Introduction
Robotics engineering is a highly multidisciplinary and rapidly evolving field that combines mechanical engineering, electronics, computer science, AI, and control systems. Building a successful career requires not just academic knowledge, but also practical experience, certifications, and continuous skill development.
At CuriosityTech.in, aspiring robotics engineers gain access to career guidance, skill-building projects, certification tutorials, and industry insights, empowering them to navigate a structured path toward becoming professional robotics engineers.
1. Overview of Robotics Engineering Career
Robotics engineers work across industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, research, logistics, defense, and AI-driven automation. Their roles include:
- Designing robotic systems: Mechanical, electrical, and control integration.
- Developing software and AI algorithms: Path planning, machine vision, and reinforcement learning.
- Maintenance and optimization: Ensuring reliability and efficiency of robotic operations.
- Human-robot interaction: Designing safe, intuitive, and collaborative systems.
Key Skills Needed:
- Mechanical design (CAD, kinematics, dynamics).
- Electronics and embedded systems (microcontrollers, sensors, actuators).
- Programming (C, C++, Python, ROS).
- AI and machine learning for perception and decision-making.
- Knowledge of industrial standards and safety protocols.
2. Career Roadmap Table
| Stage | Focus Area | Recommended Actions |
| Foundation | Basics of robotics, programming, math | Learn Python/C++, kinematics, sensors |
| Intermediate | Embedded systems, AI, ROS | Raspberry Pi/Arduino projects, ROS tutorials |
| Specialization | Industrial, healthcare, autonomous robotics | Focus on AI, SLAM, vision, human-robot interaction |
| Professional | Advanced AI integration, system design | Internships, research projects, certification |
| Expert | Leadership & R&D | Lead robotics teams, develop innovative solutions |
3. Essential Certifications
Certifications validate knowledge, demonstrate skills to employers, and boost career prospects.
| Certification | Provider / Platform | Focus Area | Level |
| Certified Robotics Technician | Robotics Industries Association | Basic robotics assembly and programming | Beginner |
| ROS Development Course | Open Robotics / Udemy | Robot Operating System, simulation, control | Intermediate |
| AI & ML for Robotics Certification | Coursera / EdX | AI integration, deep learning, reinforcement learning | Intermediate/Advanced |
| PLC & Industrial Automation | Siemens / Rockwell | Industrial control systems and automation | Professional |
| Professional Robotics Engineer | IEEE / Robotics Cbertification Board | Advanced system design, AI, and leadership | Expert |
Tip: Begin with foundational courses and gradually progress to specialized certifications.
4. Academic & Skill Pathway
- Undergraduate Degree: Mechanical, Electrical, Electronics, Mechatronics, or Computer Science.
- Hands-on Projects: Arduino, Raspberry Pi, ROS, and AI-driven robotics.
- Internships: Gain practical experience in industrial, healthcare, or service robotics.
- Graduate Studies (Optional): Specialization in robotics, AI, control systems, or biomedical robotics.
- Continuous Learning: Online courses, workshops, and research publications.
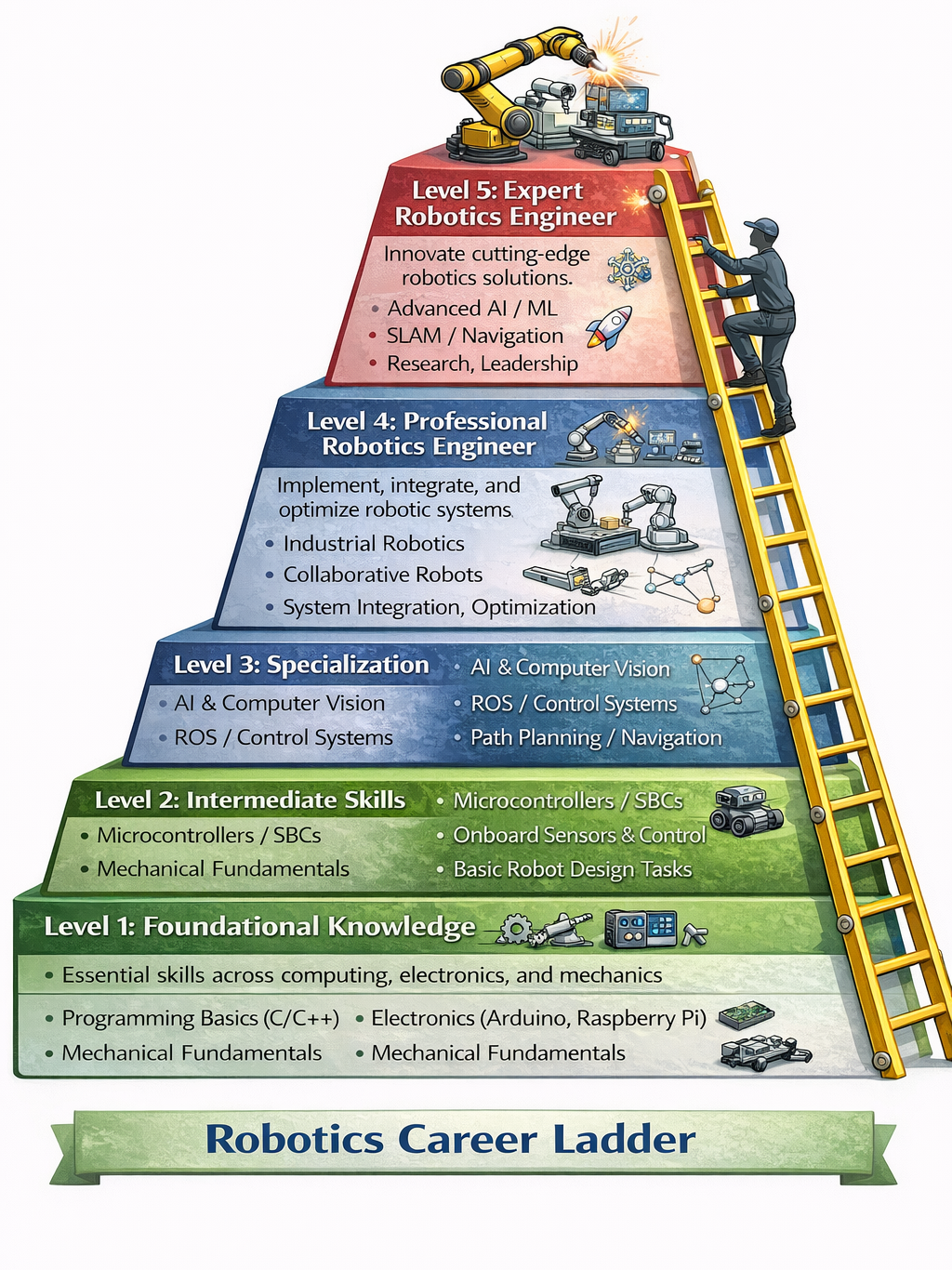
Diagram Idea: Robotics career ladder showing foundational knowledge → intermediate skills → specialization → professional → expert level.
5. Key Skills by Industry
| Industry | Core Skills Required | Recommended Tools / Platforms |
| Industrial Automation | PLC, industrial robots, ROS, sensors | Siemens, ABB, ROS, Gazebo |
| Healthcare Robotics | Surgical systems, AI, SLAM, telepresence | da Vinci, ROS, Python, TensorFlow |
| Autonomous Vehicles | Path planning, AI, LiDAR, SLAM | ROS, Python, C++, OpenCV |
| Service & Hospitality | Human-robot interaction, AI, NLP | ROS, NLP frameworks, simulation tools |
| Research & Development | AI, ML, simulation, experimental design | MATLAB, ROS, Gazebo, AI frameworks |
6. Tips for Becoming a Professional Robotics Engineer
- Master Programming Languages: C++, Python, MATLAB.
- Gain Expertise in ROS: Learn simulation, motion planning, and sensor integration.
- Hands-On Projects: Build mobile robots, manipulator arms, and AI-integrated systems.
- Specialize: Choose industrial, healthcare, autonomous, or service robotics.
- Certifications: Validate knowledge with recognized credentials.
- Networking & Community: Attend workshops, webinars, and robotics competitions.
- Stay Updated: Follow robotics journals, blogs, and industry trends.
CuriosityTech.in offers practical projects, certification guidance, and skill development tutorials for aspiring robotics engineers.
7. Emerging Roles in Robotics
- AI Robotics Engineer: Focused on machine learning and autonomous decision-making.
- Robotics System Architect: Designs integrated robotic systems.
- Human-Robot Interaction Designer: Focused on usability and ergonomics.
- Industrial Automation Specialist: Implements factory robotics and optimization.
- Healthcare Robotics Specialist: Develops surgical, diagnostic, or rehabilitation robots.
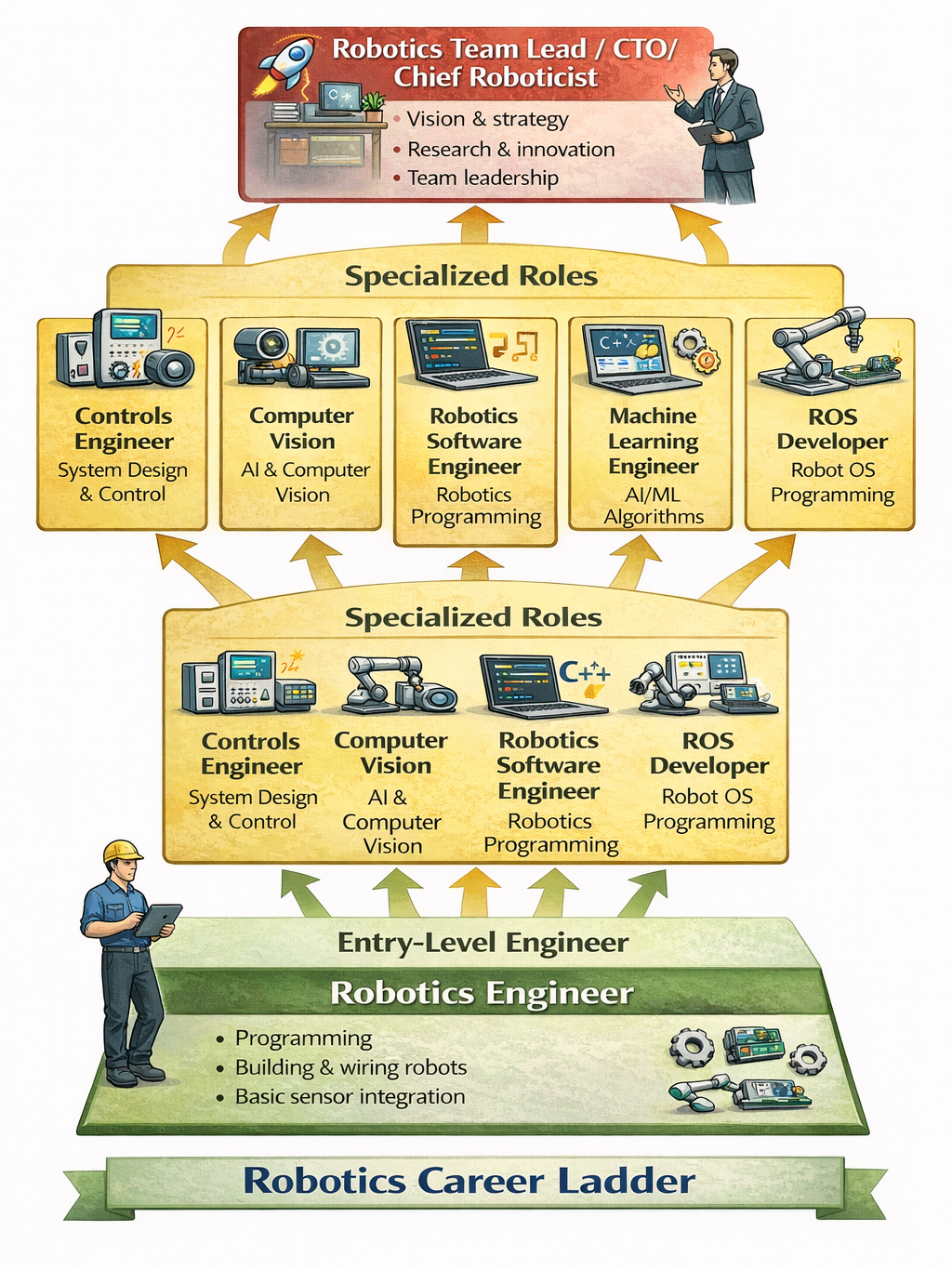
Diagram Idea: Career flowchart from entry-level engineer → specialized roles → expert/leadership positions.
8. Challenges in a Robotics Career
- Rapid technological changes require continuous learning.
- Multidisciplinary knowledge can be overwhelming for beginners.
- Hands-on experience is essential but requires access to labs or simulation tools.
- Competition is high, demanding innovation and problem-solving skills.
Tip: Combine theoretical knowledge with project-based learning to stand out in the job market.
Conclusion
A career in robotics engineering offers diverse opportunities across multiple industries, from industrial automation to healthcare and autonomous systems. By following a structured career path, acquiring certifications, hands-on experience, and multidisciplinary skills, engineers can excel in this dynamic field. Platforms like CuriosityTech.in provide guidance, tutorials, project support, and certification preparation to empower learners for successful robotics careers.