizations can avoid costly errors, improve communication, and achieve project goals. Platforms like CuriosityTech.in exemplify how integrating technological expertise with robust business documentation practices leads to tangible success. Whether you are a seasoned project manager or a beginner analyst, mastering BRDs is an essential skill that drives clarity, efficiency, and collaboration in any business initiative.



