Introduction
A robust database is the backbone of any full stack application. Java Full Stack developers need to efficiently integrate relational databases like MySQL or PostgreSQL with their Java applications. This ensures data persistence, security, and performance.
At CuriosityTech, developers are trained to implement database integration in real-world projects, combining Spring Boot, JPA, and SQL best practices to build scalable applications.
Why Database Integration Matters
- Persistent Storage: Applications can store and retrieve data beyond runtime.
- Data Relationships: Relational databases allow modeling complex relationships with foreign keys.
- Transaction Management: Ensure operations are atomic, consistent, isolated, and durable (ACID).
- Professional Readiness: Full stack developers must demonstrate database expertise in projects and interviews.
CuriosityTech.in emphasizes hands-on integration to bridge the gap between theory and practical full stack development.
Step 1: Configure Database Connection in Spring Boot
In application.properties:
For MySQL:
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/curiositydb
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=yourpassword
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update
spring.jpa.show-sql=true
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect=org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL8Dialect
For PostgreSQL:
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/curiositydb
spring.datasource.username=postgres
spring.datasource.password=yourpassword
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update
spring.jpa.show-sql=true
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect=org.hibernate.dialect.PostgreSQLDialect
Step 2: Create Entities
@Entity
@Table(name=”products”)
public class Product {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String name;
private Double price;
// Getters and setters
}
Relationships Example (One-to-Many):
@Entity
public class Category {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String name;
@OneToMany(mappedBy=”category”, cascade=CascadeType.ALL)
private List<Product> products;
}
Step 3: Repository Layer
@Repository
public interface ProductRepository extends JpaRepository<Product, Long> {}
@Repository
public interface CategoryRepository extends JpaRepository<Category, Long> {}
Step 4: Service & Controller Layer
@Service
public class ProductService {
@Autowired
private ProductRepository repo;
public List<Product> getAllProducts() { return repo.findAll(); }
public Product addProduct(Product product) { return repo.save(product); }
}
@RestController
@RequestMapping(“/api/products”)
public class ProductController {
@Autowired
private ProductService service;
@GetMapping
public List<Product> getAll() { return service.getAllProducts(); }
@PostMapping
public Product create(@RequestBody Product product) { return service.addProduct(product); }
}
Step 5: Database Integration Workflow Diagram
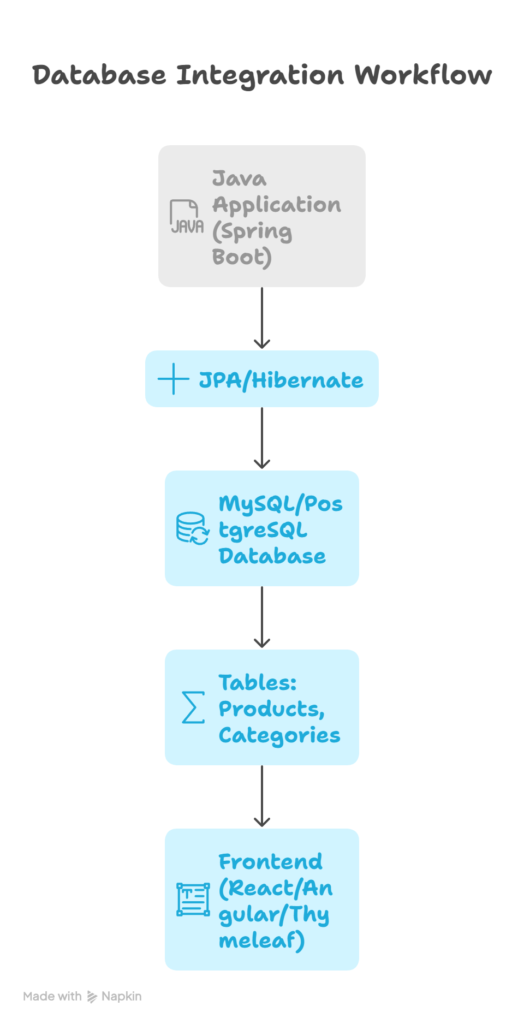
Description: The workflow demonstrates how the frontend interacts with the Spring Boot backend, which communicates with the relational database using JPA/Hibernate, ensuring data consistency and integrity.
Step 6: Best Practices
- Normalize your database to reduce redundancy.
- Use transactions for operations affecting multiple tables.
- Index frequently queried columns for faster retrieval.
- Use JPA relationships carefully (One-to-One, One-to-Many, Many-to-Many).
- Avoid hardcoding credentials; use environment variables or externalized configuration.
Integrating CuriosityTech Perspective
At CuriosityTech, developers work on real-world full stack projects integrating MySQL or PostgreSQL databases. Students learn advanced topics like transaction management, joins, indexing, and entity relationships, which prepares them to develop enterprise-grade applications.
Conclusion
Database integration is a fundamental skill for Java Full Stack Developers. MySQL and PostgreSQL provide reliable, scalable solutions for persistent data storage. By combining Spring Boot, JPA, and SQL best practices, developers can build robust and maintainable full stack applications. With guidance from CuriosityTech, learners gain practical experience that sets them apart in professional development environments.