In the ever-evolving world of software development, delivering code rapidly without sacrificing quality is paramount. This is where Continuous Integration (CI) comes into play—a methodology that allows developers to integrate code into a shared repository frequently, ideally multiple times a day. At its core, CI ensures that the new code merges seamlessly, passes automated tests, and is always in a deployable state.
At CuriosityTech.in, where we constantly embrace the latest in cloud and DevOps technologies, CI is a cornerstone of our development philosophy. Whether you are a startup aiming to streamline releases or a large enterprise scaling software delivery pipelines, understanding CI is critical. Today, we’ll dive deep into CI using Jenkins and GitHub Actions, exploring their architecture, setup, and practical use cases.
What is Continuous Integration (CI)?
Continuous Integration is a software development practice where developers regularly merge their code changes into a central repository. Each merge triggers an automated build and test process, catching errors early and reducing integration issues.
Key Benefits of CI:
● Faster Feedback Loop: Developers know immediately if their code breaks anything.
● Reduced Integration Problems: Frequent merges prevent the infamous “integration hell.”
● Higher Code Quality: Automated testing ensures reliability.
● Enhanced Collaboration: Teams work in a more synchronized and cohesive manner.
At Curiosity Tech, we teach developers to adopt CI practices not just as a technical requirement but as a cultural shift in their workflow, ensuring higher efficiency and better collaboration.
Jenkins – The Veteran CI Tool
Jenkins is one of the oldest and most widely used open-source CI tools. It provides flexible automation for building, testing, and deploying applications.
Jenkins Architecture:
Component Description
Jenkins Master Central control unit managing build jobs and worker nodes
Jenkins Agent/Node Executes build tasks assigned by the master
Plugins Extend Jenkins capabilities, e.g., Git, Maven, Docker, Slack notifications
Pipelines Define automated workflows as code
Hierarchical Diagram :
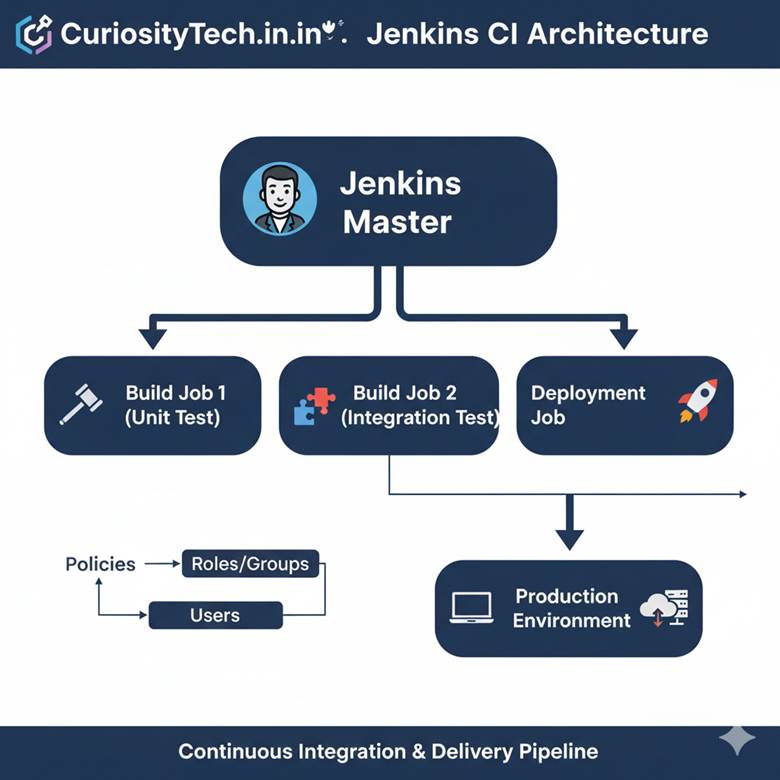
Why Jenkins is Popular:
● Open-source and highly extensible
● Supports multiple languages and platforms
● Active community and a rich plugin ecosystem
Example CI Workflow in Jenkins:
- Developer pushes code to GitHub.
- Jenkins automatically detects the commit.
- Runs automated tests.
- Generates build artifacts.
- Optionally triggers deployment to a staging or production environment.
At Curiosity Tech, we often guide beginners to set up their first Jenkins CI pipeline using real-world examples, helping them understand pipelines not just theoretically but practically.
GitHub Actions – CI with Modern Git Integration
GitHub Actions has revolutionized CI/CD by tightly integrating CI workflows with the GitHub repository itself. Unlike Jenkins, GitHub Actions doesn’t require a separate server and allows workflows to be defined using YAML files.
GitHub Actions Workflow Example:
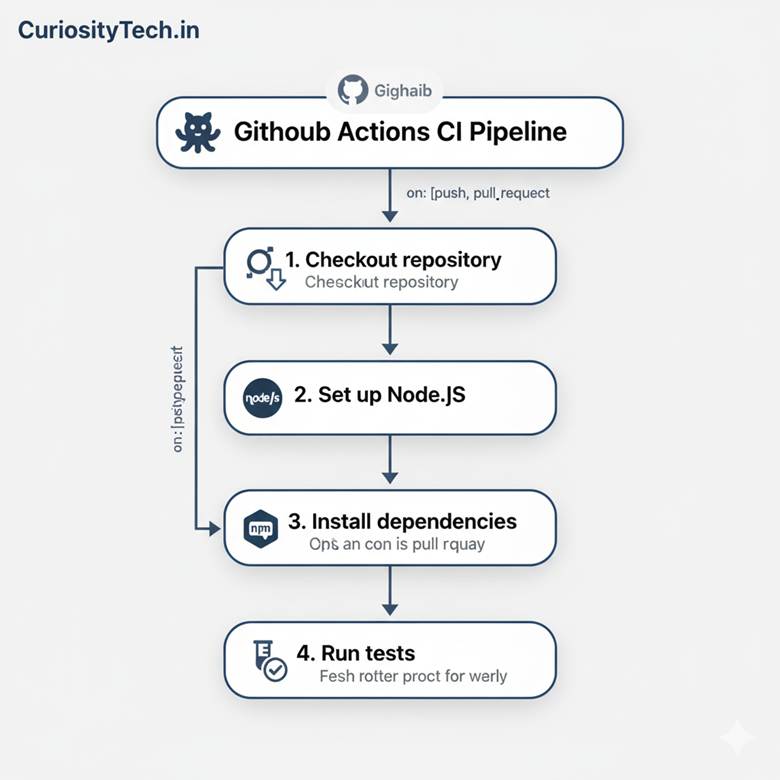
Advantages of GitHub Actions:
● No separate CI server needed; everything is cloud-hosted
● Deep GitHub integration for pull requests, releases, and notifications
● Reusable workflows for multiple projects
● Easy scaling for enterprise pipelines
At Curiosity Tech, we often combine Jenkins for heavy-duty, complex pipelines and GitHub Actions for quick, lightweight workflows. This hybrid approach allows teams to leverage the best of both worlds.
CI Best Practices
To maximize the benefits of CI, consider these industry-proven best practices:
- Commit Frequently: Smaller, frequent commits are easier to test and merge.
- Automate Everything: From testing to deployment, automation reduces human error.
- Maintain a Clean Repository: Keep the repository organized and avoid redundant code.
- Monitor and Notify: Always have feedback mechanisms in place for failed builds.
- Secure Secrets: Use encrypted environment variables for sensitive information.
Infographic Idea:
Real-World Applications
Many global companies rely on CI to ensure smooth software delivery. At Curiosity Tech, we’ve implemented CI pipelines for:
● Multi-branch application development
● Automated testing of APIs and microservices
● Deployment to cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and GCP
● Continuous monitoring and alerting of build failures
These implementations reduce downtime, catch bugs early, and allow development teams to focus on innovation rather than firefighting.
Conclusion
Continuous Integration is no longer optional—it’s a necessity for modern software development. Jenkins and GitHub Actions provide powerful, flexible tools for automating your code pipeline, reducing errors, and accelerating delivery. Whether you are an aspiring developer or a seasoned engineer, embracing CI practices enhances productivity and reliability.
At CuriosityTech.in, we combine technical expertise with hands-on guidance, helping developers and organizations adopt CI effectively. By integrating CI into your workflow today, you not only future-proof your development process but also create a culture of collaboration, speed, and quality.

