Introduction
In today’s fast-paced business environment, organizations need to adapt quickly to changing market demands. For business analysts, understanding Agile methodologies and Scrum frameworks is crucial. Unlike traditional waterfall approaches, Agile emphasizes iterative development, collaboration, and delivering value quickly. At Curiosity Tech (website:curiositytech.in, Phone: +91-9860555369, Email: contact@curiositytech.in), we empower aspiring analysts to master Agile and Scrum, helping them bridge the gap between business requirements and successful project delivery.
1. What is Agile?
Agile is a project management and software development methodology that focuses on:
- Iterative delivery of working solutions
- Continuous stakeholder collaboration
- Flexibility to adapt to changes
Core Agile Principles:
- Customer satisfaction through early and continuous delivery of valuable software
- Welcoming changing requirements, even late in development
- Delivering working solutions frequently (every 2–4 weeks)
- Collaboration between business stakeholders and developers
- Motivated individuals and empowered teams
Curiosity Tech Insight: Business analysts trained at Curiosity Tech often report a 50% improvement in requirement clarity when applying Agile principles in real-world projects.
2. Scrum Framework for Business Analysts
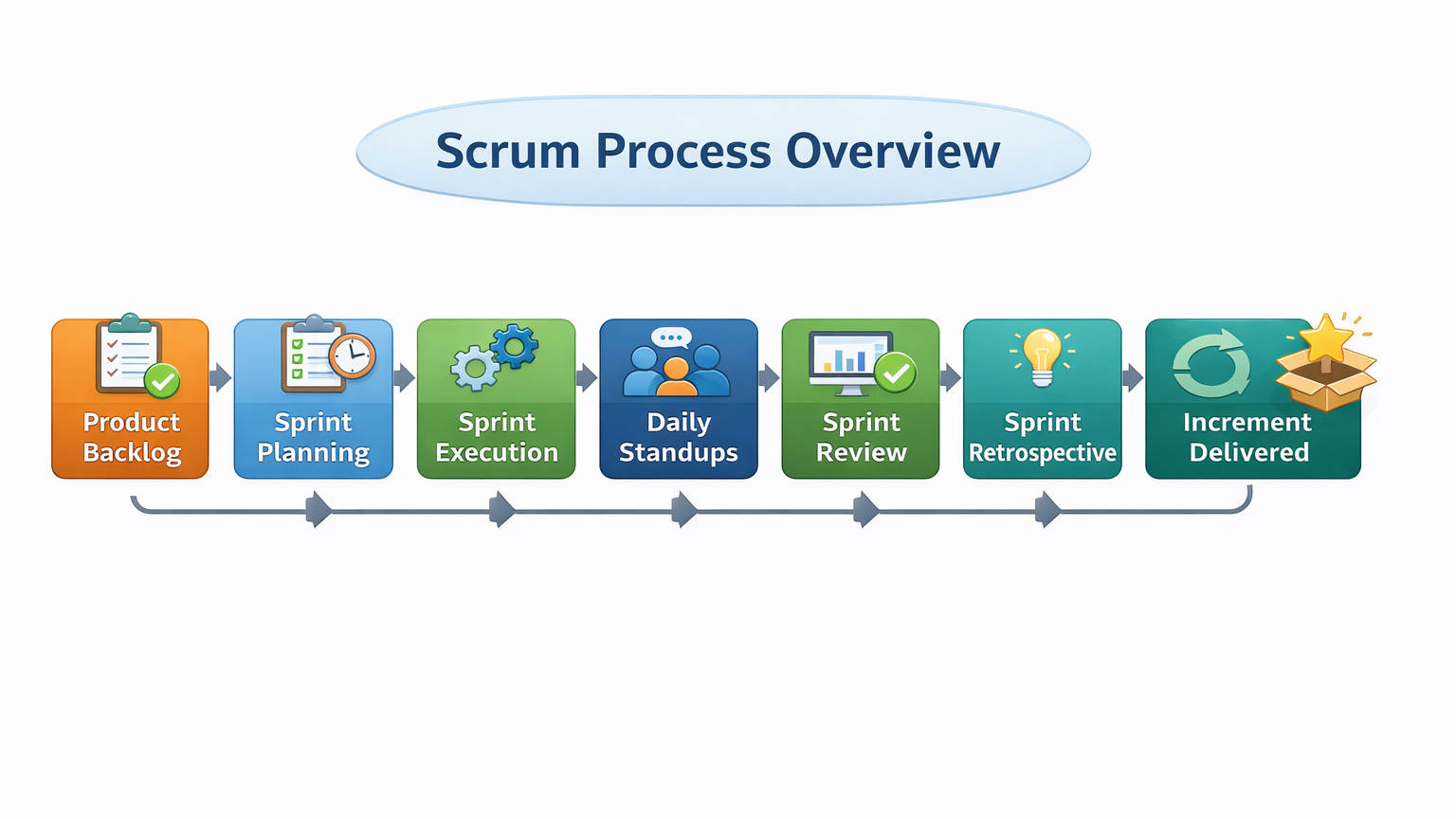
Scrum is the most popular Agile framework. It divides complex projects into manageable Sprints (time-boxed iterations, typically 2–4 weeks). Scrum encourages transparency, inspection, and adaptation.
Key Scrum Roles:
| Role | Responsibilities |
| Product Owner | Defines product vision, manages backlog, prioritizes features |
| Scrum Master | Facilitates Scrum events, removes obstacles, ensures Agile principles are followed |
| Development Team | Delivers increments of the product |
| Business Analyst (BA) | Bridges business needs with technical solutions, clarifies requirements |
Diagram: Scrum Process Overview
3. Business Analyst Responsibilities in Agile/Scrum
While Scrum traditionally doesn’t have a dedicated BA role, in practice, BAs are crucial for requirement elicitation, stakeholder communication, and backlog refinement. Key responsibilities include:
- Requirement Gathering: Conducting workshops, interviews, and surveys
- Backlog Management: Collaborating with the Product Owner to prioritize stories
- User Story Definition: Writing clear, testable user stories with acceptance criteria
- Process Modeling: Visualizing workflows for the development team
- Testing Support: Assisting QA with understanding business rules
Example User Story Format: As a [user role], I want [feature] so that [benefit].
Practical Insight from Curiosity Tech: In projects handled by our analysts, refining user stories reduced requirement ambiguities by over 40%, leading to faster development cycles and fewer reworks.
4. Agile Artifacts & Tools for BAs
| Artifact | Purpose | Notes |
| Product Backlog | Prioritized list of features and requirements | Maintained by Product Owner with BA input |
| Sprint Backlog | Tasks selected for current sprint | Updated daily, visible to all team members |
| Burndown Chart | Tracks work remaining in the sprint | Helps monitor progress and predict completion |
| Definition of Done | Ensures all requirements for a task are met | Provides clarity for QA and stakeholders |
Tools Commonly Used:
- JIRA: Manage backlog, sprints, and reports
- Confluence: Document requirements, meeting notes, and workflows
- Trello / Asana: Visual task tracking for smaller teams
At Curiosity Tech, analysts are trained to use these tools in real-world simulation projects, enhancing practical proficiency.
5. Agile Ceremonies and Their Importance
- Sprint Planning: Determines what work will be done in the upcoming sprint
- Daily Standup: 15-minute meetings for progress updates and roadblocks
- Sprint Review: Demonstrates completed work to stakeholders for feedback
- Sprint Retrospective: Reflects on successes and areas for improvement
Curiosity Tech Application: Our training emphasizes that BA participation in these ceremonies ensures alignment between business expectations and deliverables, reducing project delays significantly.
6. Case Study Example
A client from Nagpur faced frequent delays in software releases. By adopting Agile with Curiosity Tech’s guidance:
- Product backlog was properly prioritized
- User stories were refined and clarified
- Sprints were planned with clear deliverables
Result: Release cycles shortened from 3 months to 1 month, and customer satisfaction increased due to early delivery of high-value features.
7. Tips for Aspiring BAs to Master Agile & Scrum
- Gain certification like Certified Scrum Master (CSM) or PMI-ACP
- Participate in real or simulated Agile projects
- Learn how to write clear user stories and define acceptance criteria
- Use JIRA and Confluence extensively to manage backlogs and documentation
- Continuously communicate with stakeholders to refine requirements
Conclusion
Agile and Scrum are not just methodologies but mindsets. For business analysts, mastering Agile principles enables faster decision-making, effective requirement gathering, and stakeholder satisfaction. Organizations like Curiosity Tech provide hands-on learning, ensuring that aspiring analysts can transition smoothly from theory to practical application.
By understanding Agile and Scrum, BAs can become key contributors to project success, bridging the gap between business needs and technical execution.