Introduction
Managing costs efficiently in the cloud is crucial for both startups and large enterprises. Azure provides Cost Management and Billing tools to monitor, analyze, and optimize cloud expenditure. Understanding cost drivers, setting budgets, and implementing optimization strategies can reduce waste, improve ROI, and enable sustainable cloud adoption.
At curiosity tech, learners get hands-on experience analyzing real-world cloud costs, applying optimization strategies, and creating cost-efficient architectures.
1. Understanding Azure Cost Management
Azure Cost Management enables engineers to:
- Monitor Spending: Track costs by subscription, resource group, or department
- Analyze Usage: Identify underutilized resources
- Forecast Costs: Predict monthly and yearly spend
- Set Budgets: Alert when spending exceeds thresholds
Diagram: Azure Cost Management Workflow
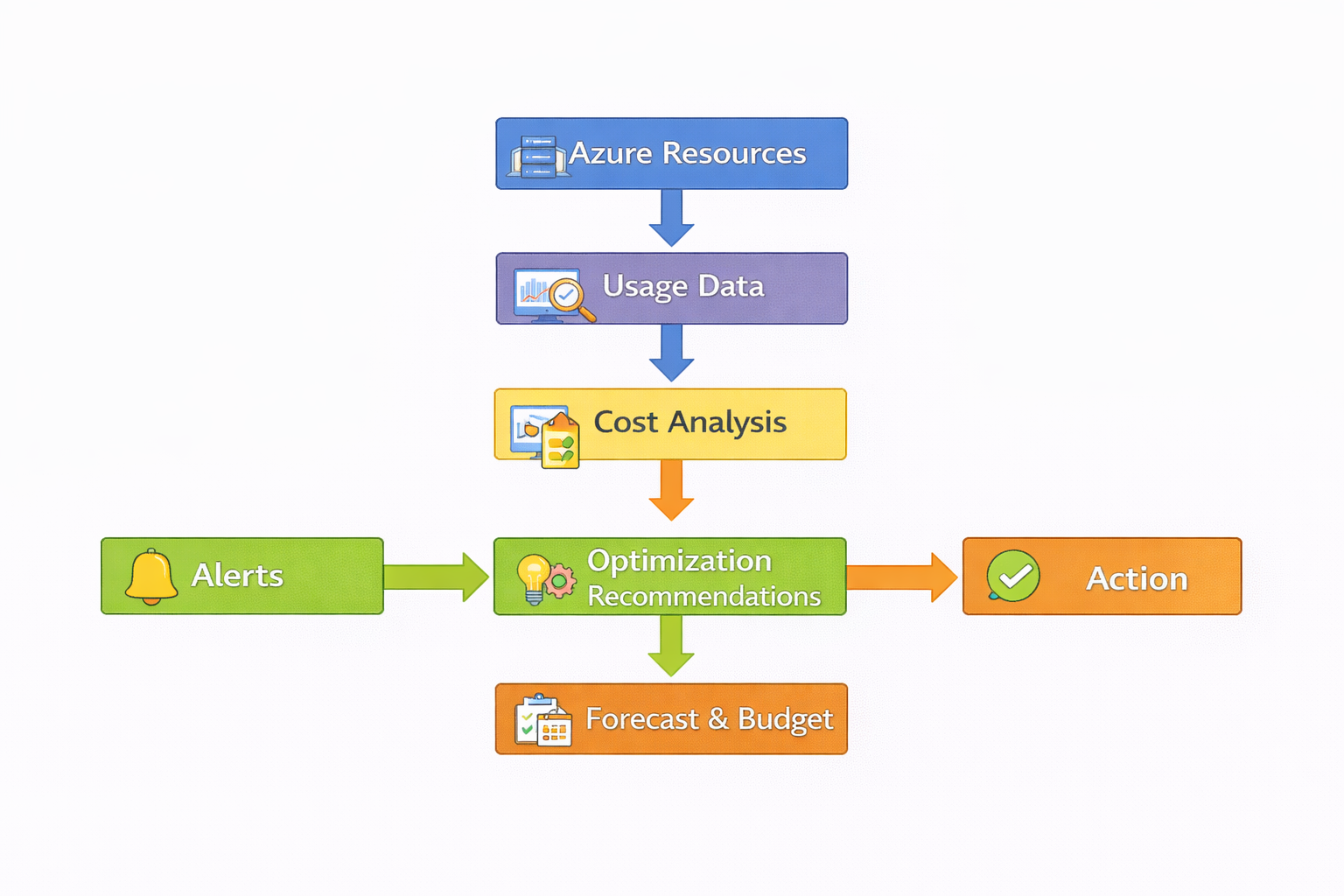
2. Key Components
| Component | Description |
| Cost Analysis | Visualize current and historical costs |
| Budgets & Alerts | Create budgets, receive notifications |
| Recommendations | Suggests rightsizing, reserved instances, and discounts |
| Cost Allocation | Assign costs to departments, projects, or teams |
| Export & API | Export usage and cost data for external analysis |
Insight: Properly categorizing resources and departments allows better accountability and transparency in cloud spending.
3. Common Cost Drivers in Azure
- Compute Resources: Virtual Machines, AKS clusters, App Services
- Storage Costs: Blob, SQL Database, Managed Disks
- Networking: Bandwidth, Load Balancers, VPN Gateway
- Licensing: Windows VMs, SQL Server licenses
- Underutilized or Idle Resources: Stopped VMs, unused storage accounts
Scenario Example:
A mid-sized company noticed high costs due to idle VMs and over-provisioned SQL databases. By applying Azure Cost Management recommendations, they reduced compute spend by 30%.
4. Step-by-Step: Setting Up Cost Management
1: Access Cost Management
- Azure Portal → Cost Management + Billing → Cost Analysis
2: Analyze Costs
- View costs by subscription, resource group, or service
- Filter by time period, location, or tags
3: Set Budgets & Alerts
- Create budget → Set threshold (e.g., 80% of expected monthly spend)
- Configure alerts → Email, Teams, or webhook
4: Review Recommendations
- Azure Advisor suggests :-
- Right-sizing VMs.
- Deleting idle resources
- Switching to reserved instances or savings plans.
5: Optimize Resources
- Implement scaling policies for App Service or AKS
- Automate shutdown of non-production VMs after business hours
- Use auto-tiering for storage to reduce costs
5. Optimization Checklist for Cloud Engineers
| Area | Optimization Action |
| Compute | Use auto-scaling, spot VMs, or reserved instances |
| Storage | Tier blobs, delete unused disks, use lifecycle policies |
| Networking | Optimize bandwidth usage, consolidate gateways |
| Databases | Right-size SQL, pause unused databases, enable auto-scaling |
| Governance | Tag resources, enforce budgets, audit usage |
6. Practical Example: E-Commerce Platform Cost Optimization
Scenario:- A SaaS e-commerce platform was running:
- 10 Standard VMs for backend
- 5 App Service instances for frontend
- SQL Database in Premium tier
Optimization Steps:
- Scale backend VMs during peak hours → reduces idle compute
- Switch SQL Database to vCore-based auto-scaling tier
- Enable Blob storage tiering for archived files
- Configure budget alerts → notify finance team at 70%, 90%, and 100%
Result: Monthly costs reduced by 25–35%, with no compromise on performance or availability.
Diagram: Cost Optimization Flow:
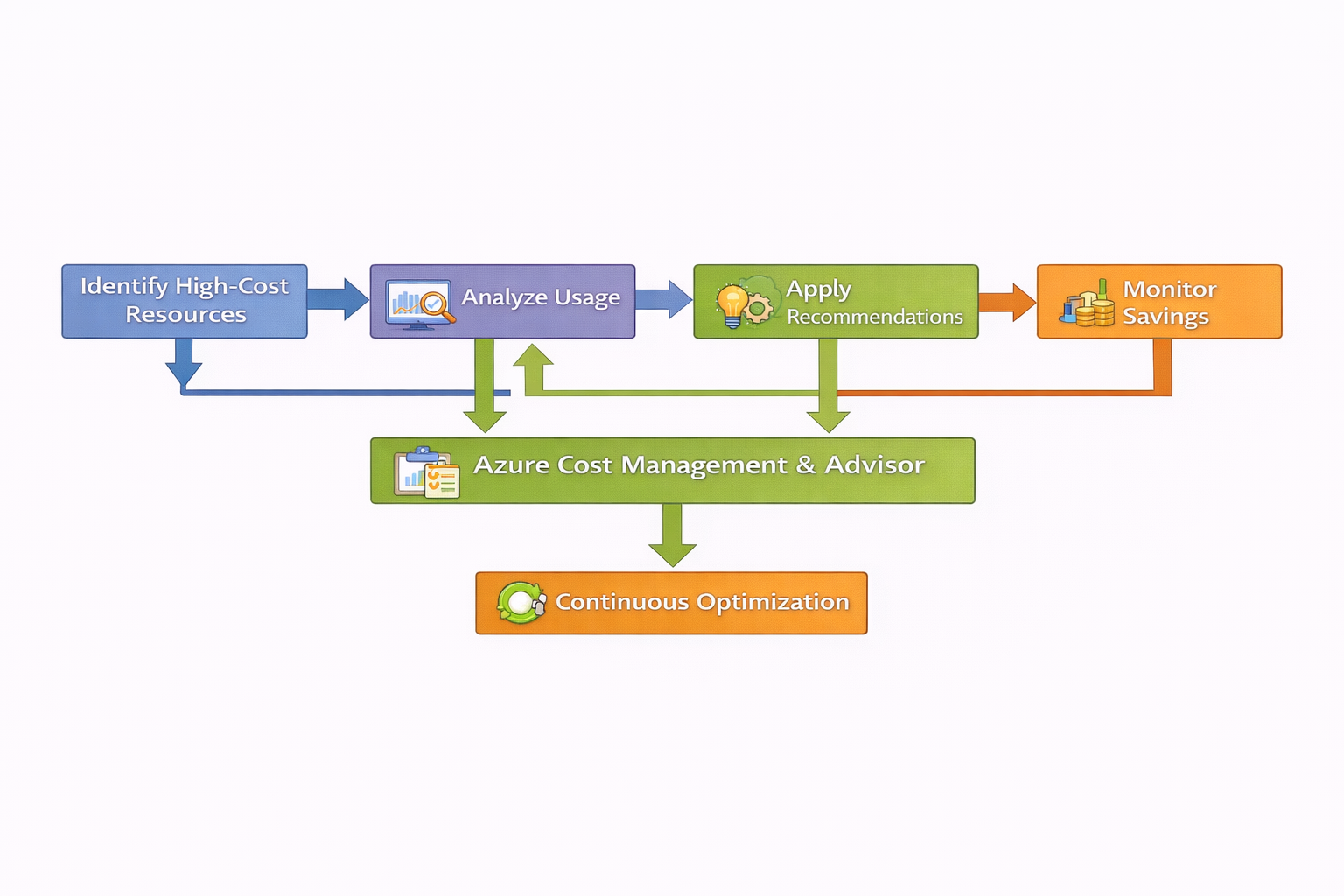
7. Advanced Tips for Expertise
- Use Azure Pricing Calculator: Plan future architecture costs
- Implement Tags Strategically: Assign department, project, or environment
- Reserved Instances & Savings Plans: Prepay for predictable workloads
- Automate Cost Governance: Combine budgets, alerts, and automation scripts
- Continuous Monitoring: Review cost trends weekly, adjust as needed
At curiositytech, learners simulate enterprise-level cost management scenarios, making them adept at real-world cloud budgeting and optimization strategies.
Conclusion
Azure Cost Management empowers cloud engineers to monitor, analyze, and optimize cloud expenditure, ensuring efficient resource usage and cost savings. By following budgeting, monitoring, and optimization best practices, engineers can maintain scalable, high-performing applications at minimal cost. Hands-on labs at curiosity tech equip learners with practical experience to master cost management and optimization.



