Introduction to Continuous Delivery
Continuous Delivery (CD) is a core practice of modern DevOps, enabling teams to automate the release of software updates with speed, reliability, and safety. For organizations aiming to shorten release cycles while maintaining high-quality standards, understanding CD is not optional—it’s essential.
Continuous Delivery refers to the process of automatically preparing code changes for release to production. Unlike Continuous Integration (CI), which focuses on automatically building and testing code, CD extends this pipeline by ensuring that every change that passes automated tests is automatically deployable. This means your software is always in a releasable state.
In today’s highly competitive tech landscape, companies like Netflix, Amazon, and Google leverage CD to accelerate innovation. As a practitioner at Curiosity Tech, we focus on not only understanding CD tools but mastering the philosophy behind reliable software releases.
Key Goals of CD:
- Reduce the manual effort in deploying software.
- Minimize human errors during release.
- Ensure faster feedback loops
- Increase deployment frequency without compromising quality.
Core Principles of Continuous Delivery
Continuous Delivery is built on several foundational principles:
| Principle | Explanation |
| Automated Testing | Every code change must pass a suite of automated tests before being considered for release. This includes unit tests, integration tests, and end-to-end tests. |
| Version Control | All code and configuration must be stored in a version-controlled repository, ensuring traceability and rollbacks. |
| Automated Deployment | Deployments to staging and production environments should be automated, predictable, and repeatable. |
| Small & Frequent Releases | Releasing smaller increments reduces risk and improves feedback cycles. |
| Rollback Capability | Always have the ability to roll back to previous versions in case of errors. |
Hierarchy Diagram of CD Pipeline:
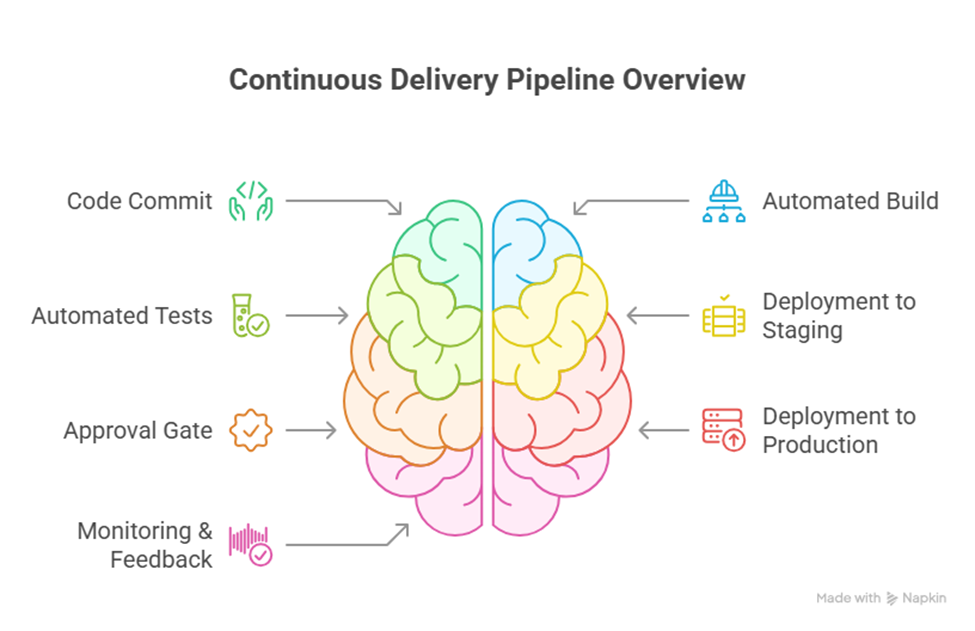
This abstraction demonstrates the seamless flow from development to production while keeping quality intact.
CD Tools & Technologies
To implement Continuous Delivery effectively, organizations rely on a combination of tools. Here’s a breakdown:
- Jenkins – The most widely used open-source automation server. Ideal for orchestrating builds, tests, and deployments.
- GitLab CI/CD – Integrated with Git repositories for easy configuration of pipelines.
- Spinnaker – Optimized for multi-cloud continuous delivery with strong rollback mechanisms.
- AWS CodePipeline / Azure DevOps / Google Cloud Build – Cloud-native CD services that reduce infrastructure management.
- ArgoCD – Kubernetes-native CD tool for deploying applications declaratively.
Tip for mastery: Experts at Curiosity Tech often recommend combining multiple tools for specific stages—like Jenkins for CI and ArgoCD for Kubernetes deployments—to balance flexibility with reliability.
Best Practices to Become a CD Expert
- Understand the Pipeline Architecture – Know each stage: build, test, deployment, monitoring.
- Automate Everything – Start small: automate builds, then tests, then deployments.
- Implement Observability – Monitor releases for failures and performance issues.
- Learn by Doing – Hands-on projects, like deploying a microservice application with automated pipelines, solidify learning.
- Stay Updated on Trends – Tools evolve rapidly; knowledge of emerging practices like GitOps or AIOps can provide a competitive edge.
At Curiosity Tech, we encourage practical exposure. For example, building a CI/CD pipeline integrating GitHub, Jenkins, and AWS can transform theoretical knowledge into market-ready expertise.
Challenges in CD and How to Overcome
| Challenge | Solution |
| Resistance to Change | Start with a small pilot project to demonstrate success. |
| Flaky Tests | Invest time in reliable automated tests. |
| Complex Deployments | Use containerization (Docker) and orchestration (Kubernetes) to standardize deployments. |
| Lack of Monitoring | Implement logging, monitoring, and alerting at each stage. |
Infographic: Continuous Delivery Lifecycle
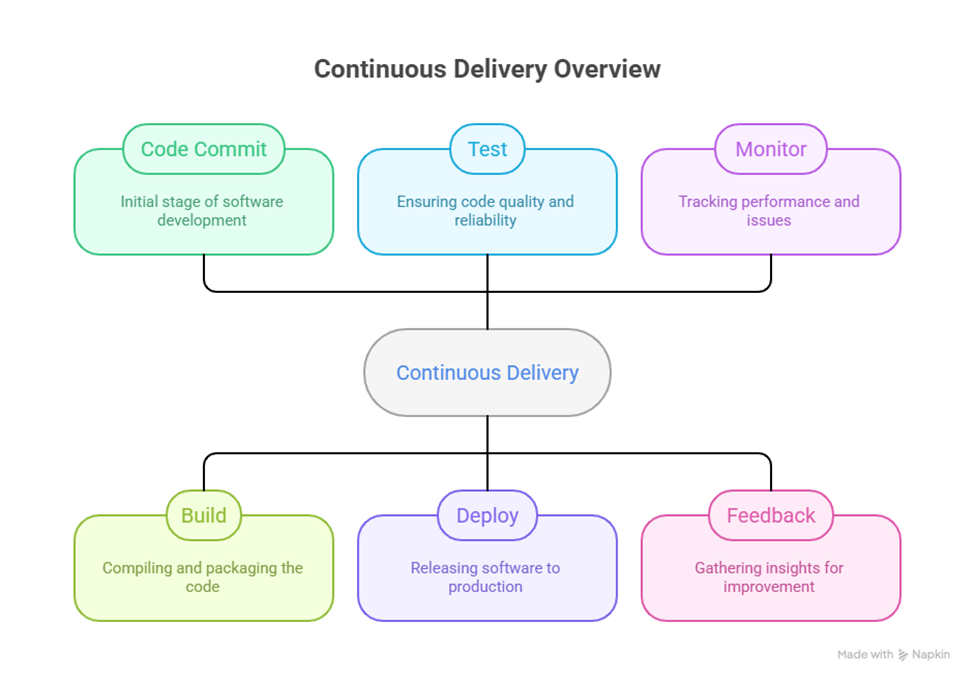
Conclusion
Continuous Delivery is not just a methodology; it’s a mindset. By automating releases, organizations can reduce errors, speed up delivery, and improve customer satisfaction. Mastery of CD requires a combination of technical skills, process understanding, and practical experience. Whether you’re deploying microservices, monoliths, or serverless applications, CD ensures your software is always ready for production.
At Curiosity Tech, we guide aspiring DevOps engineers through the principles, tools, and hands-on exercises required to excel in Continuous Delivery. By integrating learning with real-world projects, we transform beginners into experts, prepared for the evolving DevOps landscape.



