In the evolving world of cloud-native development and operations, DevOps and Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) are often mentioned together, sometimes interchangeably. While both aim to bridge the gap between development and operations, their philosophies and practices differ.
At Curiosity Tech, we guide learners through hands-on DevOps workflows and SRE principles, helping them understand how these approaches complement rather than replace each other in modern organizations.
What is DevOps?
Definition: A cultural and technical practice that unites developers and operations teams to deliver software faster, more reliably, and continuously.
Focus Areas: Collaboration, CI/CD automation, infrastructure as code, monitoring, and rapid deployments.
Goal: Shorten the software development lifecycle while maintaining quality and agility.
What is Site Reliability Engineering (SRE)?
Definition: A discipline originated at Google, applying software engineering principles to IT operations for achieving reliability at scale.
Focus Areas: Service Level Objectives (SLOs), Service Level Indicators (SLIs), error budgets, automation, and incident management.
Goal: Balance feature velocity with system reliability while minimizing toil (manual repetitive work).
Key Differences Between SRE and DevOps
| Aspect | DevOps | SRE |
| Origin | Emerged as a culture & movement for collaboration | Introduced at Google as a formal discipline |
| Focus | Collaboration, automation, CI/CD | Reliability, availability, resilience |
| Primary Role | Developers + Ops working together | Ops team with software engineering mindset |
| Key Metrics | Deployment frequency, lead time, MTTR | SLOs, SLIs, Error Budgets |
| Responsibility | Delivering features quickly | Ensuring services run reliably |
| Tools | Jenkins, Ansible, Terraform, Kubernetes | Prometheus, Grafana, SLIs dashboards, Error budget tracking |
| Philosophy | “You build it, you run it” | “Reliability is a feature” |
Visual Model: SRE vs DevOps Relationship
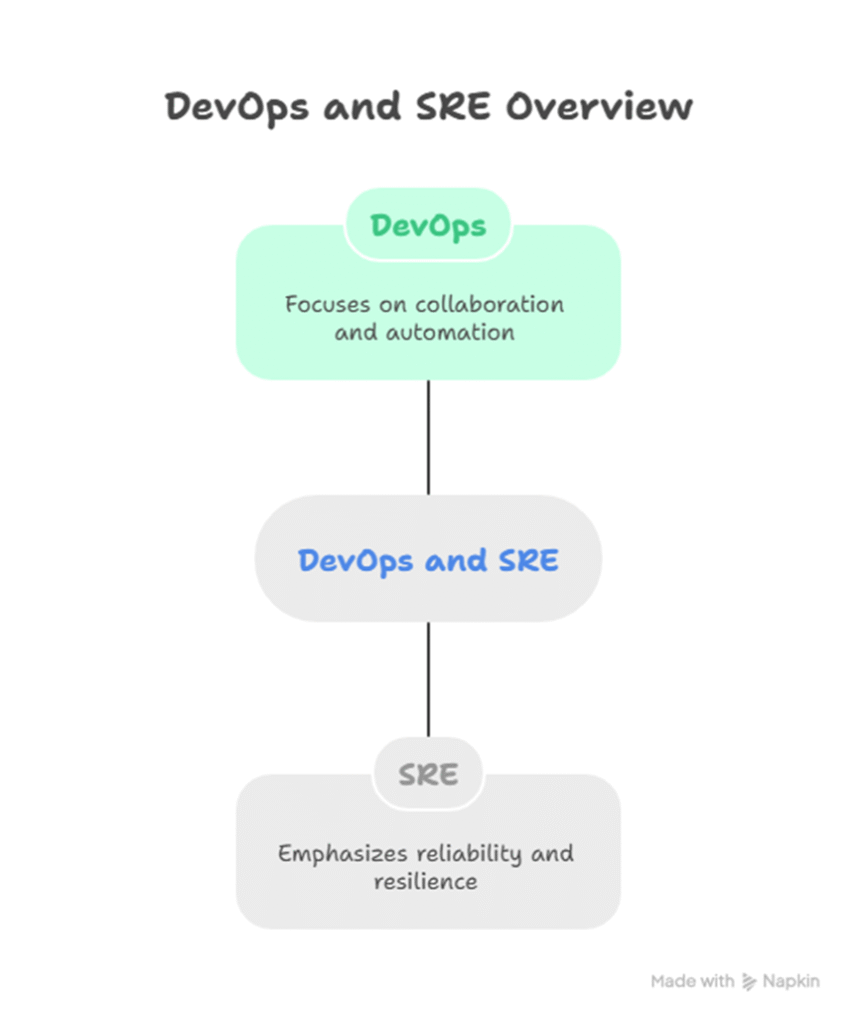
Explanation: DevOps is the broad cultural and technical movement, while SRE is a specific implementation that ensures services meet reliability goals.
Core Concepts in SRE
- SLIs (Service Level Indicators): Quantitative measures of reliability (e.g., request latency, error rate).
- SLOs (Service Level Objectives): Target values for SLIs (e.g., 99.9% uptime).
- SLAs (Service Level Agreements): Contracts with customers that include penalties if SLOs are not met.
- Error Budgets: Allowed margin for unreliability (e.g., 0.1% downtime). Helps balance innovation vs stability.
- Toil Reduction: Automating repetitive tasks (manual patching, deployments, monitoring setup).
Metrics That Matter: DevOps vs SRE
| Metric | DevOps Focus | SRE Focus |
| Deployment Frequency | High – multiple releases per day | Balanced – velocity vs stability |
| Mean Time to Recovery (MTTR) | Reduced via automation | Reduced via incident response playbooks |
| Uptime | Ensures stability via CI/CD | Measured via SLOs/SLIs and error budgets |
| Innovation vs Stability | Pushes for faster features | Protects reliability with error budgets |
| Monitoring | Continuous monitoring integrated with CI/CD | Deep observability, root cause analysis |
How They Work Together
- DevOps provides the cultural shift: breaking silos, introducing automation, enabling CI/CD.
- SRE provides the reliability framework: ensuring deployments meet defined SLOs, SLIs, and SLAs.
Example:
- DevOps pipeline deploys code to production daily.
- SRE practices ensure those deployments do not compromise 99.99% uptime SLA.
- If error budget is consumed, SRE halts new deployments until stability is restored.
Case Study: CuriosityTech.in Training Approach
At Curiosity Tech, learners are trained to:
- Build CI/CD pipelines (DevOps) using Jenkins, GitLab CI, and Terraform.
- Define SLOs and SLIs (SRE) for deployed microservices.
- Simulate outages with chaos engineering tools to understand reliability trade-offs.
- Implement dashboards in Grafana & Prometheus for SRE-style observability.
- Balance error budgets while maintaining release velocity.
This approach ensures learners can think like DevOps engineers and operate like SREs.
Challenges in Adoption
| Challenge | DevOps Issues | SRE Issues | Solution |
| Resistance to Culture Change | Developers hesitant to take ops responsibilities | Ops team hesitant to code | Strong training & cross-team collaboration |
| Measuring Success | Focuses on speed, ignores reliability | Focuses on reliability, ignores velocity | Combine metrics (velocity + SLOs) |
| Tool Overload | Too many tools for CI/CD | Too many monitoring dashboards | Unified toolchain with integrations |
Conclusion
DevOps and SRE are not competitors—they are complementary approaches to modern software delivery. DevOps establishes the culture of collaboration and automation, while SRE ensures that reliability and scalability are baked into every deployment.
At Curiosity Tech, learners get hands-on exposure to both disciplines, mastering CI/CD pipelines while applying SRE’s reliability engineering principles—equipping them for the demands of enterprise-grade DevOps and cloud-native reliability roles.