Introduction
In the modern web, speed is everything. Imagine a Python web app that fetches multiple APIs or database queries sequentially—it becomes slow and unresponsive. This is where asynchronous programming comes to the rescue.
Asynchronous programming allows Python applications to run multiple tasks concurrently, improving performance and responsiveness. The asyncio library, part of Python’s standard library, is the gateway to building fast, scalable, and efficient applications.
At Curiosity Tech, we emphasize that understanding asynchronous programming is not just an academic exercise—it’s critical for high-performance Full Stack Python development in real-world scenarios.
Synchronous vs Asynchronous
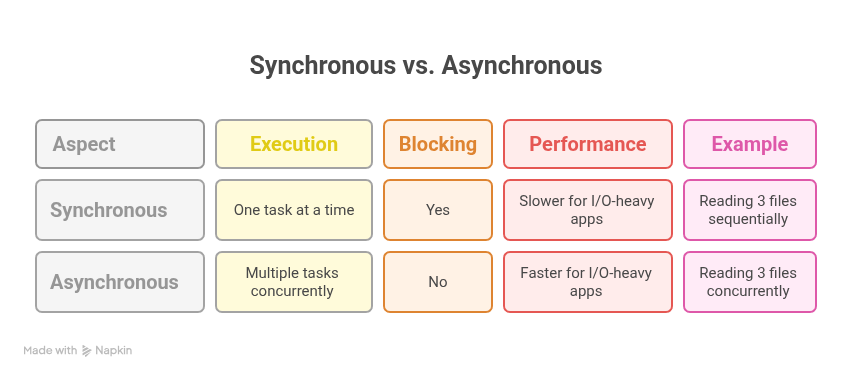
| Aspect | Synchronous | Asynchronous |
| Execution | One task at a time | Multiple tasks concurrently |
| Blocking | Yes | No |
| Performance | Slower for I/O-heavy apps | Faster for I/O-heavy apps |
| Example | Reading 3 files sequentially | Reading 3 files concurrently |
Analogy: Synchronous = waiting in line at a single cashier.
Asynchronous = multiple counters, customers served simultaneously.
Core Concepts of asyncio
- Coroutine – Functions defined with async def that can be paused and resumed.
- Event Loop – Manages the execution of asynchronous tasks.
- Task – Wraps coroutines and schedules them concurrently.
- Await – Pauses coroutine execution until the awaited task completes.
Basic Example: Asyncio in Action
import asyncio
async def fetch_data(name, delay):
print(f”Fetching {name}…”)
await asyncio.sleep(delay)
print(f”{name} fetched after {delay} seconds”)
return f”Data-{name}”
async def main():
task1 = asyncio.create_task(fetch_data(“API1”, 2))
task2 = asyncio.create_task(fetch_data(“API2”, 3))
results = await asyncio.gather(task1, task2)
print(“All data fetched:”, results)
asyncio.run(main())
Output:
Fetching API1…
Fetching API2…
API1 fetched after 2 seconds
API2 fetched after 3 seconds
All data fetched: [‘Data-API1’, ‘Data-API2’]
This example shows concurrent execution, reducing overall waiting time.
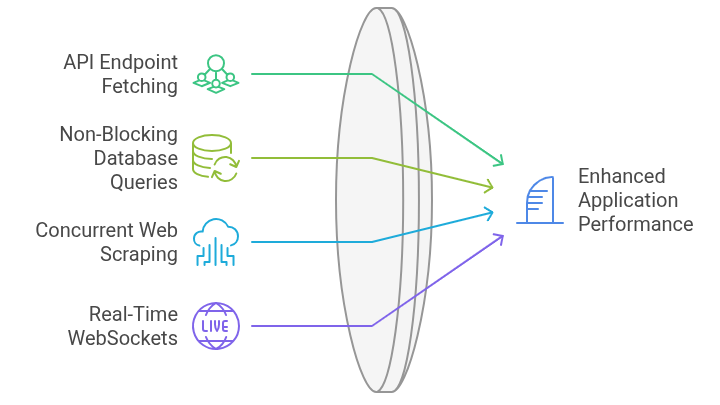
Real-World Use Cases
- Fetching multiple API endpoints in a dashboard simultaneously.
- Database queries that don’t block the main application.
- Web scraping where multiple pages are scraped concurrently.
- WebSockets and real-time apps for chat, notifications, or stock prices.
At Curiosity Tech, learners implement async programming when building real-time dashboards, combining Flask or Django backend with asyncio for maximum performance.
Asyncio with HTTP Requests
import aiohttp
import asyncio
async def fetch(session, url):
async with session.get(url) as response:
return await response.text()
async def main():
urls = [‘https://example.com’, ‘https://curiositytech.in’]
async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session:
results = await asyncio.gather(*(fetch(session, url) for url in urls))
for url, content in zip(urls, results):
print(f”{url} length:”, len(content))
asyncio.run(main())
- Makes multiple HTTP requests concurrently.
- Perfect for Full Stack applications with microservices.
Combining Asyncio with Flask/Django
- Flask: Use libraries like Quart (async Flask alternative) to enable async routes.
- Django: From Django 3.1+, support for async views and ORM queries is available.
Example: Django Async View
from django.http import JsonResponse
import asyncio
async def async_view(request):
await asyncio.sleep(2)
return JsonResponse({“message”: “Async Response from CuriosityTech Demo”})
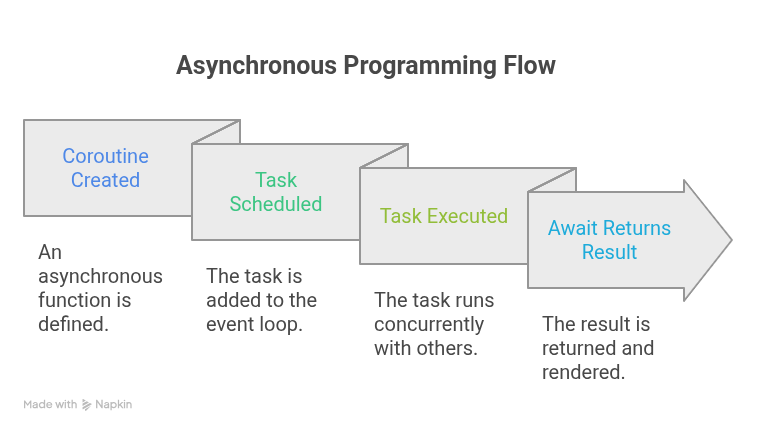
Infographic Idea – “Async Programming Flow”
- Step 1: Coroutine created → async function
- Step 2: Task scheduled in event loop
- Step 3: Task executed concurrently
- Step 4: Await returns result → render to frontend
Best Practices
- Use async only where necessary – avoid mixing sync-heavy computations.
- Handle exceptions in coroutines using try/except.
- Limit concurrent tasks if making many network requests to avoid overload.
- Integrate with frontend – async Python backend + React/Vue SPA = real-time updates.
Real-World Project – CuriosityTech Example
Students at CuriosityTech built a Python Full Stack stock market app:
- Backend fetched stock prices from multiple APIs asynchronously.
- Frontend React SPA displayed live updates using WebSockets + async tasks.
- Result: Users saw real-time dashboards without lag, demonstrating async programming’s power in action.
Conclusion
Asynchronous programming is a must-have skill for Full Stack Python developers, especially when building high-performance, real-time applications. asyncio empowers developers to execute multiple I/O-bound tasks concurrently, improving efficiency and user experience.
At Curiosity Tech, learners apply asyncio in real-world projects, ensuring that they are not just familiar with syntax but also comfortable integrating it into full-stack workflows.



