As organizations worldwide continue to migrate to the cloud, Amazon Web Services (AWS) stands out as a dominant platform offering a vast ecosystem of services. Understanding the core AWS services is the foundation for anyone aiming to become proficient in cloud computing. Welcome to Day 2 of our AWS learning journey, where we explore four critical services: EC2, S3, RDS, and Lambda. This blog will provide an in-depth exploration, with practical insights, best practices, and guidance to help beginners evolve into experts.
At Curiosity Tech., our mission is to bridge the gap between theoretical understanding and hands-on mastery. Through training, real-world projects, and consultation, we empower learners to leverage AWS for secure, scalable, and cost-effective solutions.
Understanding AWS Core Services
AWS provides over 200 fully-featured services, but EC2, S3, RDS, and Lambda are the pillars upon which many applications are built. Let’s break them down:
| Service | Purpose | Use Case |
| EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud) | Virtual servers in the cloud | Running applications, hosting websites, scalable computing |
| S3 (Simple Storage Service) | Object storage with high durability | Storing files, backups, data lakes, media content |
| RDS (Relational Database Service) | Managed relational databases | MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, or SQL Server databases without server management |
| Lambda | Serverless computing | Event-driven applications, automations, real-time file processing |
EC2 – The Backbone of Cloud Computing
Amazon EC2 is a service that provides scalable virtual servers, allowing businesses to deploy applications without investing in physical hardware. EC2’s flexibility is unmatched:
- Instance Types: EC2 offers a range of instance types designed for different workloads, from general-purpose and compute-optimized to memory-intensive and GPU-powered instances. Understanding which instance type suits your workload is critical for cost optimization and performance.
- Elasticity: EC2 allows automatic scaling to meet traffic demands, making it ideal for startups experiencing unpredictable user loads or enterprises managing global applications.
- Security & Access: EC2 instances integrate seamlessly with IAM roles, VPCs, and Security Groups, ensuring both network-level and identity-based security.
Example: A media streaming platform can run EC2 instances with GPU-optimized types for video transcoding while dynamically scaling based on user demand.
S3 – Storage Without Limits
Amazon S3 provides object storage that is durable, scalable, and highly available. Unlike traditional storage, S3 handles petabytes of data efficiently:
- Durability: AWS guarantees 99.999999999% durability (11 nines) for stored objects, making it suitable for critical backups and archival.
- Storage Classes: Standard, Intelligent-Tiering, Glacier, and Deep Archive allow cost optimization based on access patterns.
- Data Management: Versioning, lifecycle policies, and replication features help maintain data integrity and compliance.
Example: An e-commerce company can store product images, customer data, and order histories in S3, integrating with EC2 and Lambda for processing and analytics.
RDS – Managed Relational Databases
Amazon RDS simplifies database management, freeing developers from administrative burdens:
- Supported Engines: MySQL, PostgreSQL, MariaDB, Oracle, and SQL Server.
- Automatic Management: Backup, patching, scaling, and replication are automated.
- High Availability: Multi-AZ deployments ensure fault tolerance and disaster recovery.
Example: A fintech startup can use RDS for transactional data storage, ensuring consistency and high availability without managing database servers manually.
Lambda – Event-Driven, Serverless Computing
AWS Lambda revolutionizes the way applications are built by removing the need to manage servers:
- Event Triggers: Lambda functions can respond to events in S3, DynamoDB, Kinesis, or HTTP endpoints.
- Cost-Efficiency: Pay only for execution time, not idle resources.
- Scalability: Automatically scales to handle thousands of concurrent events without manual intervention.
Example: Automatically resize images uploaded to S3 using Lambda functions or process IoT sensor data in real-time.
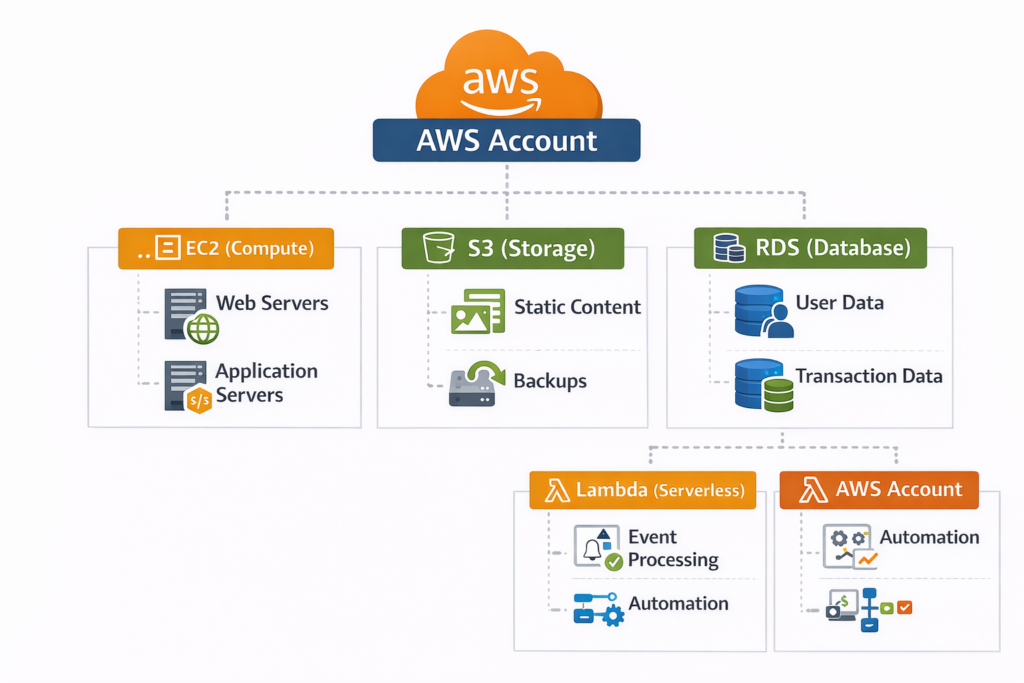
AWS Services Hierarchy & Interaction
Understanding how these services interact is essential for designing robust cloud solutions. Below is a conceptual hierarchy diagram:
Becoming an AWS Expert
Mastering AWS services requires more than theoretical knowledge:
- Hands-On Practice: Launch EC2 instances, upload data to S3, configure RDS databases, and implement Lambda triggers.
- Integration Knowledge: Learn how services interact, e.g., S3 triggering Lambda functions or EC2 connecting to RDS.
- Best Practices: Implement security best practices, cost optimization strategies, and automated monitoring.
- Continuous Learning: AWS constantly innovates; staying updated with new features and services is key.
At Curiosity Tech, we provide hands-on labs, structured training, and real-world projects to accelerate this learning curve, helping learners gain confidence and practical expertise.
Infographic & Visual Concepts
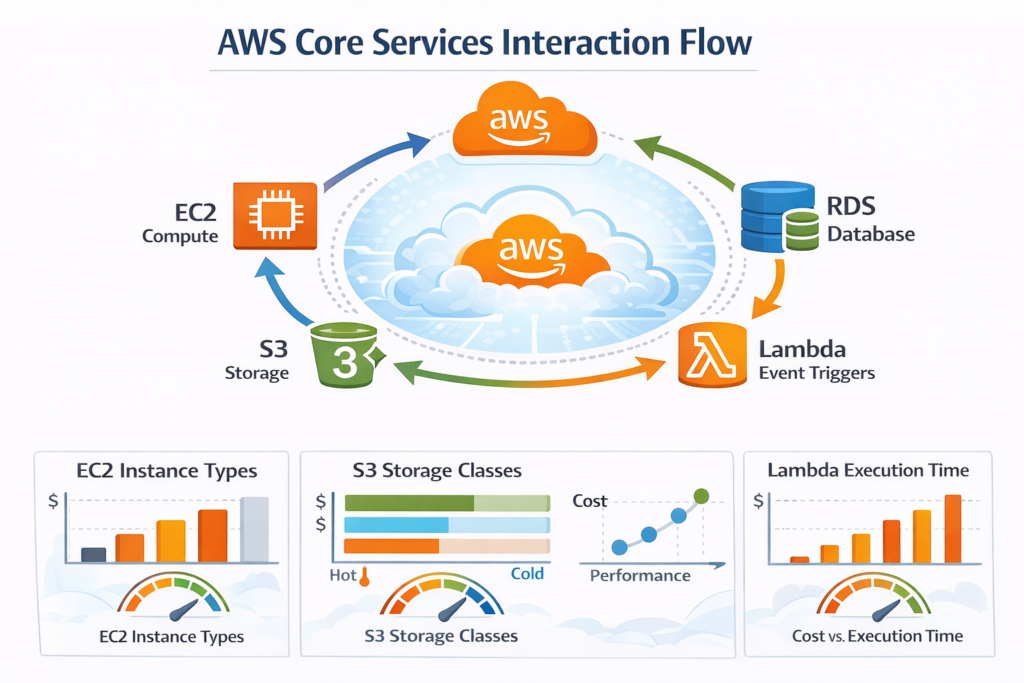
- Infographic Idea: “AWS Core Services Interaction Flow” showing EC2, S3, RDS, and Lambda in a circular workflow, with arrows indicating data flow and triggers.
- Abstraction Image: Cloud architecture abstraction showing EC2 as compute layer, RDS as database layer, S3 as storage layer, and Lambda connecting events seamlessly.
- Tables & Charts: Cost vs. performance comparison of EC2 instance types, S3 storage classes, and Lambda execution times.
These visual aids enhance understanding and make complex concepts digestible for beginners.
Conclusion
AWS EC2, S3, RDS, and Lambda form the backbone of modern cloud solutions. By understanding their features, use cases, and integration patterns, beginners can build secure, scalable, and cost-effective applications. Mastery comes from a mix of conceptual knowledge, hands-on practice, and continuous learning.
Curiosity Tech is committed to empowering learners and enterprises with the skills needed to excel in cloud computing. Through immersive training, live projects, and expert guidance, anyone can evolve from a beginner to an AWS proficient professional, ready to tackle real-world challenges confidently.