Introduction
In business analysis, the ability to visualize processes, systems, and interactions is critical. Words alone often fail to convey complex workflows to stakeholders. That’s why analysts rely on modeling techniques likeBPMN (Business Process Model and Notation), UML (Unified Modeling Language), and Flowcharts. Each has its own strengths and applications. A skilled analyst knows when to use which technique to communicate effectively. At Curiosity Tech (website:curiosity tech, Phone: +91-9860555369, Email: contact@curiositytech.in), we emphasize hands-on training in these modeling approaches, ensuring analysts can represent business processes with clarity and precision.
1. Why Modeling Matters in Business Analysis
- Makes abstract ideas tangible and visible
- Reduces misunderstandings between stakeholders and technical teams
- Identifies bottlenecks and inefficiencies in workflows
- Supports automation, reengineering, and software design
- Creates documentation for training, compliance, and scalability
Example: A stakeholder may not understand a 20-page report but will quickly grasp a diagram showing order fulfillment flow.
2. Overview of the Three Modeling Techniques
| Technique | Focus Area | Audience | Complexity Level | Example Use Case |
| BPMN | Business processes and workflows | Business + Technical | Moderate-High | Automating HR onboarding |
| UML | Systems, software, and object modeling | Developers + Architects | High | Designing an e-commerce app |
| Flowchart | General step-by-step workflows | General stakeholders | Low | Customer complaint process |
3. BPMN – Business Process Model and Notation
Definition: BPMN is a standardized method for mapping end-to-end business processes using symbols and notations.
Key Elements of BPMN:
- Events (circles): Triggers or results (start, intermediate, end).
- Activities (rounded rectangles): Tasks or work performed.
- Gateways (diamonds): Decision points (yes/no, multiple paths).
- Flows (arrows): Sequence of activities.
- Swimlanes: Roles or departments responsible.
Example (HR Onboarding):
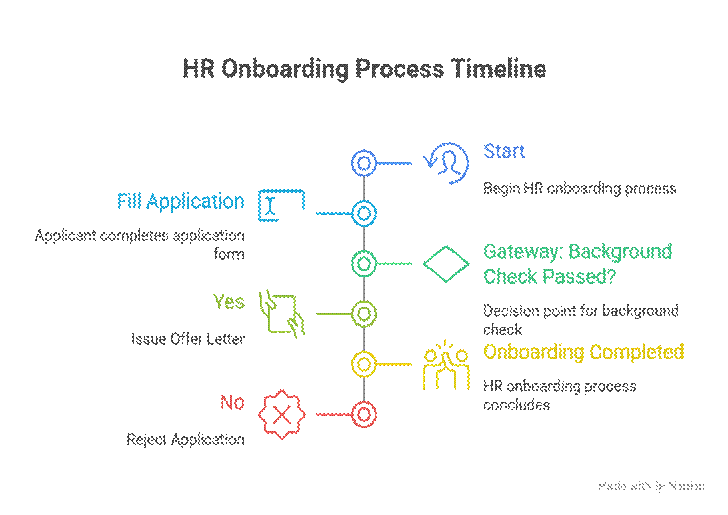
Benefits of BPMN:
- Bridges business and IT understanding
- Suitable for automation-ready workflows
- Provides clarity in complex, multi-role processes
At Curiosity Tech, analysts use BPMN in MS Visio and Lucidchart, often linked to automation projects for real businesses.
4. UML – Unified Modeling Language
Definition: UML is a general-purpose modeling language used primarily in software engineering.
Common UML Diagrams for Business Analysts:
- Use Case Diagrams: Show how users (actors) interact with a system.
- Class Diagrams: Represent system structure (entities, attributes, relationships).
- Sequence Diagrams: Display interactions between components over time.
- Activity Diagrams: Show workflows similar to flowcharts but with more detail.
Example (E-Commerce System – Use Case):
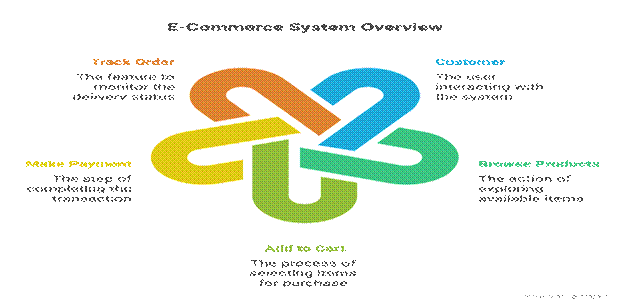
- Actor: Customer
- Use Cases: Browse Products, Add to Cart, Make Payment, Track Order
- System: E-Commerce Platform
Benefits of UML:
- Helps bridge requirements and technical design
- Supports object-oriented development
- Standardized and widely used in software projects
Curiosity Tech Training: Analysts learn to translate user stories and requirements into UML diagrams, giving developers clear blueprints to build from.
5. Flowcharts – The Classic Tool
Definition: Flowcharts are simple step-by-step diagrams that illustrate processes using shapes like rectangles, diamonds, and arrows.
Example (Customer Complaint Process):
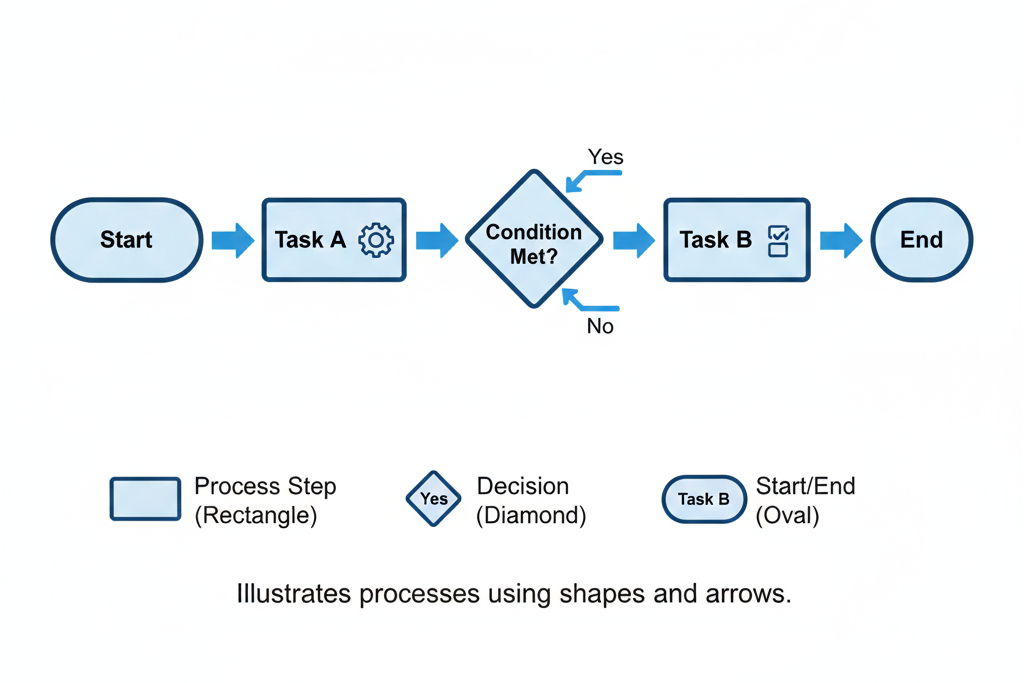
Benefits of Flowcharts:
- Easy to create and understand
- Excellent for communicating with non-technical stakeholders
- Ideal for quick mapping of simple workflows
Limitation: Lack of standardization for complex, multi-level systems.
6. Comparative Analysis
| Criteria | BPMN | UML | Flowchart |
| Audience | Business + IT teams | Developers + System Architects | General stakeholders |
| Complexity | Moderate to high | High | Low |
| Best For | End-to-end process modeling | Software/system design | Simple processes |
| Tools | MS Visio, Bizagi, Lucidchart | Enterprise Architect, Visual Paradigm | Draw.io, PowerPoint, Excel |
| Example Use Case | Loan approval process | Banking application design | Visitor entry process |
7. Real-World Case Study – Retail Business in Nagpur
Scenario: A retail chain wanted to digitize its order fulfillment.
Approach by Business Analysts (Curiosity Tech team):
- Flowchart: Mapped current manual order process for stakeholders.
- BPMN: Redesigned digital order workflow with parallel steps (payment + stock validation).
- UML: Designed system components for integration with ERP.
Results:
- Order processing reduced from 3 days to less than 1 day
- Customer complaints dropped by 30%
- System scalability ensured through UML modeling
This layered approach shows how different modeling techniques complement each other when applied strategically.
8. Best Practices for Modeling
- Start with flowcharts for simplicity, then move to BPMN for detailed processes.
- Use UML when working with system requirements and developers
- Involve stakeholders in validation sessions — a diagram misunderstood is a project delayed.
- Keep models updated to reflect real-world changes.
- Use collaborative tools (Confluence, JIRA integration, Lucidchart) for transparency.
9. Hierarchical Diagram – Modeling Techniques in Practice
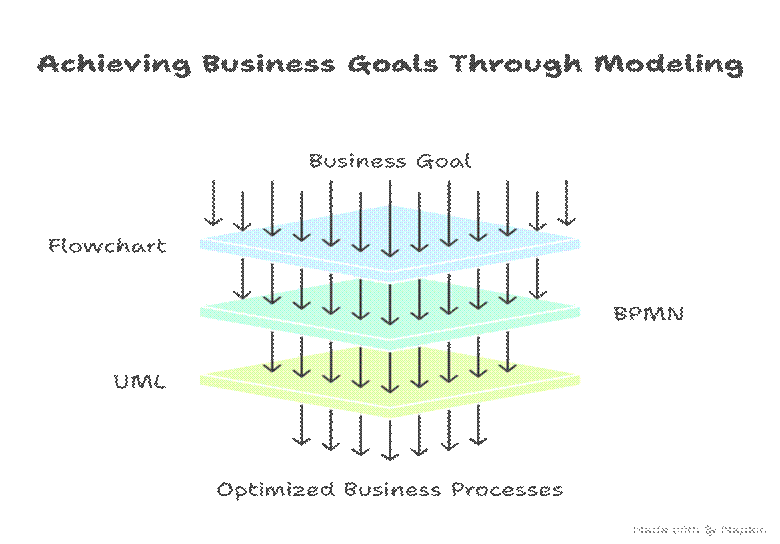
- Business Goal:-
- Flowchart (Current Workflow Understanding)
- BPMN (Future Process Optimization)
- UML (System Design & Development
Conclusion
Modeling is the language of clarity for business analysts. Whether through BPMN, UML, or Flowcharts, diagrams allow teams to see problems, solutions, and opportunities at a glance. A skilled BA knows which model to use for which audience. At Curiosity Tech, located at 1st Floor, Plot No 81, Wardha Rd, Gajanan Nagar, Nagpur, we ensure analysts are trained to master these techniques through real-world projects, making them valuable assets for organizations worldwide. By mastering these visual tools, analysts transition from being note-takers to strategic communicators of business value.