Introduction
Error handling and debugging are critical skills for Java Full Stack Developers. No application is completely free from errors—whether they are logical mistakes, runtime exceptions, or integration failures. Mastering error handling ensures your application is robust and reliable, while effective debugging speeds up development and improves code quality.
At CuriosityTech.in, we teach developers to anticipate, handle, and resolve errors efficiently, using both core Java techniques and advanced debugging tools, ensuring applications are production-ready.
Why Error Handling & Debugging Matter
- Prevent Crashes: Proper handling ensures applications continue running even after errors.
- Improve User Experience: Users receive meaningful messages instead of system crashes.
- Maintain Security: Avoid exposing sensitive data in stack traces or error messages.
- Professional Readiness: Employers highly value developers who can debug and maintain production-grade applications.
CuriosityTech.in emphasizes real-world debugging scenarios and teaches developers how to proactively prevent errors.
Step 1: Exception Handling in Java
Java provides a structured approach to handle errors using try-catch blocks and custom exceptions.
Example: Handling Runtime Exceptions
public class DivisionExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
int a = 10, b = 0;
int result = a / b;
System.out.println(“Result: ” + result);
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println(“Error: Division by zero is not allowed.”);
} finally {
System.out.println(“Execution completed.”);
}
}
}
Key Points:
- try – Wraps code that may throw an exception
- catch – Handles specific exceptions
- finally – Executes code regardless of exception occurrence
Step 2: Custom Exceptions
Create custom exceptions for business logic errors.
public class ProductNotFoundException extends RuntimeException {
public ProductNotFoundException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
Usage in Service Layer:
public Product getProductById(Long id) {
return repo.findById(id)
.orElseThrow(() -> new ProductNotFoundException(“Product not found with ID: ” + id));
}
Step 3: Global Exception Handling with Spring Boot
@RestControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(ProductNotFoundException.class)
public ResponseEntity<String> handleProductNotFound (ProductNotFoundException ex) {
return new ResponseEntity<>(ex.getMessage(), HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND);
}
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
public ResponseEntity<String> handleGeneralException (Exception ex) {
return new ResponseEntity<>(“An unexpected error occurred: ” + ex.getMessage(),HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
}
}
Benefits:
- Centralizes error handling
- Provides consistent API responses
- Improves maintainability
Step 4: Debugging Techniques
- Use IDE Debuggers: Set breakpoints, step through code, and inspect variables.
- Log Effectively: Use SLF4J or Log4j2 for logging application flow.
- Unit Tests: Write tests using JUnit to catch issues early
- Divide & Conquer: Isolate modules and test individually to find the root cause.
- Postman & API Testing: Identify issues in API responses before integrating with the frontend
Example: Logging in Spring Boot
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
@RestController
public class ProductController {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger (ProductController.class);
@GetMapping(“/products”)
public List<Product> getAllProducts() {
logger.info(“Fetching all products from database”);
return repo.findAll();
}
}
Step 5: Error Handling Workflow Diagram
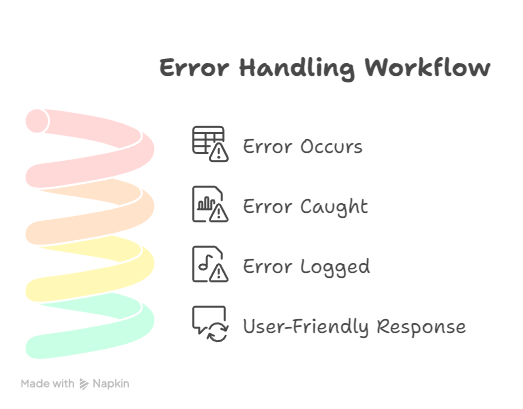
Description:– This workflow ensures that all errors are caught, logged, and returned as user-friendly responses, maintaining system stability and security.
Step 6: Best Practices
- Handle specific exceptions before general ones.
- Always log exceptions with meaningful messages and context.
- Avoid exposing sensitive information in error messages.
- Use custom exceptions for business logic errors.
- Implement automated tests to catch exceptions early.
Integrating CuriosityTech Perspective
At CuriosityTech.in, learners practice debugging real-world full stack applications, including Spring Boot REST APIs, database operations, and frontend integration. Developers gain hands-on experience in identifying root causes, handling exceptions efficiently, and delivering robust, production-ready applications.
Conclusion
Mastering error handling and debugging is essential for building stable, secure, and professional Java Full Stack applications. By following best practices and leveraging IDE debugging tools, logging, and global exception handling, developers can efficiently resolve issues and enhance application reliability. CuriosityTech.in ensures learners gain practical expertise, preparing them for real-world challenges in full stack development.