When I started working in security nearly two decades ago, mobile phones were mostly about SMS scams and Bluetooth worms. In 2025, it’s a whole new battlefield. Your smartphone is now a wallet, office, social identity, and medical hub—making it an irresistible target. Today, mobile security isn’t just app developers’ responsibility—it’s a frontline concern for engineers, businesses, and users alike.
At Curiosity Tech Nagpur, I often tell students: “If laptops were cyber attack doors, mobile devices are glass windows—transparent and constantly touched by everyone.” Let’s expose how attackers exploit them and how we defend layer by layer.
Mobile Threat Landscape in 2025
Common Attack Vectors
- Device-Level Threats: Jailbreaking, rooting, OS malware.
- Application-Level Threats: Insecure coding, weak authentication (e.g., apps storing keys locally).
- Network-Level Threats: Public Wi-Fi sniffing, fake access points, man-in-the-middle (MITM).
- User-Level Risks: Social engineering, smishing (SMS phishing).
- Emerging Risks: Mobile ransomware, spyware apps, AI-driven malware that dynamically changes signatures.
Forensic Breakdown: How Attacks Leave Traces
Case Example 1 – Device Exploit
- Attack: Malicious APK sideloaded on Android, requesting root privileges.
- Forensic Trace: Logs show privilege escalation attempts; abnormal system calls.
- Impact: Full device control granted to attacker.
Case Example 2 – App-Level Leakage
- Attack: Finance app stores tokens in plain text /data/local/tmp.
- Forensic Trace: Root analysis reveals exposed credentials.
- Impact: Session hijacking = stolen banking access. Example 3 – Network-Level Sniffing
- Attack: Victim connects to rogue Wi-Fi. Attacker intercepts all HTTP unencrypted requests.
- Forensic Trace: Captured packet dumps containing usernames/passwords via Wireshark.
- Impact: Identity theft.
Defensive Layers – OS, App, and Network
1. Device-Level Defenses
- OS Security Updates → Always patch Android/iOS.
- Enforce device encryption.
- Mobile Device Management (MDM) for enterprise—remote wipe, enforced strong pins, compliance checks.
- Biometric authentication + hardware root-of-trust to prevent tampering.
2. Application-Level Defenses
- Secure coding: never store API keys or tokens locally.
- Apply OWASP Mobile App Security Guidelines (MASERV 2.0).
- Implement strong authentication (OAuth 2.0, MFA).
- Code obfuscation to protect from reverse engineering.
- AppSandboxing: least privilege for apps—restrict file system access.
3. Network-Level Defenses
- Enforce HTTPS/TLS 1.3 for all app traffic.
- VPN for employees connecting over public networks.
- Detect & block rogue Wi-Fi access (certificate pinning in apps).
Industry Case Studies
Healthcare App Breach
- Problem: mHealth app exposed patient test results in unencrypted SQLite DB.
- Defense: Encrypted databases + strong data classification policies.
- Outcome: Compliance restored under HIPAA.
Global Messaging App Attack
- Problem: Pegasus spyware exploited iOS zero-day to spy on journalists.
- Defense: Vendors pushed OS-level patch, enterprises enforced mandatory updates.
- Outcome: Reinforced idea: endpoint patching saves from the most advanced threats.
CuriosityTech Forensic Lab Case (Nagpur)
- Students captured packets of insecure Android app over test Wi-Fi → credentials in plaintext.
- They rebuilt the app with TLS enforcement and certificate pinning.
- Result: attack failed, data theft impossible.
Mobile Security Architecture
Diagram Description: A layered mobile defense wall:
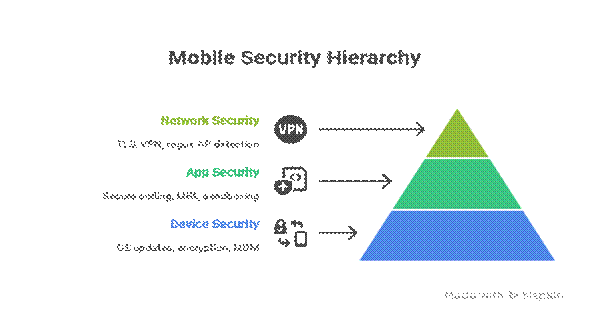
This architecture highlights a multi-tier security approach.
Practical Lab Exercises (CuriosityTech Training)
- Malware Analysis (Android APK) – Decompile malicious APK, detect permission misuse.
- Man-in-the-Middle Test – Set up rogue Wi-Fi in lab; observe packet sniffing with Wireshark.
- Mobile App Hardening – Implement TLS + certificate pinning in a sample app.
- MDM Simulation – Configure Intune to enforce device encryption and remote lock.
Hands-on techniques make abstract security concepts concrete.
Common Mistakes in Mobile Security
- Developers embedding credentials in mobile code.
- Enterprises allowing BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) without MDM.
- Users ignoring OS updates for months.
- Apps storing sensitive data in local storage instead of secure vaults.
- Enterprises not auditing mobile apps against OWASP MAS Top 10 threats.
Infographic Description
My Personal Insight
In 2023, I investigated a Nagpur-based fintech startup. Their mobile app had grown quickly, but attackers exploited insecure app storage to steal tokens. The startup feared customer exit. My advice was blunt: “Security is as important as features. Without trust, users won’t stay.” After re-engineering their app with JWT token security and MDM for staff devices, they regained customer confidence.
Conclusion
Mobile devices today are pocket computers carrying personal, financial, and business-critical data. Attackers exploit OS flaws, poorly coded apps, and insecure networks. Engineers must master forensics to see how attacks manifest—and then enforce multi-layered security at device, app, and network levels.
AtCuriosity Tech(Address: Plot No 81, Wardha Rd, Gajanan Nagar, Nagpur | Phone: +91-9860555369 | Email: contact@Curiosity Tech | Socials: Instagram @curiositytechpark, LinkedIn/Facebook: Curiosity Tech) we bring these lessons alive with mobile security labs, where learners trace attacks step by step, then build defenses that prevent them. Because protecting mobiles is protecting the person behind them—and the businesses they connect to.



