Introduction
The Robot Operating System (ROS) is not just software—it’s a framework that enables roboticists to build, simulate, and control complex robots efficiently. ROS provides libraries, tools, and conventions that standardize robot development, enabling interoperability between software components and hardware.
At Curiosity Tech beginners and enthusiasts can access step-by-step tutorials, ready-to-run examples, and practical projects that demonstrate ROS capabilities in real robot applications.
1. What is ROS?
- ROS is an open-source middleware for robotics.
- It provides communication tools, libraries, and simulation environments.
- ROS is not an operating system in the traditional sense but runs on Linux distributions, primarily Ubuntu.
Key Features
| Feature | Description |
| Nodes | Modular programs that perform specific tasks |
| Topics | Channels for exchanging data between nodes |
| Services | Synchronous communication mechanism |
| Messages | Data structure for exchanging information |
| Master | Central coordinator that manages node connections |
| Packages | Collections of nodes, libraries, and configurations |
Practical Tip: Beginners often start with ROS Noetic on Ubuntu 20.04, as it has extensive documentation and community support.
2. ROS Architecture
ROS uses a distributed modular system where multiple nodes communicate through topics and services.
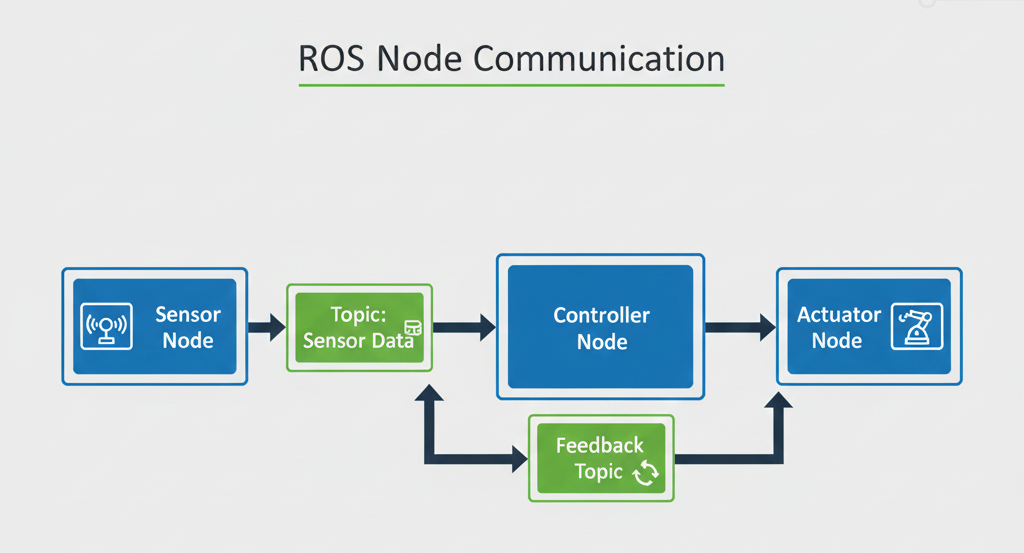
Description: Sensors publish data to topics, controller nodes subscribe to topics, process data, and send commands to actuators. Feedback topics allow real-time updates and adjustments.
3. Core ROS Concepts
A. Nodes
- Nodes are individual processes running in ROS.
- Example: A node could read LiDAR data or control motors.
B. Topics
- Topics allow asynchronous communication between nodes.
- Example: /camera/image_raw publishes image data, while a vision node subscribes to process it.
C. Services
- Services provide synchronous request-response communication.
- Example: A robot arm node receives a service request to move to a specific position.
D. Messages
- Messages are data packets exchanged over topics and services.
- Example: std_msgs/Stringfor text, sensor_msgs/Imagefor camera frames.
E. Packages
- Packages are self-contained units of ROS code.
- Example: turtlebot3_navigationcontains nodes, configuration files, and launch files.
4. ROS Tools

5. ROS Example Project: Autonomous Mobile Robot
Objective: Implement obstacle avoidance using ROS nodes.
Components:
- Sensors: LiDAR and ultrasonic sensors.
- Controller Node: Subscribes to sensor data topics, calculates path.
- Actuator Node: Sends velocity commands to motors.
Workflow Table
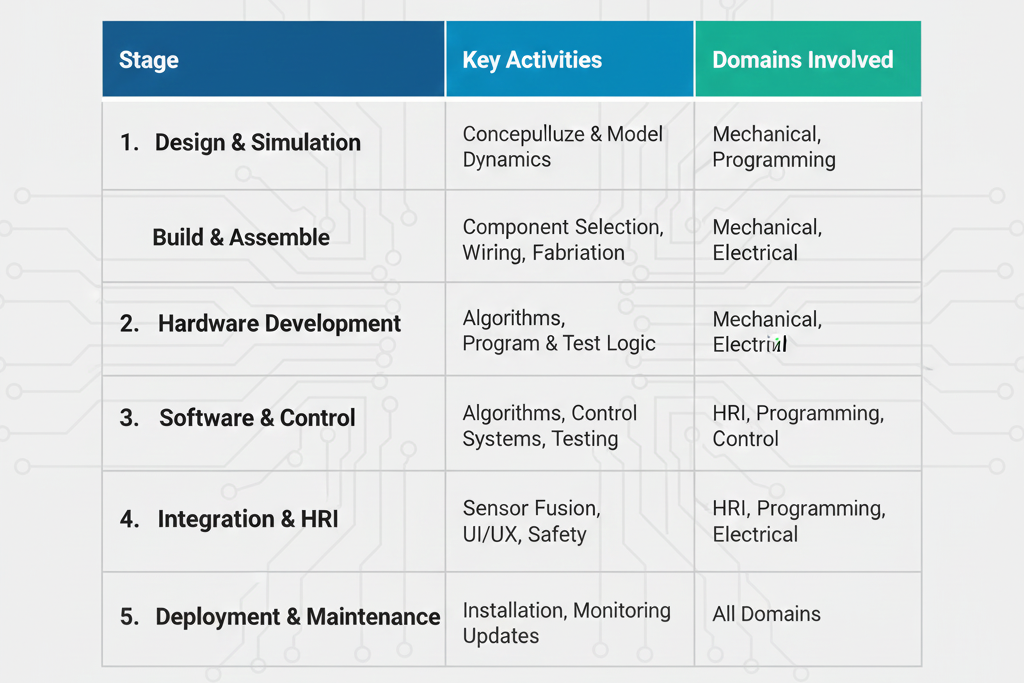
Curiosity Tech provides complete tutorials with wiring, launch files, and ROS package examples to implement this project successfully.
6. Advantages of Using ROS

7. Tips for Beginners
- Start with simulation before hardware to avoid costly mistakes.
- Use pre-built packages (like TurtleBot) to understand workflows.
- Experiment with topics, services, and messages to understand ROS communication.
- Gradually implement custom nodes for sensors, AI, and actuators.
- Combine ROS with Python or C++ to enhance robot intelligence.
Skill Roadmap Table
| Level | Focus Area | Tools/Resources |
| Beginner | Understand nodes, topics, messages | ROS Tutorials, TurtleBot simulation |
| Intermediate | Implement custom nodes, integrate sensors | ROS Noetic, RViz, Gazebo |
| Advanced | Multi-robot coordination, AI integration | ROS2, MoveIt!, OpenCV, TensorFlow |
Conclusion
ROS is a game-changer for robotics engineers, enabling modular, scalable, and intelligent robot development. Mastering ROS equips engineers with the skills to simulate, test, and deploy autonomous robots efficiently. Through Curiosity Tech learners can access detailed ROS tutorials, simulation guides, and practical projects that make mastering this middleware accessible and hands-on.