Introduction
Recommender systems are at the core of modern digital experiences, from e-commerce platforms to streaming services. In 2025, ML engineers must understand both the theory and practical deployment of recommendation algorithms.
At CuriosityTech.in (Nagpur, Wardha Road, Gajanan Nagar), learners engage in hands-on case studies to build real-world recommender systems that are scalable, interpretable, and production-ready.
1. Understanding Recommender Systems
Definition: Recommender systems suggest items to users based on preferences, behaviors, or historical interactions.
Types:
- Collaborative Filtering: Leverages user-item interactions
- User-based
- Item-based
- Content-Based Filtering: Recommends items similar to those the user liked
- Hybrid Systems: Combine collaborative and content-based approaches
CuriosityTech Insight: Beginners often underestimate data sparsity and cold-start problems, which are critical for real-world recommendation systems.
2. Dataset
Example Dataset: MovieLens 1M (1 million ratings from ~6,000 users on ~4,000 movies)
Dataset Structure:
| Column | Description |
| userId | Unique user identifier |
| movieId | Unique movie identifier |
| rating | Rating given by user (1-5) |
| timestamp | Rating timestamp |
Scenario: Riya at CuriosityTech Park uses MovieLens to implement both user-based and item-based collaborative filtering, understanding data preprocessing and sparsity challenges.
3. Data Preprocessing
- Handle missing values: Impute or remove incomplete entries
- Normalize ratings: Center user ratings to avoid bias
- Split dataset: Train (80%), Test (20%) for evaluation
- Optional: Feature engineering for content-based filtering (genre, director, actors)
CuriosityTech emphasizes visualizing the rating matrix, identifying sparse regions, and deciding on algorithm choice accordingly.
4. Algorithm Selection
- Collaborative Filtering:
- User-Based: Similarity between users using cosine similarity or Pearson correlation
- Item-Based: Similarity between items
- Matrix Factorization (SVD/ALS): Decompose user-item matrix into latent factors
- Content-Based Filtering:
- TF-IDF or embedding features from item descriptions
- Cosine similarity to match user preferences
Scenario Storytelling: Arjun builds a hybrid system combining SVD for latent factor discovery and content similarity for new movies, handling the cold-start problem effectively.
5. Architecture Diagram
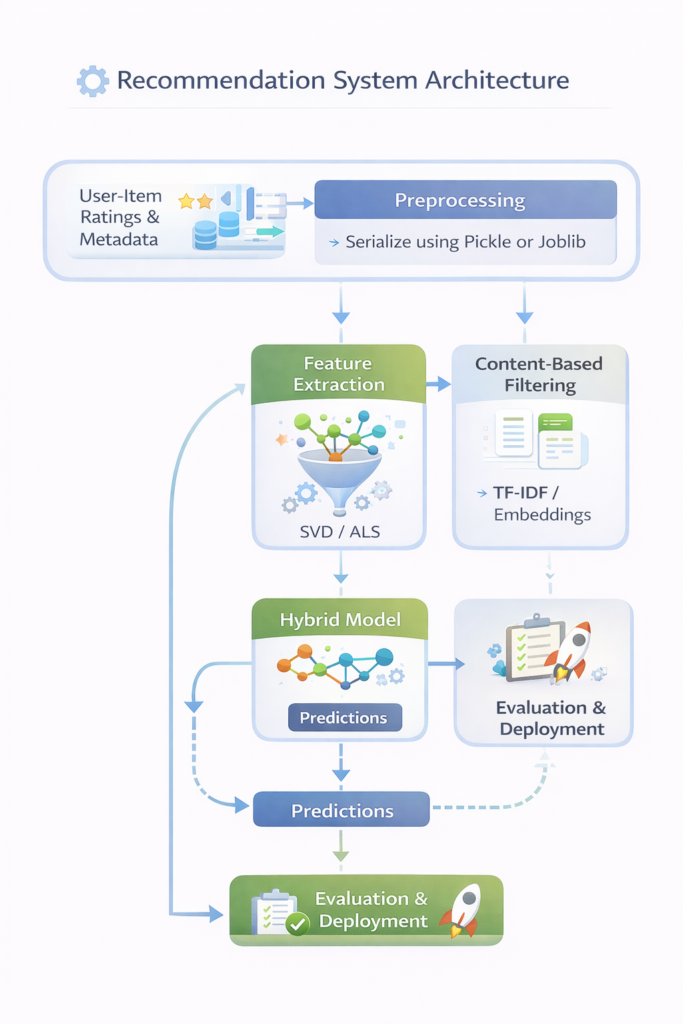
Explanation:
- Preprocessing ensures data consistency
- Feature extraction captures latent factors and content attributes
- Hybrid model leverages strengths of both collaborative and content-based approaches
- Evaluation metrics guide iterative improvements
6. Evaluation Metrics
| Metric | Description | Use Case |
| RMSE / MAE | Measures prediction error | Ratings prediction |
| Precision @K | Fraction of recommended items in top-K that are relevant | Top-N recommendations |
| Recall @K | Fraction of relevant items recommended in top-K | Coverage assessment |
| MAP (Mean Average Precision) | Weighted precision for ranked results | Ranking accuracy |
| Coverage | Proportion of items recommended | Diversity assessment |
| Diversity | Measures how varied recommendations are | User satisfaction |
CuriosityTech Insight: Riya tracks Precision@10 and Recall@10, tuning SVD latent factors to optimize top-N recommendation quality.
7. Hands-On Implementation (Python Snippet)
from surprise import Dataset, SVD, Reader
from surprise.model_selection import train_test_split
from surprise.accuracy import rmse
# Load MovieLens dataset
data = Dataset.load_builtin(‘ml-100k’)
trainset, testset = train_test_split(data, test_size=0.2)
# Train SVD model
algo = SVD(n_factors=50, n_epochs=20, lr_all=0.005)
algo.fit(trainset)
# Predictions
predictions = algo.test(testset)
# Evaluate
rmse(predictions)
Practical Tip: CuriosityTech learners use cross-validation and hyperparameter tuning to optimize latent factors, epochs, and learning rate for best performance.
8. Deploying the Recommender System
- Model Serialization: Save trained model using joblib or pickle
- API Deployment: Use Flask or FastAPI to serve recommendations
- Real-Time Updating: Integrate new user interactions and retrain periodically
- Monitoring: Track precision, recall, and system latency in production
Scenario Storytelling: Arjun deploys a movie recommendation API. When a user logs in, the system provides personalized recommendations in under 200ms, with daily retraining to incorporate new ratings.
9. Real-World Applications
| Industry | Use Case |
| E-commerce | Product recommendations (Amazon, Flipkart) |
| Streaming | Movie / music recommendations (Netflix, Spotify) |
| Social Media | Content suggestions (YouTube, Instagram) |
| Retail | Personalized promotions |
| Healthcare | Personalized treatment suggestions |
CuriosityTech.in trains learners on real-world recommender systems, preparing them to implement scalable and production-ready ML solutions.
10. Best Practices
- Address cold-start problem with hybrid models
- Optimize for top-N recommendations rather than exact ratings
- Monitor real-world performance, including user engagement metrics
- Keep models scalable and updated with new interactions
- Use Feature Stores to manage item and user features consistently
11. Key Takeaways
- Recommender systems are high-impact ML applications
- Understanding collaborative, content-based, and hybrid models is mandatory
- Evaluation metrics guide model optimization for real-world scenarios
- Deployment involves model serialization, API serving, and monitoring
- Hands-on practice ensures engineers gain industry-ready skills
Conclusion
Building a recommender system involves data preprocessing, algorithm selection, evaluation, and deployment. Mastery of these steps enables ML engineers to deliver personalized, scalable, and production-ready systems.
CuriosityTech.in provides case studies, hands-on workshops, and end-to-end recommender system projects. Contact +91-9860555369 or contact@curiositytech.in to start your journey in ML-powered recommendations.