In the rapidly evolving world of cloud computing, businesses often face a crucial choice: Multi-Cloud or Hybrid Cloud? While both strategies offer significant advantages, understanding their differences, benefits, and real-world applications can help organizations make smarter infrastructure decisions. At Curiosity Tech, where we explore innovative cloud solutions and emerging technologies, we emphasize the importance of clarity in cloud adoption strategies for modern businesses.
Understanding the Basics
Hybrid Cloud refers to a computing environment that combines private cloud (on-premises) and public cloud services, allowing organizations to maintain control over critical workloads while leveraging public cloud flexibility for scalability and cost optimization.
Multi-Cloud, on the other hand, is the use of multiple public cloud providers simultaneously. This approach aims to prevent vendor lock-in, optimize performance, and take advantage of specialized services from different cloud providers.
Think of it this way: a hybrid cloud is like a hybrid car—part electric, part gasoline, giving you the best of both worlds. Multi-cloud is like owning multiple vehicles from different manufacturers, each serving a unique purpose, depending on your needs.
Key Differences Between Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud
| Feature | Hybrid Cloud | Multi-Cloud |
| Definition | Combination of private and public clouds | Multiple public cloud providers |
| Primary Goal | Flexibility & control over sensitive workloads | Avoid vendor lock-in & leverage best-of-breed services |
| Workload Distribution | Critical workloads on private, scalable on public | Distributed across different public providers |
| Cost Management | Optimized for workload types | Can be complex due to multiple providers |
| Security | High security for private cloud segments | Security depends on each provider’s measures |
| Management Complexity | Moderate, with integrated orchestration tools | High, requires cross-platform management tools |
This table simplifies the decision-making process, but remember, the choice often depends on organizational priorities, regulatory requirements, and existing IT infrastructure.
Benefits of Hybrid Cloud
- Enhanced Security and Compliance – Keep sensitive data on-premises while leveraging public cloud scalability.
- Cost Efficiency – Use public cloud resources only when needed, minimizing infrastructure expenses.
- Flexibility – Quickly adapt to changing workloads without compromising performance.
Benefits of Multi-Cloud
- Avoid Vendor Lock-In – You’re not tied to one provider, allowing better negotiation and flexibility.
- High Availability & Reliability – If one provider experiences downtime, workloads can run on another provider.
- Optimized Performance – Choose providers based on specific capabilities, geographic location, or latency requirements.
When to Use ? Which to Use ?
- Hybrid Cloud is ideal for businesses that handle sensitive data, require regulatory compliance, or have existing on-premise infrastructure.
- Multi-Cloud suits organizations looking for flexibility, redundancy, or access to specialized services across different cloud platforms.
Infographic Idea: Hierarchical Cloud Strategy
You could create an infographic showing a top-level “Cloud Strategy” node branching into Hybrid Cloud and Multi-Cloud, with their sub-components and benefits listed visually.
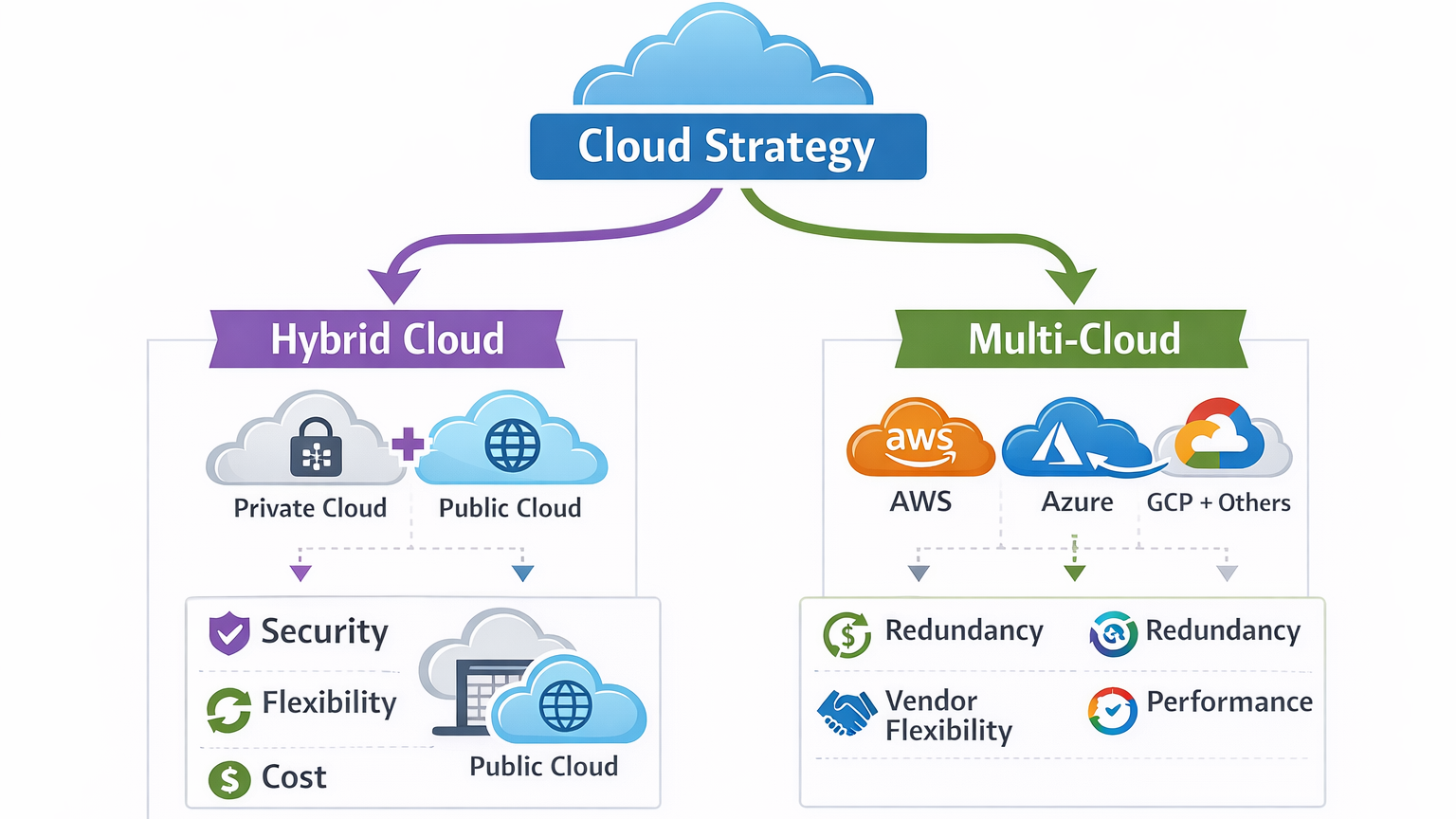
This visual representation helps readers quickly grasp the structural differences.
Real-World Example
A financial institution may adopt hybrid cloud to store sensitive client data in a private cloud while running AI-based analytics in the public cloud. Meanwhile, an e-commerce giant could use multi-cloud to distribute traffic across AWS and Azure to ensure seamless customer experience even during peak loads.
At Curiosity Tech, we guide businesses in choosing the right cloud architecture for their unique needs, combining technical expertise with practical insights. Whether you are a startup or an established enterprise, understanding these differences ensures your cloud investment delivers the expected value.
Conclusion
Choosing between hybrid and multi-cloud isn’t about “better vs worse.” It’s about aligning technology with business goals. Hybrid cloud prioritizes control and security, while multi-cloud maximizes flexibility and performance. By assessing workload requirements, budget constraints, and compliance needs, organizations can craft a cloud strategy that drives innovation and efficiency.
At Curiosity Tech, we continually explore these strategies to empower businesses with the latest cloud innovations, helping them thrive in a competitive digital landscape.