Security is the foundation of cloud computing. Without proper identity and access management, even the most robust cloud architectures can be compromised. On Day 5, we focus on AWS IAM, the service that allows you to securely manage access to AWS resources.
At CuriosityTech.in, we often see beginners misconfigure permissions, creating vulnerabilities. Our structured approach ensures learners understand IAM deeply and implement best practices from day one.
1. What is AWS IAM?
AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) is a service that helps control who can do what in your AWS environment. It’s not just about security—it’s about governance, compliance, and operational efficiency.
IAM allows you to:
- Create users and assign them permissions.
- Organize users into groups.
- Assign roles for temporary or cross-service access.
Analogy: Think of IAM as a company’s HR and security combined—it decides who enters which office, what tools they can use, and what actions they can perform.
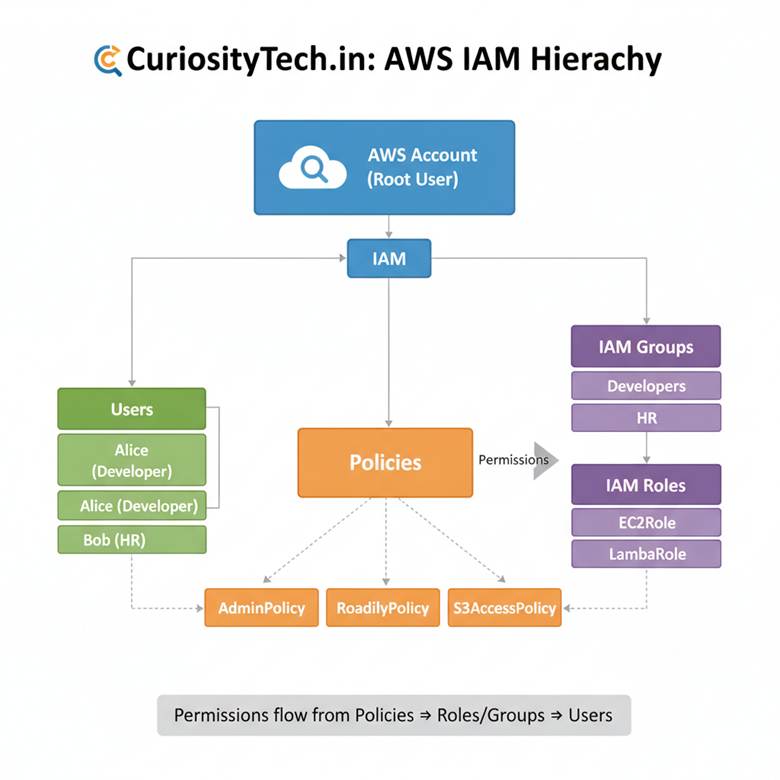
2. Core Components of IAM
| Component | Description | Example |
| Users | Individual accounts with credentials | Developer, HR Manager |
| Groups | Collection of users with shared permissions | Developers Group, Finance Group |
| Roles | Temporary permissions for users/services | EC2Role for automation |
| Policies | JSON documents specifying allowed/denied actions | S3ReadOnlyPolicy, AdminPolicy |
| Permissions | Actions that users/roles/groups can perform | s3:PutObject, ec2:StartInstances |
This diagram helps visualize how permissions flow from policies → roles/groups → users, making IAM structure easier to understand.
3. IAM Hierarchy Diagram
4. How IAM Works – Beginner-Friendly Example
Imagine a startup at Nagpur deploying a web application:
- Developers need full access to EC2 and S3.
- HR needs read-only access to employee data.
- Finance team accesses billing and cost management.
By creating groups and attaching policies, IAM ensures secure, structured access, reducing risk and making auditing easier.
5. Step-by-Step Beginner Setup
Step 1 – Create IAM Users
- Navigate to AWS Console → IAM → Users → Add User
- Provide username and select programmatic access or AWS Management Console access
Step 2 – Create Groups
- Navigate to Groups → Create Group
- Attach pre-defined policies or custom ones
- Add IAM users to groups
Step 3 – Assign Roles
- Roles are ideal for EC2 instances, Lambda functions, or cross-account access
- Choose trusted entity (AWS service, another account, web identity)
- Attach relevant policies
Step 4 – Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
- Select user → Security credentials → Assign MFA
- Use virtual MFA app for convenience
CuriosityTech.in Insight: Beginners often skip MFA, but even simple labs in our training programs enforce it for hands-on security awareness.
6. Best Practices for IAM
| Practice | Why It Matters |
| Use groups instead of individual permissions | Easier management and scaling |
| Enable MFA for all users | Adds extra security layer |
| Apply least privilege principle | Minimize accidental damage |
| Rotate access keys regularly | Prevent compromise |
| Use roles for services | Avoid embedding credentials in code |
7. Infographic Concept

8. Common Beginner Mistakes
- Using root account for everyday tasks
- Over-assigning admin privileges
- Forgetting to clean up unused roles or keys
- Ignoring logging and auditing
By practicing hands-on labs, learners at CuriosityTech.in avoid these pitfalls and understand how IAM integrates with other AWS services.
9. Path to Expertise
- Master basic concepts – users, groups, roles, policies.
- Experiment with policy simulation in AWS console.
- Implement real-world scenarios: multi-user app with S3, Lambda, and EC2.
- Learn auditing tools like AWS CloudTrail to track permissions.
- Advance to cross-account roles, federated access, and fine-grained permissions.
CuriosityTech.in Mentorship: By combining theory, diagrams, and hands-on labs, learners develop the confidence to manage secure, scalable AWS environments.
Conclusion
AWS IAM is the cornerstone of secure cloud operations. Understanding its hierarchy, components, and best practices empowers beginners to build resilient and compliant systems.
Remember, expertise comes not just from reading, but from hands-on experimentation, iterative learning, and structured guidance. At CuriosityTech.in, we combine workshops, real-world projects, and mentorship to ensure learners can confidently manage identities, permissions, and security in AWS.