Introduction
In modern Full Stack Python development, separating the frontend and backend is a standard practice. While frameworks like Flask and Django handle backend logic and APIs, React and Vue are among the most popular frontend frameworks to build dynamic, responsive, and user-friendly interfaces.
At Curiosity Tech, we emphasize that the true power of a Full Stack developer comes from mastering both ends and making them communicate efficiently. This blog will explore how to integrate React or Vue with Python backend frameworks in detail, including real-world examples and best practices.
Why Frontend-Backend Separation Matters
| Aspect | Monolithic Frontend-Backend | Frontend-Backend Separation |
| Development Speed | Slower (tightly coupled) | Faster (parallel teams) |
| Scalability | Limited | High (can scale separately) |
| Flexibility | Less | High (switch frontend easily) |
| User Experience | Moderate | Enhanced (dynamic SPA) |
Hierarchical diagram
SPA (Single Page Applications) powered by React or Vue allow smooth navigation, dynamic content updates, and better performance.
Setting Up React with Flask/Django
Step 1: Create Backend API
Flask Example:
# app.py
from flask import Flask, jsonify
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route(‘/api/posts’)
def get_posts():
return jsonify([
{“id”: 1, “title”: “First Post”, “content”: “Welcome to CuriosityTech!”},
{“id”: 2, “title”: “Second Post”, “content”: “React + Flask Integration Example”}
])
if __name__ == ‘__main__’:
app.run(debug=True)
- The backend now exposes a REST API endpoint /api/posts.
Step 2: Create React Frontend
- Initialize React app:
npx create-react-app my-app
cd my-app
npm start
- Fetch data from Flask API:
// App.js
import React, { useEffect, useState } from ‘react’;
function App() {
const [posts, setPosts] = useState([]);
useEffect(() => {
fetch(‘http://127.0.0.1:5000/api/posts’)
.then(res => res.json())
.then(data => setPosts(data));
}, []);
return (
<div>
<h1>Blog Posts from CuriosityTech Backend</h1>
{posts.map(post => (
<div key={post.id}>
<h2>{post.title}</h2>
<p>{post.content}</p>
</div>
))}
</div>
);
}
export default App;
Result: Dynamic content fetched from Flask API is displayed in React SPA.
Vue Integration with Django
- Create a Django REST API using DRF:
# views.py
from rest_framework.views import APIView
from rest_framework.response import Response
class PostList(APIView):
def get(self, request):
posts = [
{“id”: 1, “title”: “Hello from CuriosityTech”, “content”: “Vue + Django example”},
]
return Response(posts)
- Create Vue frontend:
vue create my-vue-app
cd my-vue-app
npm run serve
- Fetch Django API data in Vue component:
// Posts.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1>Blog Posts</h1>
<div v-for=”post in posts” :key=”post.id”>
<h2>{{ post.title }}</h2>
<p>{{ post.content }}</p>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return { posts: [] }
},
mounted() {
fetch(‘http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/posts/’)
.then(res => res.json())
.then(data => { this.posts = data })
}
}
</script>
Result: Vue SPA consuming Django REST API dynamically.
Frontend-Backend Integration Workflow
Hierarchical Diagram Idea:
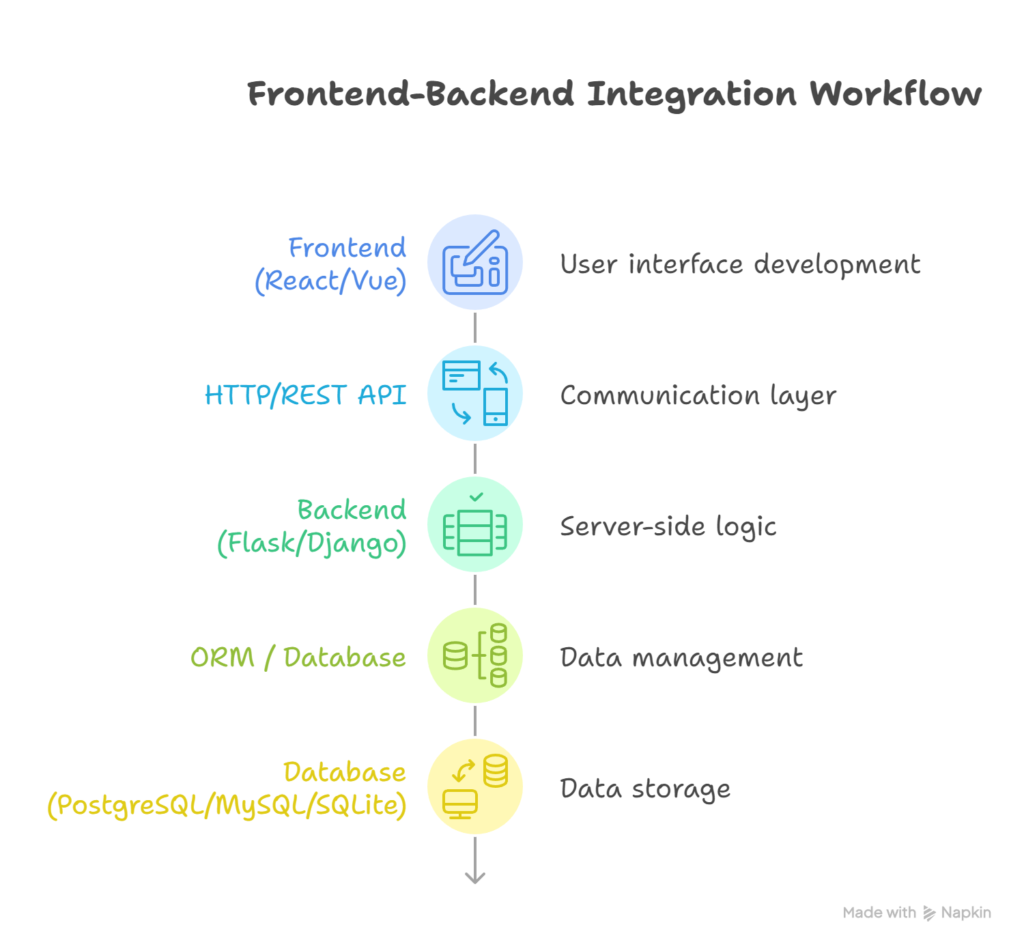
- Step 1: User interacts with frontend
- Step 2: Frontend makes HTTP request to API
- Step 3: Backend processes request, fetches data
- Step 4: Backend sends JSON response
- Step 5: Frontend renders dynamic content
Handling Cross-Origin Requests (CORS)
When frontend and backend run on different ports:
Flask:
from flask_cors import CORS
CORS(app)
Django:
pip install django-cors-headers
# settings.py
INSTALLED_APPS += [‘corsheaders’]
MIDDLEWARE += [‘corsheaders.middleware.CorsMiddleware’]
CORS_ALLOWED_ORIGINS = [“http://localhost:8080”]
Best Practices for Integration
- Use RESTful APIs or GraphQL for communication.
- Environment Variables to store API URLs securely.
- Error Handling – Always handle API errors in frontend.
- Token-Based Authentication – Use JWT for secure API calls.
- Component-Based Frontend – Break UI into reusable React/Vue components.
Real-World Use Case – Curiosity Tech Training Project
- Students built a Python Full Stack Job Portal:
- Backend :- Django REST Framework.
- Frontend :- React SPA
- Features :- Job listings, Application Form, Dynamic Dashboard
- Outcome: Students learned real-world API consumption, frontend state management, and secure backend integration.
Infographic Idea
Title: “Full Stack Python Frontend Integration”
- Two columns: Frontend vs Backend
- Arrows showing API request → JSON → Dynamic rendering
- Color-code for React/Vue vs Flask/Django
Conclusion
Integrating React or Vue with Python backend frameworks allows Full Stack developers to build modern, interactive, scalable web applications. At Curiosity Tech, students practice these integrations through hands-on projects, ensuring they can go from API design to dynamic frontend in real-world scenarios.
Mastering this skill transforms a Python developer into a versatile Full Stack professional, ready for 2025 and beyond.



