Introduction
Programming is the brain of a robot. Without software, even the most sophisticated mechanical and electronic systems cannot function. Robotics programming combines embedded programming, algorithm development, and artificial intelligence to create intelligent behaviors in robots. Mastering programming languages like C, C++, and Python is essential for any aspiring robotics engineer.
CuriosityTech.in provides hands-on tutorials, projects, and examples that allow beginners to start programming robots immediately while understanding the theory behind each language and its applications.
Why Programming is Critical in Robotics
- Robot Control: Translating sensor input into actuator commands.
- Automation: Designing robots to execute repetitive tasks efficiently.
- Decision Making: Implementing AI or logic algorithms for autonomous behavior.
- Communication: Integrating multiple robotic systems using networks or ROS.
Example: A mobile robot uses infrared sensors to detect obstacles. The microcontroller executes a programmed algorithm in C++ to change the robot’s path, ensuring safe navigation.
Comparative Overview: C, C++ & Python for Robotics
| Feature | C | C++ | Python |
| Type | Procedural | Object-Oriented + Procedural | High-level, Interpreted |
| Performance | High (low-level control) | High (with object-oriented benefits) | Moderate (slightly slower execution) |
| Ease of Learning | Moderate | Difficult (requires OOP concepts) | Easy |
| Best Use Cases | Embedded microcontroller programming | Complex robotics systems, ROS integration | AI, machine learning, scripting, ROS |
| Libraries/Tools | AVR/Arduino SDK | ROS, OpenCV, Eigen, Boost | OpenCV, TensorFlow, Numpy, ROS |
| Memory Management | Manual | Manual / Object-oriented | Automatic |
Insight: Beginners often start with C for microcontroller projects, C++ for structured ROS-based robots, and Python for AI and image processing integration.
Step-by-Step Flowchart: Programming Workflow in Robotics
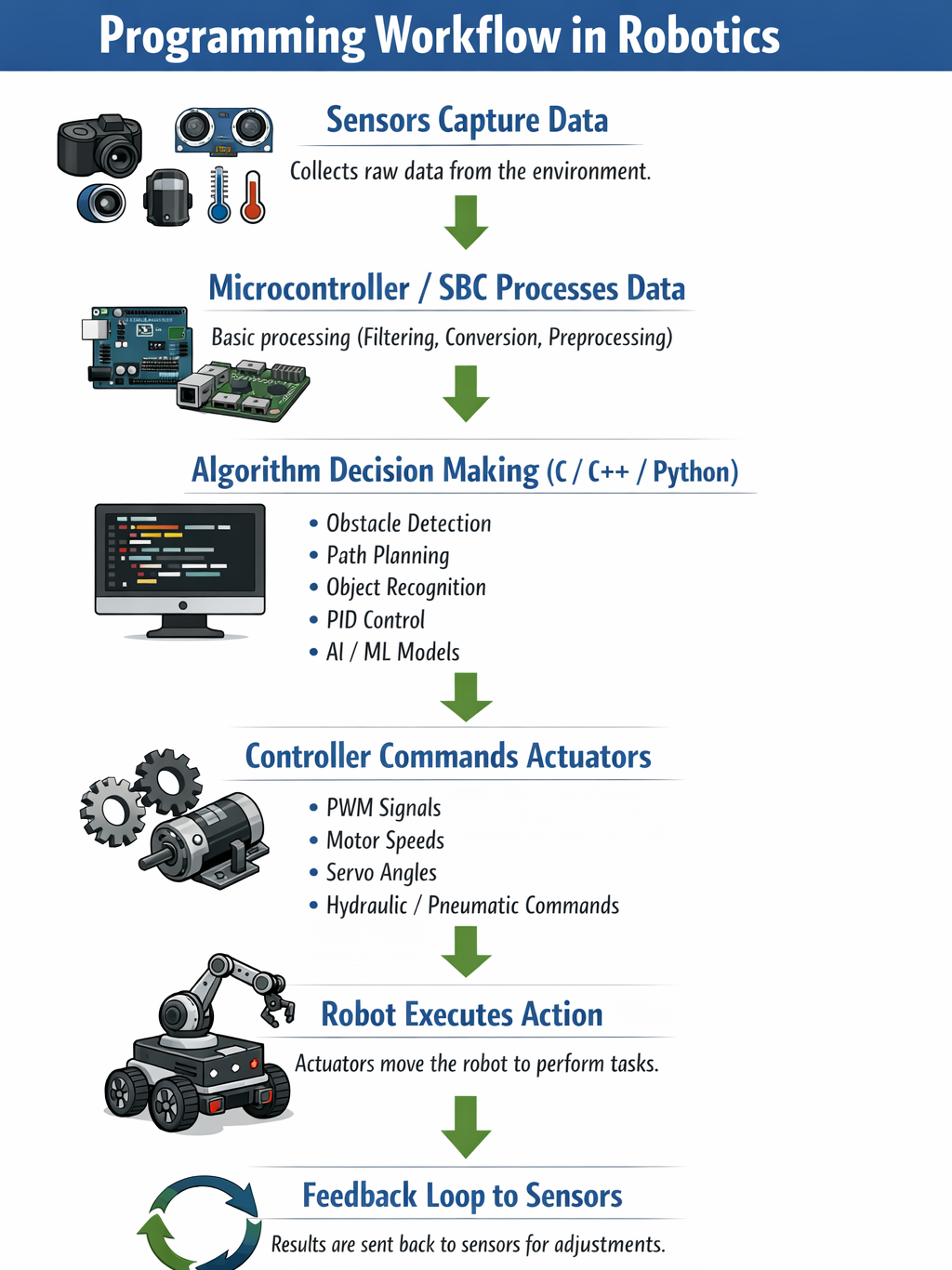
Description: This closed-loop ensures real-time response and adaptability in robots.
Language-Specific Use Cases
1. C Programming
- Microcontroller Programming: Arduino, STM32, and PIC controllers.
- Embedded Systems: Low-level control of motors, sensors, and real-time operations.
- Example Project: Build a simple LED blinking robot or line-following bot using Arduino with C.
2. C++ Programming
- Robotics Middleware: ROS integration for modular, scalable robot applications.
- Object-Oriented Design: Managing complex robotic systems like robotic arms.
- Example Project: Implementing a robot arm controller with modular classes for joints, sensors, and end-effectors.
3. Python Programming
- AI & Machine Learning: Path planning, object recognition, and predictive algorithms.
- Rapid Prototyping: Testing algorithms quickly without low-level memory management.
- Example Project: Use Python + OpenCV to create a robot that detects and follows a colored object.
Hands-On Beginner Project: Object-Following Robot
- Sensors: Camera module.
- Controller: Raspberry Pi with Python.
- Actuators: Servo motors for wheels.
- Algorithm:
- Capture video frames.
- Detect color or shape using OpenCV.
- Move robot toward object by sending PWM signals to motors.
- Outcome: Robot autonomously follows an object in real-time.
CuriosityTech.in provides detailed tutorials for each step, including Python scripts, wiring diagrams, and troubleshooting tips.
Tips for Becoming an Expert Robotics Programmer
- Practice Low-Level Programming: Start with C for microcontrollers to understand timing, interrupts, and memory.
- Master C++: Learn object-oriented programming and ROS to build scalable robotic applications.
- Explore Python Libraries: OpenCV, TensorFlow, and NumPy for AI-based robotics.
- Simulation First: Use Gazebo or V-REP before hardware implementation to avoid errors.
- Project-Based Learning: Build simple bots first, then integrate sensors, AI, and ROS for advanced functionality.
Hierarchy of Programming Mastery:
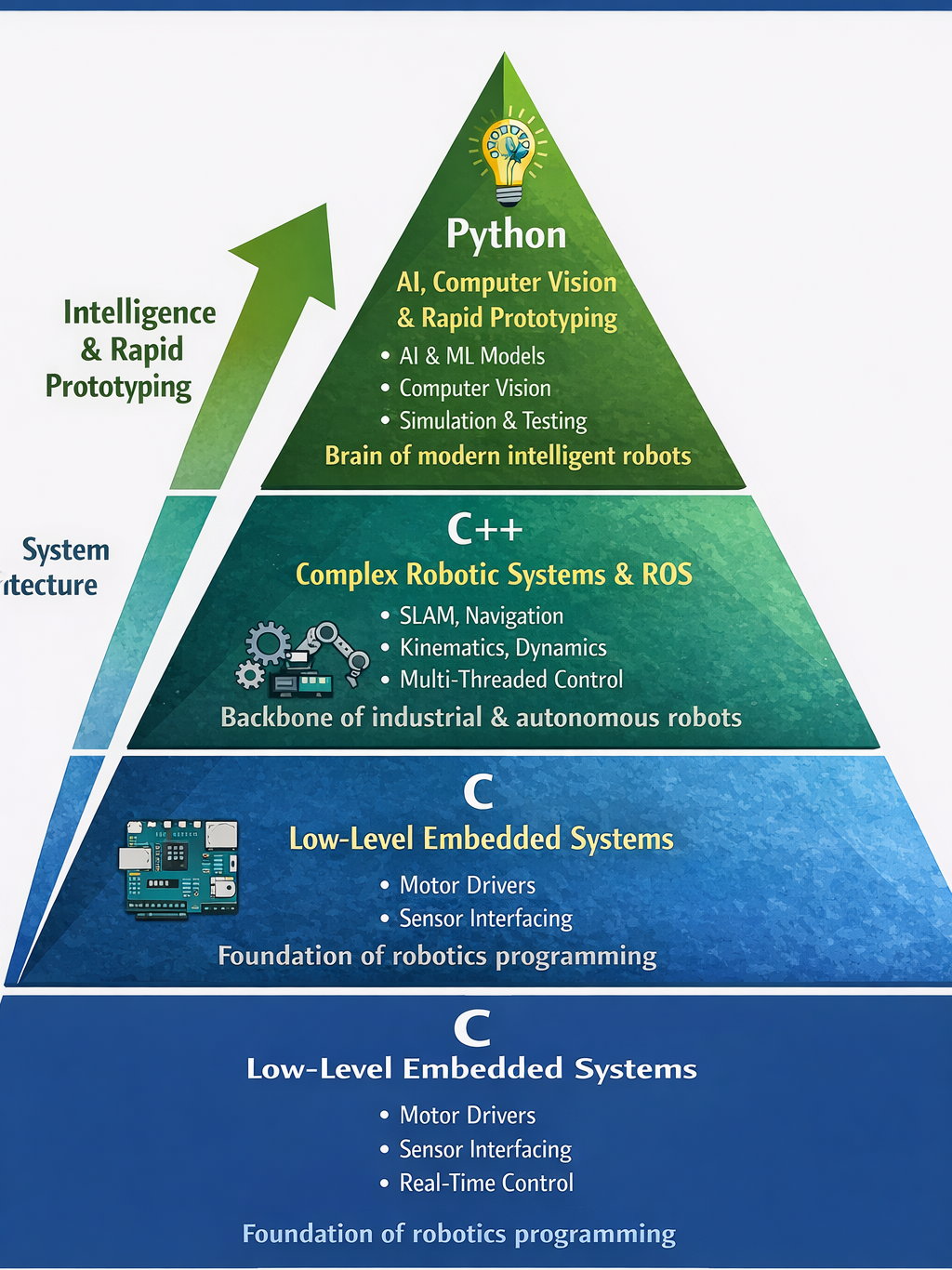
- C → Low-Level Embedded Systems
- C++ → Complex Robotic Systems & ROS
- Python → AI, Computer Vision & Rapid Prototyping
Conclusion
Robotics programming forms the core of intelligent robot design. Mastering C, C++, and Python enables engineers to handle everything from low-level hardware control to AI-based decision-making. Beginners can gain confidence by starting with microcontroller projects, moving to ROS-based systems, and integrating Python for advanced AI applications. Resources at CuriosityTech.in provide curated tutorials and real-life projects that help learners develop both technical mastery and practical experience.