Introduction
Performance tuning is critical for scalable and responsive FullStack applications. FullStack .NET developers need to optimize backend APIs, database queries, and frontend interactions to deliver fast, reliable user experiences.
At CuriosityTech.in, learners master caching strategies, asynchronous programming, and profiling techniques to ensure high-performing .NET applications.
1. Common Performance Bottlenecks
| Area | Bottleneck | Impact |
| Database | Inefficient queries, missing indexes | Slow response times |
| Backend | Blocking calls, synchronous operations | Thread starvation, delayed responses |
| Frontend | Large payloads, unoptimized assets | Slow page load, poor UX |
| Logging | Excessive synchronous logging | High I/O overhead |
2. Caching Strategies in .NET
Types of Caching:
| Type | Description | Example |
| In-Memory | Store frequently used data in server memory | IMemoryCache |
| Distributed | Share cache across multiple servers | Redis, Memcached |
| Response Caching | Cache HTTP responses | [ResponseCache(Duration = 60)] |
In-Memory Cache Example:
public class JobService : IJobService
{
private readonly IMemoryCache _cache;
private readonly ApplicationDbContext _db;
public JobService(IMemoryCache cache, ApplicationDbContext db)
{
_cache = cache;
_db = db;
}
public List<Job> GetAllJobs()
{
return _cache.GetOrCreate(“jobs”, entry =>
{
entry.AbsoluteExpirationRelativeToNow = TimeSpan.FromMinutes(10);
return _db.Jobs.ToList();
});
}
}
Benefits:
- Reduces database load
- Improves API response times
- Simple to implement for read-heavy applications
3. Asynchronous Programming
Async/Await in .NET
public async Task<List<Job>> GetJobsAsync()
{
return await _db.Jobs.ToListAsync();
}
Advantages:
- Non-blocking I/O
- Efficient thread usage
- Improves scalability under high load
Async Best Practices:
- Avoid async void except for event handlers
- Use ConfigureAwait(false) in library code
- Keep methods fully asynchronous to avoid blocking threads
4. Profiling and Monitoring
| Tool | Purpose |
| dotTrace / JetBrains Rider Profiler | CPU and memory profiling |
| Visual Studio Profiler | Identify slow methods and bottlenecks |
| Application Insights | Monitor performance in Azure |
| MiniProfiler | Lightweight profiling for web requests |
Sample Profiling Workflow:
- Run profiler during load testing
- Identify slow queries and heavy operations
- Apply caching, async methods, or query optimization
- Re-test and measure improvement
5. Real-World Project: CuriosityTech Course Portal Performance Optimization
- Scenario: Optimize Course Portal API for high traffic
- Applied Techniques:-
- Cached frequently accesssed course list (IMemory Cache)
- Converted blocking database calls to async EF Core queries.
- Profiled endpoints using Application ‘insights to detect slow queries.
- Outcome:-
- Reduced average API response time by 40%.
- Improved user experience on frontend.
- Reduced server load and frontend.
Performance Flow Diagram:
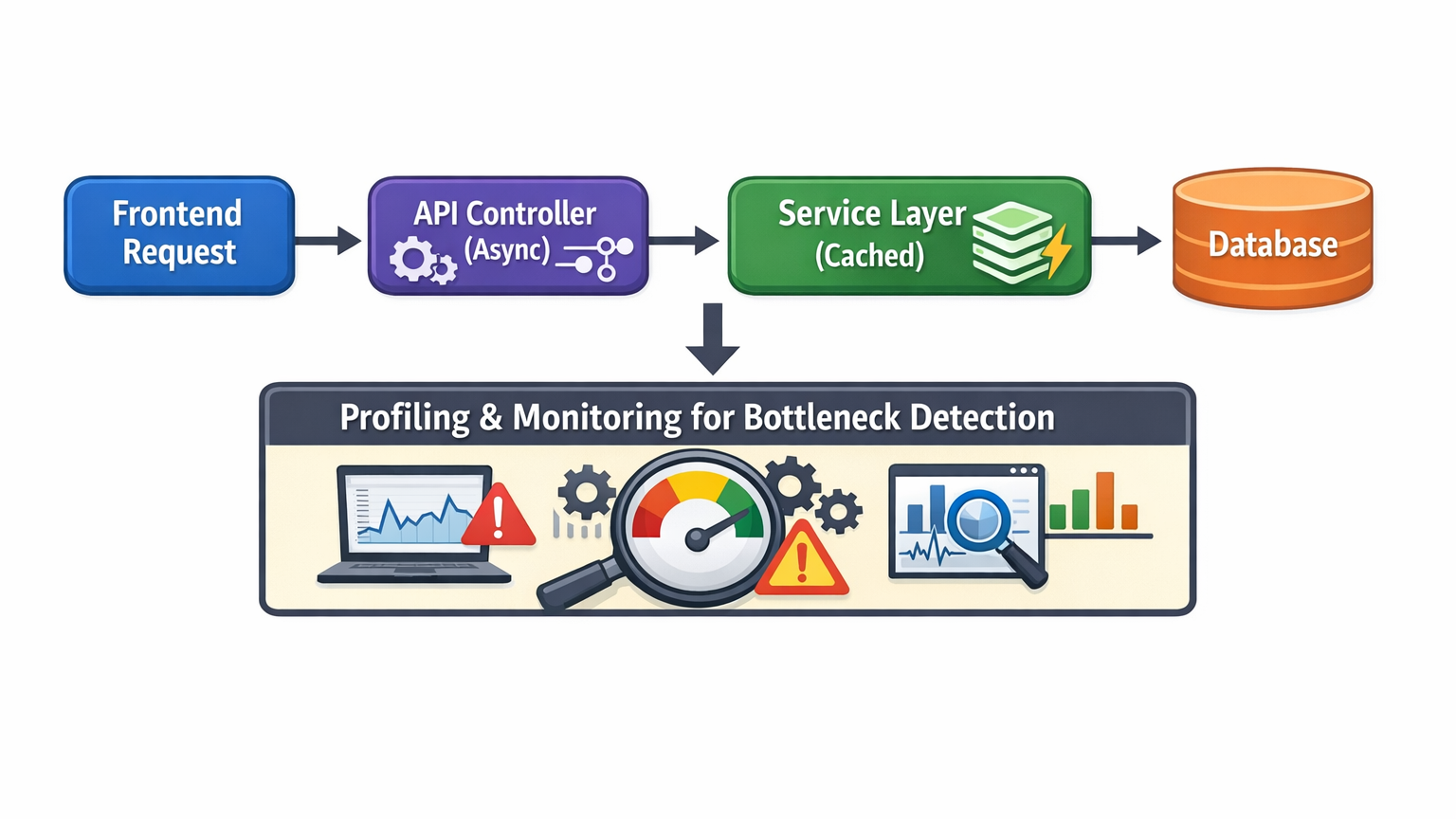
6. Best Practices
- Implement caching wisely to avoid stale data
- Prefer async programming for I/O-bound operations
- Optimize EF Core queries using Include, AsNoTracking, and Select
- Profile applications regularly to detect memory leaks or CPU bottlenecks
- Monitor production performance using Azure Application Insights or AWS CloudWatch.
7. CuriosityTech.in Mentorship Insights
Conclusion
Performance tuning is a critical skill for FullStack .NET developers. By applying caching, async programming, and profiling techniques, developers can deliver high-performance, scalable applications. At CuriosityTech.in, learners practice these optimizations in real-world projects, ensuring they are ready for industry-standard FullStack development.
The next step is Day 22 – Unit Testing and Test-Driven Development (TDD) in .NET, focusing on writing robust, maintainable code with automated testing.