Introduction
Creating a Job Portal is an ideal real-world FullStack .NET project. It integrates frontend, backend, database, authentication, and deployment, giving learners hands-on experience in building scalable, secure, and responsive applications.
At CuriosityTech.in, students learn step-by-step how to design, develop, and deploy a fully functional Job Portal, applying concepts like ASP.NET Core, React/Angular, EF Core, Identity, JWT, and Cloud deployment.
1. Project Requirements
Features:
| Feature | Description |
| User Registration & Login | Secure authentication for job seekers and employers |
| Job Listings | Employers can post jobs; seekers can browse |
| Job Application | Candidates apply for jobs via portal |
| Admin Panel | Manage users, jobs, and applications |
| Notifications | Email alerts for new jobs and applications |
2. Architecture Design
Architecture Diagram:
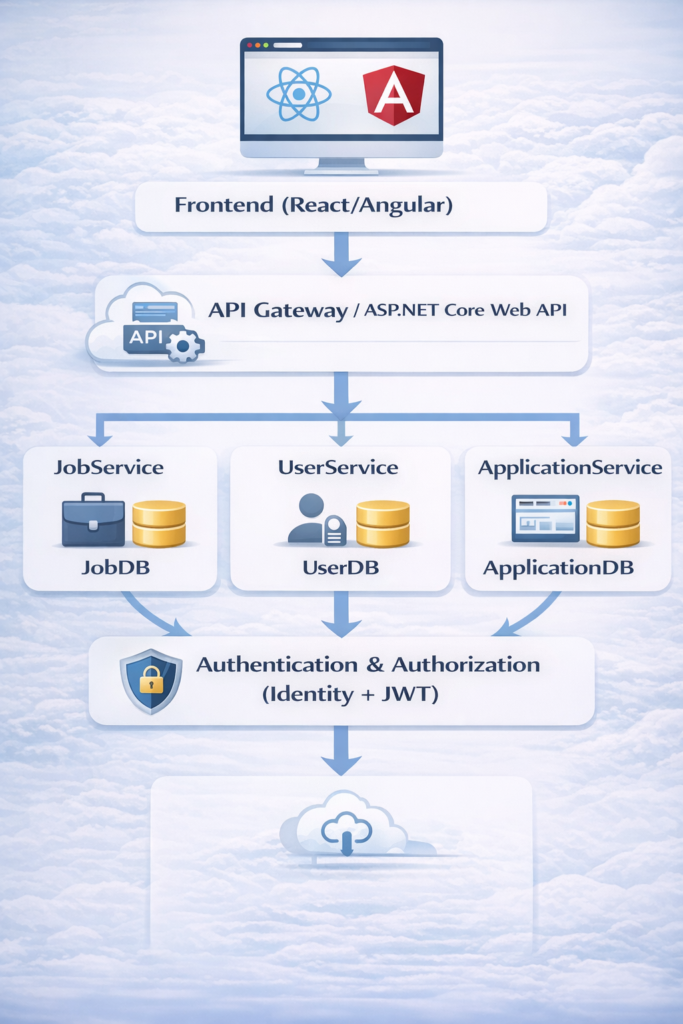
- Frontend: Dynamic UI with React or Angular
- Backend: ASP.NET Core Web API
- Database: SQL Server with EF Core ORM
- Authentication: ASP.NET Identity + JWT for secure API access
3. Backend Implementation
Job Model Example:
public class Job
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Title { get; set; }
public string Description { get; set; }
public string Location { get; set; }
public DateTime PostedDate { get; set; }
}
Job Controller Example:
[ApiController]
[Route(“api/[controller]”)]
public class JobsController : ControllerBase
{
private readonly IJobService _jobService;
public JobsController(IJobService jobService)
{
_jobService = jobService;
}
[HttpGet]
public IActionResult GetAllJobs() => Ok(_jobService.GetAllJobs());
[Authorize(Roles = “Employer”)]
[HttpPost]
public IActionResult PostJob(Job job)
{
_jobService.CreateJob(job);
return Ok();
}
}
4. Frontend Implementation
React Job Listing Example:
import React, { useEffect, useState } from ‘react’;
function JobList() {
const [jobs, setJobs] = useState([]);
useEffect(() => {
fetch(‘https://api.curiositytech.in/api/jobs’)
.then(res => res.json())
.then(data => setJobs(data));
}, []);
return (
<div>
<h2>Available Jobs</h2>
<ul>
{jobs.map(job => (
<li key={job.id}>{job.title} – {job.location}</li>
))}
</ul>
</div>
);
}
export default JobList;
Features:
- Dynamic rendering of jobs
- Integrated with JWT-secured APIs
- Role-based rendering (Employer vs Job Seeker)
5. Database Design
Tables:
| Table | Description |
| Users | Job seekers and employers |
| Jobs | Job postings with metadata |
| Applications | Job applications linked to users and jobs |
| Roles | Role-based access control |
Relationships:
- One user can have multiple applications
- One job can have multiple applications
- Role-based access for Admin, Employer, Job Seeker
6. Security Integration
- ASP.NET Identity for user registration & login
- JWT tokens for frontend API access
- Role-based authorization for job posting and management
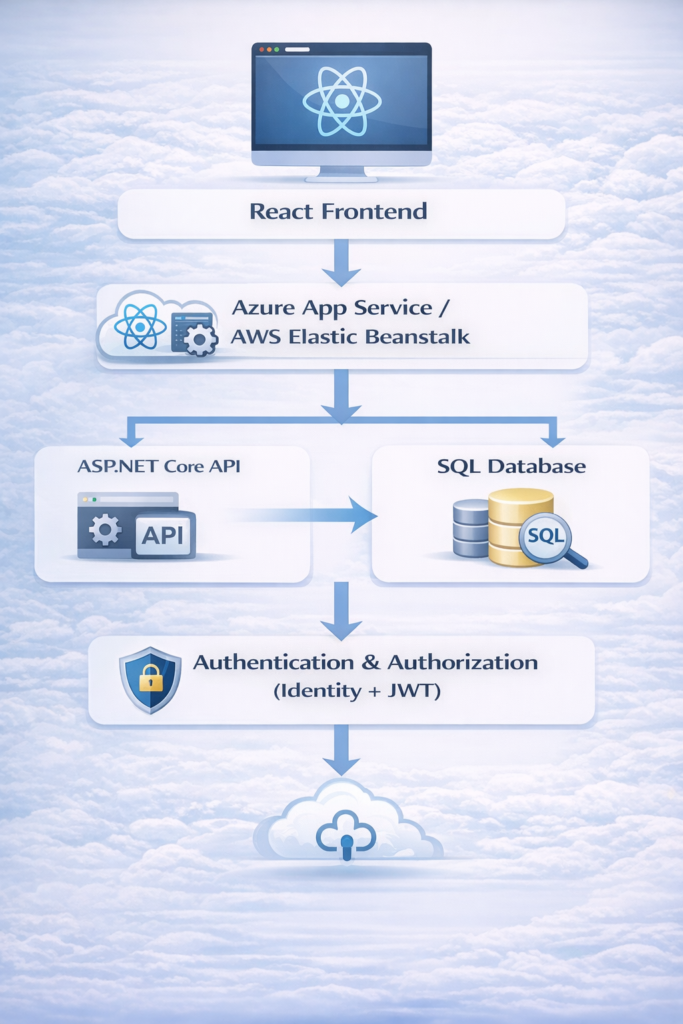
7. Deployment Strategy
- Backend: Azure App Service or AWS Elastic Beanstalk
- Frontend: Azure Static Web App or S3 + CloudFront
- Database: Azure SQL Database or AWS RDS
- CI/CD: Azure DevOps or GitHub Actions for automated deployment
Deployment Diagram:
8. Best Practices
- Keep services modular for maintainability
- Apply input validation and error handling
- Use environment-based configuration for DB & API endpoints
- Implement logging & monitoring for production readiness
- Optimize frontend performance for dynamic rendering
9. CuriosityTech.in Mentorship Insights
- Step-by-step guidance for FullStack project building
- Covers frontend-backend integration, database, authentication, and cloud deployment
- Prepares learners for real-world FullStack development roles
Conclusion
Building a Job Portal with .NET Full Stack is an excellent project to practice all learned concepts: frontend integration, backend services, database management, authentication, security, and cloud deployment. At CuriosityTech.in, learners gain practical experience implementing professional-grade applications, preparing them for industry-standard FullStack roles.
The next step is Day 21 – Performance Tuning for .NET Applications, focusing on caching, async programming, and profiling for high-performance apps.