Data is the backbone of any mobile application. Whether it’s user preferences, app settings, messages, or offline content, iOS developers must understand how to store, retrieve, and manage data efficiently. Core Data, Apple’s object graph and persistence framework, provides a robust solution for managing complex data models and ensuring your app runs smoothly, even with large datasets. At CuriosityTech.in, we teach Core Data not just as a tool, but as a conceptual framework for structuring and managing app data in real-world scenarios.
What is Core Data?
Core Data is more than a database; it’s an object graph management system. It allows you to define your app’s data model, track relationships between objects, and persist this data seamlessly. Unlike flat storage solutions like UserDefaults or simple file storage, Core Data provides:
- Efficient querying for large datasets
- Relationship management between objects
- Undo/redo capabilities for user actions
- Automatic change tracking and versioning
It’s designed for apps where data complexity matters, such as task managers, note-taking apps, social networks, or e-commerce applications.
Core Data Architecture
Understanding Core Data requires knowing its main components:
- Managed Object Model (MOM) – Represents the schema of your data. Think of it as the blueprint of your app’s data, defining entities (tables), attributes (columns), and relationships.
- Managed Object Context (MOC) – The workspace for your objects. This is where you create, update, or delete objects before saving them persistently. It acts like a staging area, ensuring that changes are consistent before committing to storage.
- Persistent Store Coordinator (PSC) – Mediates between the MOC and physical storage, such as SQLite files. It ensures that data is saved correctly and efficiently.
- Persistent Store – The actual storage (SQLite, binary, or in-memory) where Core Data persists your objects.
Hierarchical Diagram of Core Data Workflow:
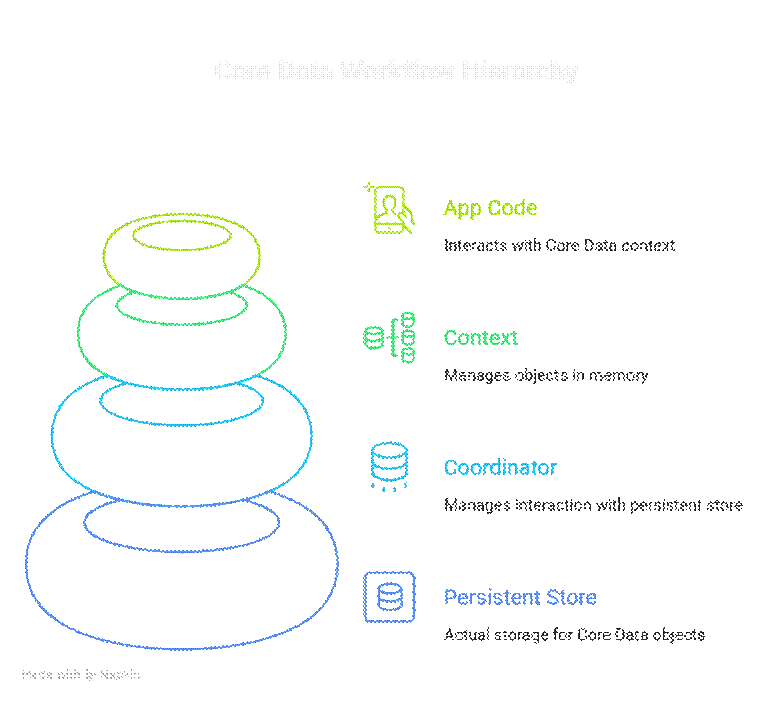
At CuriosityTech.in, learners are encouraged to visualize this workflow to understand how objects move from memory to permanent storage, which is critical for debugging and optimizing app performance.
Defining Data Models
Core Data uses entities and attributes to model your app’s data.
- Entity Example: User
- Attributes: username (String), email (String), profilePicture (Binary Data)
- Relationships: posts (one-to-many with Post entity)
- Attributes: username (String), email (String), profilePicture (Binary Data)
- Entity Example: Post
- Attributes: title (String), content (String), timestamp (Date)
- Relationships: author (inverse of posts)
- Attributes: title (String), content (String), timestamp (Date)
Table Representation:
| Entity | Attribute | Type | Relationship |
| User | username | String | posts (1→M) |
| User | String | – | |
| Post | title | String | author (M→1) |
| Post | timestamp | Date | – |
This relational approach allows for powerful queries and efficient data retrieval.
CRUD Operations in Core Data
Core Data supports Create, Read, Update, and Delete operations.
1. Creating Objects
Objects are instantiated in the MOC and then saved to the persistent store:
- let user = User(context: managedObjectContext)
- user.username = “curiosity”
- try? managedObjectContext.save()
2. Reading Objects
Core Data uses NSFetchRequest to query objects.
- Example: Fetch all users with username starting with “C”:
let fetchRequest: NSFetchRequest<User> = User.fetchRequest()
fetchRequest.predicate = NSPredicate(format: “username BEGINSWITH %@”, “C”)
let results = try? managedObjectContext.fetch(fetchRequest)
3. Updating Objects
- Fetch object → modify attributes → save context
user.email = “newemail@curiositytech.in”
try? managedObjectContext.save()
4. Deleting Objects
- Fetch object → delete from context → save
managedObjectContext.delete(user)
try? managedObjectContext.save()
At CuriosityTech.in, students practice building apps like note-taking apps or task managers, where CRUD operations are implemented on multiple entities with real-time relationships.
Relationships and Data Integrity
Core Data excels at managing relationships, which is critical for apps with interconnected data:
- One-to-One: e.g., User → Profile
- One-to-Many: e.g., User → Posts
- Many-to-Many: e.g., Users → Groups
Best Practices:
- Define inverse relationships to maintain data integrity.
- Use fetched properties for derived relationships to optimize queries.
- Avoid heavy computations in relationships; consider background contexts.
Performance Optimization
Large datasets or complex relationships can affect app performance. Advanced iOS developers focus on:
- Batch Fetching: Retrieve only needed data.
- Faulting: Core Data automatically loads objects on demand.
- Background Contexts: Perform heavy data operations off the main thread.
- Indexes: Improve query speed on frequently accessed attributes.
CuriosityTech.in emphasizes real-world scenarios like offline-first apps and high-traffic social platforms, where efficient Core Data usage can mean the difference between a smooth app and crashes.
Advanced Tips to Become an Expert
- Understand Context Hierarchies: Use parent-child contexts for undo/redo and background operations.
- Leverage NSFetchedResultsController: Perfect for table and collection views to automatically manage UI updates.
- Versioning and Migration: Handle schema changes with lightweight migration to maintain data integrity across app updates.
- Test with Large Datasets: Simulate thousands of records to ensure your app scales.
- Integrate with CloudKit: Synchronize Core Data with iCloud for cross-device persistence.
By mastering these skills, learners at CuriosityTech.in become capable of building robust, enterprise-level iOS apps that handle complex data scenarios with ease.
Conclusion
Core Data is not just a storage solution—it’s a strategic framework for structuring, managing, and optimizing data in iOS apps. By understanding entities, relationships, contexts, and performance optimization techniques, developers can build apps that are scalable, reliable, and user-friendly. Combining these principles with Swift and interface design ensures that your iOS apps are not only functional but also professional and efficient, ready for real-world deployment.



