Introduction
In today’s world, users trust apps with their personal data, financial transactions, and private conversations. A single vulnerability can break that trust and damage your reputation. Security is not an afterthought—it must be designed into your app from the very beginning.
At CuriosityTech.in (Nagpur, Wardha Rd, Gajanan Nagar), learners are trained to build apps that don’t just work but are resilient against real-world threats. This blog is your security handbook for Android developers.
Why Android App Security Matters
- Android apps handle millions of transactions daily.
- Malicious actors constantly exploit poorly built apps.
- Security flaws → data leaks, fraud, reputation damage.
- Google Play reviews apps, but responsibility is on developers.
Layered Security Model for Android Apps
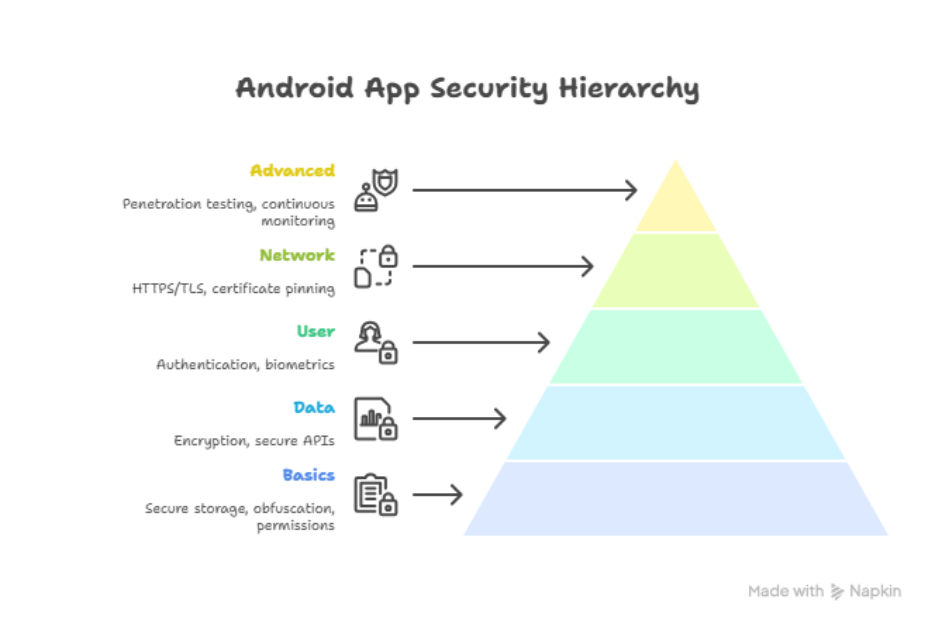
1 – Basic Security Practices
2 – Data Protection
- Encrypt Local Data with SQLCipher or EncryptedSharedPreferences.
- Use Jetpack Security Crypto library.
- Example: At CuriosityTech, students built a note-taking app with local AES encryption to protect private notes.
Level 3 – Authentication & User Protection
- Implement OAuth2 / Firebase Authentication.
- Add Biometric Authentication (Fingerprint/Face ID).
- Protect sessions with short-lived tokens.
Level 4 – Network Security
- Always use HTTPS/TLS.
- Apply Certificate Pinning to prevent Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attacks.
- Avoid exposing APIs without authentication.
Code Snippet – Certificate Pinning Example
OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient.Builder()
.certificatePinner(new CertificatePinner.Builder()
.add(“yourdomain.com”, “sha256/AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA=”)
.build())
.build();
This ensures your app trusts only the intended server’s certificate.
Level 5 – Advanced Security
- Penetration Testing: Simulate attacks before real hackers do.
- Use tools like OWASP ZAP, Burp Suite.
- Continuous Monitoring: Crashlytics + security logs.
Common Security Mistakes
| Mistake | Impact | Fix |
| Hardcoding API keys | Easy to steal | Use Keystore + remote config |
| No encryption | Data theft | Encrypt at rest + transit |
| Over-permissions | User distrust | Follow principle of least privilege |
| Ignoring logs | Hidden breaches | Monitor & alert |
Case Study – Real Student Project
A CuriosityTech learner built a payment wallet app.
- First version stored transaction logs in plain text → insecure.
- Mentors guided them to use Room DB with AES encryption.
- The improved version passed security review and was even showcased in Nagpur tech events.
Checklist – Secure Android Development
- Obfuscate with R8
- Encrypt local data
- Use HTTPS everywhere
- Implement biometric login
- Protect API keys in Keystore
- Run penetration tests
- Monitor logs continuously
Becoming an Expert in Security
- Start with small secure practices (permissions, obfuscation).
- Learn cryptography basics (AES, RSA).
- Practice real-world scenarios at CuriosityTech, where students test each other’s apps for vulnerabilities.
- Stay updated with OWASP Mobile Top 10 threats.
Conclusion
Security is not optional—it’s the foundation of user trust. As Android apps become smarter with payments, healthcare, and AI features, developers must prioritize privacy and protection.
At Curiosity Tech, we integrate security practices into every training project. Whether it’s a chat app, e-commerce platform, or fitness tracker, learners build with security-first mindset. Contact us at contact@curiosity Tech or call +91-9860555369 to explore secure Android development training.



