Introduction
Flutter, powered by Dart, has become one of the most popular frameworks for cross-platform mobile development in 2025. Its combination of expressive UI components, near-native performance, and a single codebase makes it ideal for developers at all levels.
Understanding Dart (Flutter’s programming language) and Flutter’s core concepts is the foundation for building scalable, maintainable apps. At CuriosityTech (Website: https://curiositytech.in, Phone: +91-9860555369, Email: contact@curiositytech.in), we guide beginners to not just code, but think in Flutter, mastering state management, widgets, and UI architecture from day one.
1. Introduction to Dart
Dart is a modern, object-oriented language developed by Google. It is optimized for client-side development, making it ideal for Flutter apps.
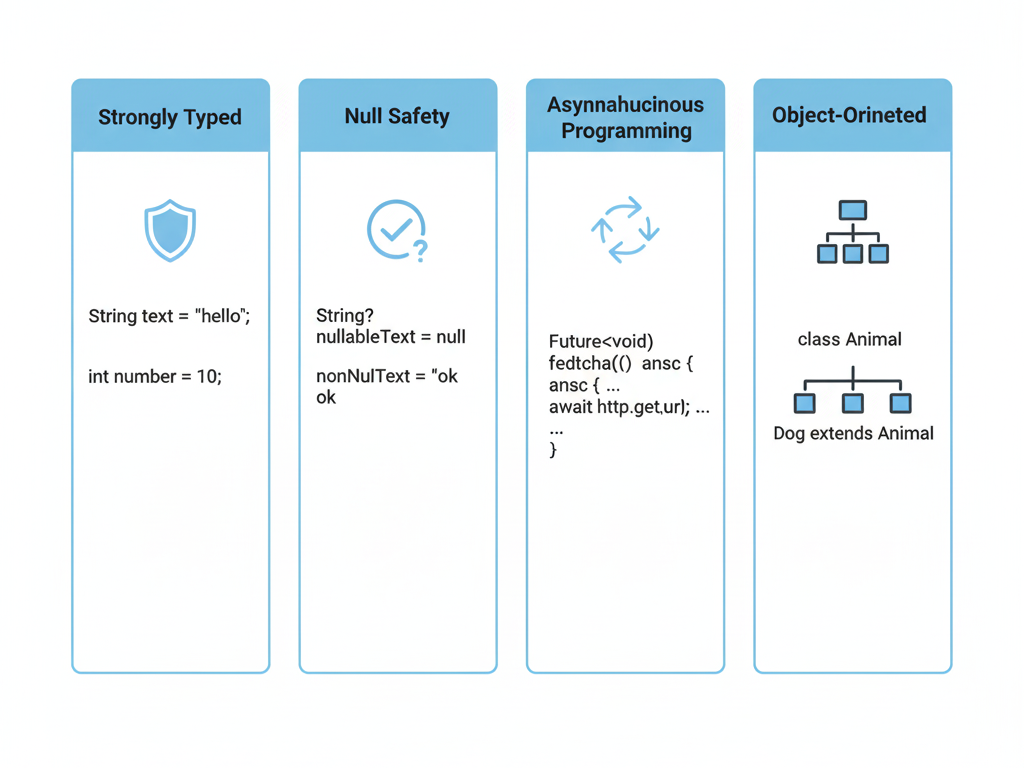
Key Features of Dart
- Strongly Typed: Helps catch errors at compile-time
- Null Safety: Prevents null reference error
- Asynchronous Programming: Supports async/await for network request
- Object-Oriented: Classes, inheritance, and mixins for modular code
Basic Dart Syntax
void main() {
String name = “CuriosityTech”;
int year = 2025;
print(“Welcome to $name Flutter tutorial, $year”);
}
Explanation:
- String and int demonstrate strong typing
- $name is string interpolation
- void main() is the entry point of Dart programs
2. Flutter Basics
Flutter uses widgets as its building blocks. Every element of the UI, from buttons to layouts, is a widget.
Types of Widgets
- StatelessWidget :-
- Immutable, UI doesn’t change dynamically
- StatefulWidget :-
- Maintains internal state, UI can update dynamically
Example: StatelessWidget
import ‘package:flutter/material.dart’;
void main() => runApp(MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
home: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: Text(‘Hello Flutter’)),
body: Center(child: Text(‘Welcome to CuriosityTech!’)),
),
);
}
}
Explanation:
- MaterialApp sets up basic app structure
- Scaffold provides default app layout
- Center positions content
- Text displays simple content across iOS & Android
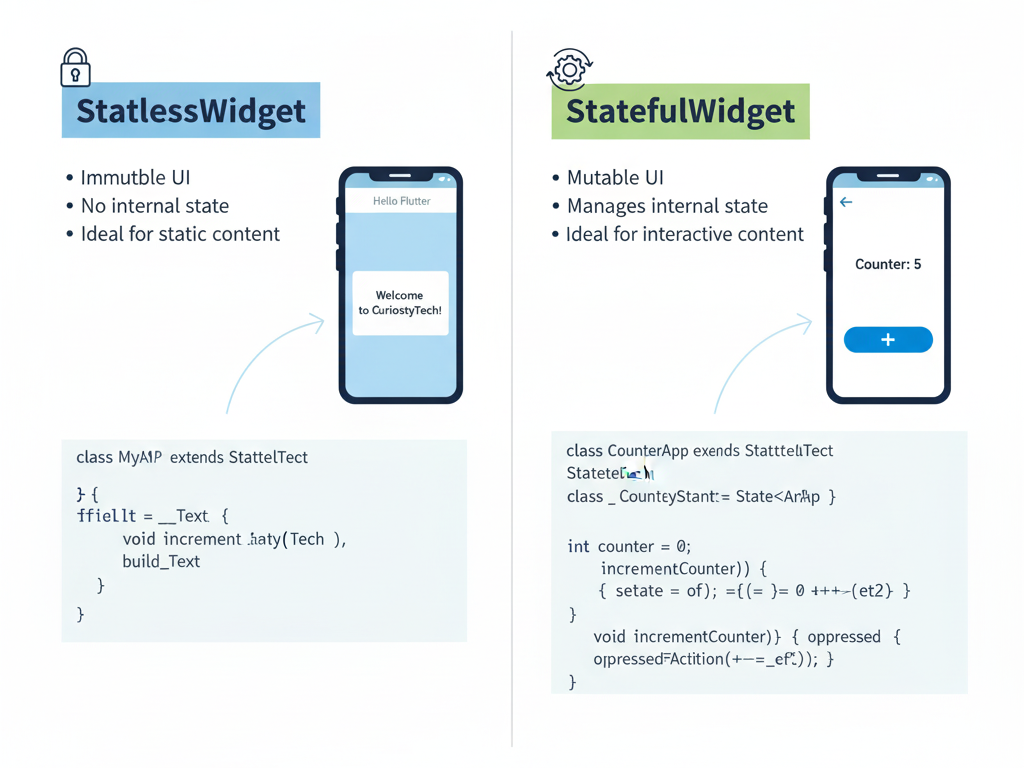
Example: StatefulWidget
class CounterApp extends StatefulWidget {
@override
_CounterAppState createState() => _CounterAppState();
}
class _CounterAppState extends State<CounterApp> {
int counter = 0;
void incrementCounter() {
setState(() {
counter++;
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
home: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: Text(‘Counter Example’)),
body: Center(child: Text(‘Counter: $counter’)),
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: incrementCounter,
child: Icon(Icons.add),
),
),
);
}
}
Explanation:
- StatefulWidget allows dynamic UI updates
- setState() triggers UI refresh
- Floating Action Button increments counter interactively
3. Layouts in Flutter
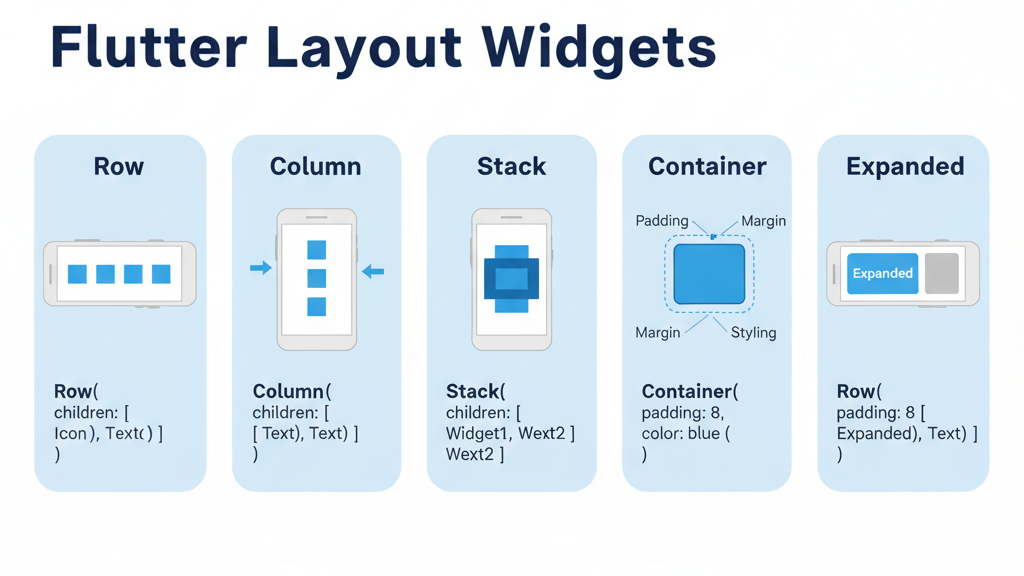
Flutter provides flexible layout widgets:
| Widget | Purpose |
| Row | Horizontal layout |
| Column | Vertical layout |
| Stack | Overlapping elements |
| Container | Styling, padding, margins |
| Expanded | Flexible space distribution |
Practical Layout Example:
Column(
children: [
Text(‘Welcome’),
Row(
children: [
Icon(Icons.star),
Text(‘CuriosityTech Flutter Guide’),
],
),
],
)
4. How to Become an Expert in Dart & Flutter Basics
- Master Dart Fundamentals: Classes, functions, async/await, and null safety.
- Practice Widgets: Build small apps experimenting with Stateless & Stateful Widgets.
- Learn Layouts: Explore Rows, Columns, Stack, and Container for responsive UI.
- Understand App Lifecycle: State management and navigation basics.
- Use Curiosity Tech Resources: Tutorials, example projects, and mentorship help accelerate learning. Socials: Instagram: curiositytechpark, LinkedIn: Curiosity Tech, Facebook: Curiosity Tech.
Conclusion
Understanding Dart and Flutter basics is essential for every cross-platform developer. From simple “Hello World” apps to dynamic counter apps, these foundational skills enable developers to build complex, maintainable, and scalable applications.
With structured learning, hands-on practice, and guidance from Curiosity Tech, beginners can quickly transition from learning fundamentals to creating professional-grade mobile apps in 2025



