In modern DevOps environments, maintaining continuous service availability and quick recovery from failures is essential. Organizations running cloud-native applications benefit from implementing High Availability (HA) and Disaster Recovery (DR) strategies to enhance reliability and resilience. At Curiosity Tech, we help engineers learn how to design HA architectures, plan DR strategies, and set up failover pipelines across multi-cloud and on-premise systems.
Understanding High Availability (HA)
High Availability ensures that applications and services remain operational even in the face of failures. Key aspects:
- Redundancy: Duplicate critical components to prevent single points of failure.
- Failover Mechanisms: Automatic or manual switching to backup systems.
- Load Balancing: Distribute traffic to ensure no server is overwhelmed.
- Monitoring & Alerts: Detect failures and performance degradation proactively.
HA is measured as uptime percentage, typically expressed as “nines” (e.g., 99.99% uptime)
High Availability Architecture Diagram
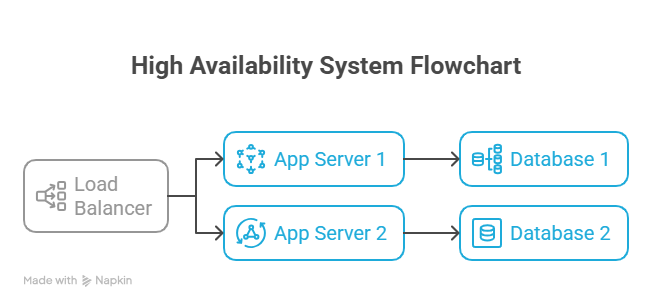
HA is measured as uptime percentage, typically expressed as “nines” (e.g., 99.99% uptime)
Understanding Disaster Recovery (DR)
Disaster Recovery refers to the strategies and processes used to restore services after catastrophic failures, such as:
- Natural disasters (earthquake, flood)
- Cyberattacks or ransomware
- Regional cloud outages
DR focuses on:
- Recovery Point Objective (RPO) – How much data loss is acceptable.
- Recovery Time Objective (RTO) – How quickly services must be restored.
- Backup & replication strategies – Local, cross-region, or multi-cloud.
Disaster Recovery Tiers
DR Tier | Description | RPO | RTO |
| Tier 0 | Zero downtime, instant failover | 0 | Seconds |
| Tier 1 | Hot standby, full replication | Minutes | Minutes |
| Tier 2 | Warm standby, partial replication | Hours | Hours |
| Tier 3 | Cold standby, offline backup | Days | Days |
At Curiosity Tech, learners practice implementing Tier 1 and Tier 2 DR strategies using AWS, Azure, and GCP.
Multi-Cloud HA & DR Strategy
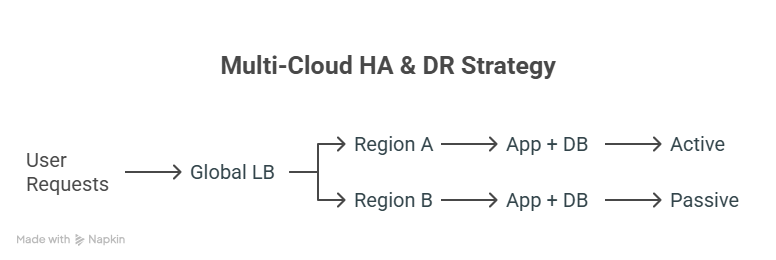
Explanation: Traffic is directed to the active region. If Region A fails, Region B takes over automatically, ensuring zero to minimal downtime.
Key Strategies for HA & DR in DevOps
| Strategy | Explanation |
| Automated CI/CD Pipelines | Deploy to multiple regions with version control and rollback capabilities |
| Infrastructure as Code (IaC) | Terraform, CloudFormation, or ARM templates to provision redundant resources consistently |
| Cross-Region Replication | Database and storage replication across cloud regions to prevent data loss |
| Load Balancing & Auto-Scaling | Dynamically distribute traffic and scale instances during failures |
| Monitoring & Alerts | Proactively detect outages using Prometheus, Grafana, CloudWatch, or Azure Monitor |
| Backup Management | Scheduled snapshots, encrypted storage, and versioned backups |
Practical Implementation Example
Scenario: Deploying a mission-critical web application with HA & DR
- Infrastructure: Deploy app servers and databases in two AWS regions.
- Load Balancer: Route traffic to primary region; failover to secondary region if primary fails.
- Database Replication: Use RDS cross-region read replicas for redundancy.
- CI/CD Integration: Jenkins pipelines deploy application updates to both regions automatically.
- Monitoring & Alerts: Prometheus monitors latency, error rate, and resource utilization; Grafana dashboards visualize health.
- Disaster Recovery Drill: Simulate regional outage and measure RTO and RPO to ensure DR plan is effective.
Challenges in HA & DR
| Challenge | Solution |
| Regional Cloud Failures | Use multi-region deployments with automated failover |
| Data Consistency Across Regions | Implement replication strategies with eventual consistency or conflict resolution |
| Cost Management | Optimize standby resources; use auto-scaling and spot instances where applicable |
| Testing DR Plans | Conduct regular drills and simulate outages |
Conclusion
High Availability and Disaster Recovery are essential pillars of modern DevOps environments. HA ensures continuous service uptime, while DR enables rapid recovery after catastrophic failures.
At Curiosity Tech, learners implement HA and DR strategies in multi-cloud environments, integrate CI/CD automation, and monitor system reliability with Prometheus and Grafana. This hands-on approach ensures that engineers are prepared to design resilient, scalable, and fault-tolerant applications for enterprise workloads.