Databases are the heart of every application. On Day 10, we explore Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service), a fully managed service that simplifies deployment, scaling, and management of relational databases on AWS.
At Curiosity Tech, we teach learners that understanding RDS is not just about launching a database—it’s about designing secure, high-performance, and highly available data solutions.
1. What is Amazon RDS?
Amazon RDS is a managed relational database service that automates tasks such as:
- Database provisioning
- Patching and updates
- Backup and recovery
- High availability and replication
- Monitoring and scaling
With RDS, cloud engineers can focus on application development rather than database administration.
Analogy: Think of RDS as a self-driving car for databases—it handles maintenance, backups, and scaling while you focus on building the application.
2. Supported Database Engines
| Engine | Description | Use Case | Notes |
| Amazon Aurora | High-performance MySQL/PostgreSQL compatible | Enterprise apps, high throughput | Cloud-native, highly available |
| MySQL | Popular open-source relational DB | Web apps, startups | Free-tier eligible |
| PostgreSQL | Advanced open-source relational DB | Analytics, complex queries | Free-tier eligible |
| MariaDB | MySQL fork, open-source | Web apps, medium workloads | Compatible with MySQL tools |
| Oracle | Commercial relational DB | Enterprise apps | License required |
| SQL Server | Microsoft SQL Server | Windows-based applications | License included/bring-your-own |
Expert Tip: Beginners often select familiar engines (MySQL, PostgreSQL). Aurora is ideal for performance and reliability at scale.
3. Key Components of Amazon RDS
| Component | Description | Example |
| DB Instance | The database server | rds-curiositytech |
| DB Cluster (Aurora) | Collection of DB instances | Primary + read replicas |
| Storage | SSD or magnetic storage for DB | 20 GB General Purpose SSD |
| Parameter Group | Configuration template for DB settings | default.mysql8.0 |
| Security Group | Controls inbound/outbound traffic | Allow app server IP only |
| Multi-AZ Deployment | High availability | Automatic failover to secondary AZ |
4. RDS Deployment Architecture Diagram
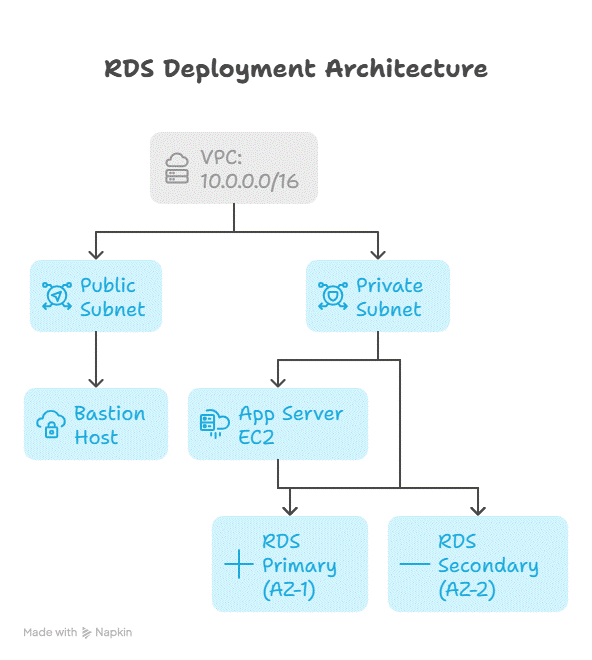
Explanation:
- Database instances reside in private subnets for security.
- Multi-AZ deployment ensures automatic failover in case of AZ failure.
- Bastion host in public subnet allows secure SSH access to private resources.
5. Step-by-Step: Launching Your First RDS Instance
1 – Choose Database Engine
- Navigate to AWS Console → RDS → Create Database
- Select engine (e.g., MySQL, Free Tier)
2 – Specify DB Details
- DB instance identifier: rds-curiositytech
- Master username/password: secure credentials
- DB instance class: db.t2.micro (Free Tier)
3 – Configure Storage
- Allocate 20 GB General Purpose SSD
- Enable storage autoscaling if desired
4 – Configure Connectivity
- Place DB in private subnet
- Assign VPC security group allowing app server access only
- Public accessibility: No (recommended for security)
5 – Advanced Settings
- Enable Multi-AZ deployment for high availability
- Enable automated backups (retain 7 days)
- Enable performance insights for monitoring
6 – Launch DB
- Review configuration
- Click Create database
- Monitor status until Available
Curiosity Tech Insight: Beginners often struggle with connectivity from EC2. Our labs emphasize VPC routing, security groups, and parameter group settings, ensuring seamless database connectivity.
6. Backup, Recovery, and High Availability
| Feature | Description | Best Practice |
| Automated Backups | Daily snapshots + transaction logs | Enable for all production DBs |
| Manual Snapshots | On-demand backups | Before schema changes or upgrades |
| Multi-AZ Failover | Automatic promotion of standby instance | Production environments |
| Read Replicas | Offload read-heavy traffic | Reporting and analytics workloads |
Expert Tip: Start with automated backups and multi-AZ deployment to ensure resilience even in beginner projects.
7. Scaling and Performance Optimization
- Vertical Scaling (Instance Size): Upgrade CPU, RAM, or storage
- Horizontal Scaling (Read Replicas): Add replicas for read-heavy workloads
- Storage Autoscaling: Automatically adjusts storage as database grows
- Performance Insights: Monitor queries, latency, and bottlenecks
Curiosity Tech Approach: Students create practice labs with read replicas and autoscaling, simulating real-world high-load scenarios for hands-on learning.
8. Common Beginner Mistakes
- Launching databases in public subnets → security risk
- Using weak passwords or not rotating credentials
- Ignoring backup configuration → data loss
- Overlooking parameter groups → performance issues
Tip: Always follow security and best-practice guidelines from day one.
9. Path to Expertise
- Begin with Free Tier MySQL/PostgreSQL instances
- Explore Multi-AZ deployments and read replicas
- Integrate EC2 and RDS for full application stack
- Monitor performance using CloudWatch and Performance Insights
- Learn advanced features like Aurora global databases, cross-region replication, and encryption with KMS
At Curiosity Tech, learners progress from basic database creation to architecting scalable, secure, and highly available database systems, gaining production-ready skills.
Conclusion
Amazon RDS is a cornerstone service for managed relational databases in AWS. By understanding instances, storage, high availability, backups, and scaling, beginners gain the ability to design secure, performant, and cost-efficient database architectures.
Hands-on labs, real-world simulations, and expert mentorship at CuriosityTech.in empower learners to go beyond theory, ensuring they can deploy, manage, and optimize RDS for professional cloud applications.