Introduction
MERN Stack interviews are comprehensive, covering frontend, backend, database, API design, security, performance, and deployment. Preparation is not just about memorizing answers; it’s about understanding concepts, articulating solutions, and demonstrating real-world project experience.
CuriosityTech.in emphasizes practical interview guidance, helping developers become confident, articulate, and industry-ready.
50 Most Important MERN Stack Interview Questions & Answers
1. What is MERN Stack and why is it popular?
Ans :- MERN stands for MongoDB, Express.js, React.js, and Node.js. It is a full-stack JavaScript framework enabling developers to use a single language for frontend and backend, streamlining development. MongoDB provides a flexible NoSQL database, Express.js handles server-side logic, React.js manages interactive UIs, and Node.js executes backend code efficiently. Its popularity stems from speed, scalability, strong community support, and modern web development trends.
2. Explain the difference between SQL and NoSQL databases.
Ans :- SQL databases are relational, store structured data in tables with defined schemas, and support ACID transactions. NoSQL databases, like MongoDB, are non-relational, store unstructured or semi-structured data, allow dynamic schemas, and are scalable horizontally. MERN uses MongoDB for its flexibility, rapid development, and ability to handle large-scale data efficiently.
3. What are the advantages of using Node.js?
Ans :- Node.js provides non-blocking, event-driven architecture, allowing high-performance server-side operations. It uses JavaScript on the backend, enabling full-stack development with a single language, has a rich NPM ecosystem, supports scalable applications, and is ideal for real-time applications like chat apps and collaborative platforms.
4. Explain the role of Express.js in MERN.
Ans :- Express.js is a lightweight web framework for Node.js. It simplifies routing, middleware integration, and API development. It allows developers to handle HTTP requests, implement RESTful APIs, manage sessions, and secure endpoints, acting as the bridge between the frontend and MongoDB database.
5. What are the key features of React.js?
Ans :- React.js is a component-based UI library. Key features include JSX syntax, virtual DOM for efficient rendering, hooks for state management, reusable components, and unidirectional data flow. React enables building interactive, responsive, and scalable user interfaces.
6. Explain the virtual DOM in React.
Ans :- The virtual DOM is a lightweight JavaScript representation of the real DOM. When state changes, React updates the virtual DOM first, compares it with the previous version using diffing algorithms, and applies minimal updates to the real DOM. This process improves performance and ensures efficient UI rendering.
7. What are React hooks?
Ans :- Hooks are functions that allow functional components to use state and lifecycle features. Common hooks include useState for state management, useEffect for side effects, useMemo for memoization, and useCallback for optimizing function references. Hooks replace class component complexities and enhance code readability.
8. How do you handle state management in React?
Ans :- State management can be local (useState, useReducer) or global (Redux, React Context, Zustand, or React Query). Redux Toolkit is preferred for large applications, providing predictable state updates, middleware integration, and debugging tools.
9. What is JSX?
Ans :- JSX is JavaScript XML, a syntax extension allowing developers to write HTML-like code within JavaScript. It is transpiled by Babel into standard JavaScript, combining UI structure and logic seamlessly.
10. Explain Node.js event loop.
Ans :- The event loop allows Node.js to perform non-blocking I/O operations. It continuously checks the call stack and callback queue. When asynchronous operations complete, their callbacks are pushed to the call stack, enabling Node.js to handle thousands of concurrent requests efficiently.
11. Difference between synchronous and asynchronous code in Node.js.
Ans :- Synchronous code executes line by line, blocking the event loop until completion. Asynchronous code uses callbacks, promises, or async/await to perform operations in the background, improving performance by not blocking the main thread.
12. Explain REST API and its principles.
Ans :- REST (Representational State Transfer) is an architectural style for designing networked applications. It uses stateless, cacheable HTTP requests and defines CRUD operations via standard HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE). REST ensures scalable and maintainable API design.
13. Difference between REST and GraphQL.
Ans :- REST uses multiple endpoints for resources, which can lead to over-fetching. GraphQL has a single endpoint, allowing clients to fetch only required fields. GraphQL is flexible and type-safe, while REST is simpler and widely supported.
14. How do you connect React frontend with Node.js backend?
Ans :- Typically, Axios or Fetch API is used in React to make HTTP requests to Node.js endpoints. Backend routes return JSON data, which React consumes and updates the UI dynamically. CORS configuration ensures secure cross-origin communication.
15. Explain JWT authentication.
Ans :- JWT (JSON Web Token) is a stateless authentication mechanism. On login, the server generates a token containing user info, signed with a secret key. The client stores it (localStorage/cookies) and sends it with API requests for verification. It’s secure, scalable, and widely used in MERN applications.
16. How do you secure a MERN application?
Ans :- Security involves password hashing (bcrypt), JWT authentication, input validation, HTTPS, CORS policies, Helmet headers, and database role-based access. Additionally, CSRF protection, XSS prevention, and rate limiting safeguard against common attacks.
17. What is CORS and why is it important?
Ans :- CORS (Cross-Origin Resource Sharing) is a security feature in browsers that restricts requests to different domains. Configuring CORS in Express ensures that frontend applications can securely interact with backend APIs without exposing vulnerabilities.
18. Explain CRUD operations in MERN.
Ans :- CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) is the foundation of data management. MongoDB stores the data, Express.js provides endpoints, Node.js handles logic, and React consumes APIs to render UI updates dynamically.
19. How do you implement file uploads in MERN?
Ans :- Use Multer middleware in Express to handle multipart/form-data uploads. Files are stored in server directories or cloud storage (AWS S3, Cloudinary), with URLs saved in MongoDB for frontend access.
20. What are web sockets, and how do you use them in MERN?
Ans :- WebSockets enable real-time, bi-directional communication between client and server. Socket.IO is commonly used in MERN apps for chat, notifications, and live updates.
21. Explain Redux and its benefits.
Ans :- Redux is a predictable state container for JavaScript apps. It centralizes the app state, making it easier to debug, test, and maintain large applications. Redux Toolkit simplifies boilerplate and integrates middleware efficiently.
22. What is the difference between local and global state?
Ans :- Local state is component-specific (useState), while global state affects multiple components (Redux, Context API). Global state is essential for authentication, theming, and shared data.
23. How do you optimize performance in MERN apps?
Ans :- Frontend: lazy loading, memoization, virtual DOM, image optimization
Backend: async operations, caching, connection pooling
Database: indexes, query optimization, pagination
Network: CDN, compression, HTTP/2, caching headers
24. Explain how to deploy a MERN app.
Ans :- Build React using npm run build, serve static files in Express, configure environment variables, and deploy backend on Heroku, AWS EC2, or Vercel. Connect MongoDB Atlas or cloud database, implement SSL, and monitor performance.
25. How do you handle errors in Node.js?
Ans :- Use middleware for centralized error handling. Combine try/catch for async/await, return standardized responses, and log errors for monitoring.
26. What is the difference between useEffect and useLayoutEffect?
Ans :- useEffect runs after render, non-blocking the UI.
useLayoutEffect runs synchronously after DOM mutations, useful for measuring layout or animation adjustments.
27. How do you handle authentication in a single-page application?
Ans :- Use JWT tokens, session storage or cookies, and protect routes using React Router with authentication guards.
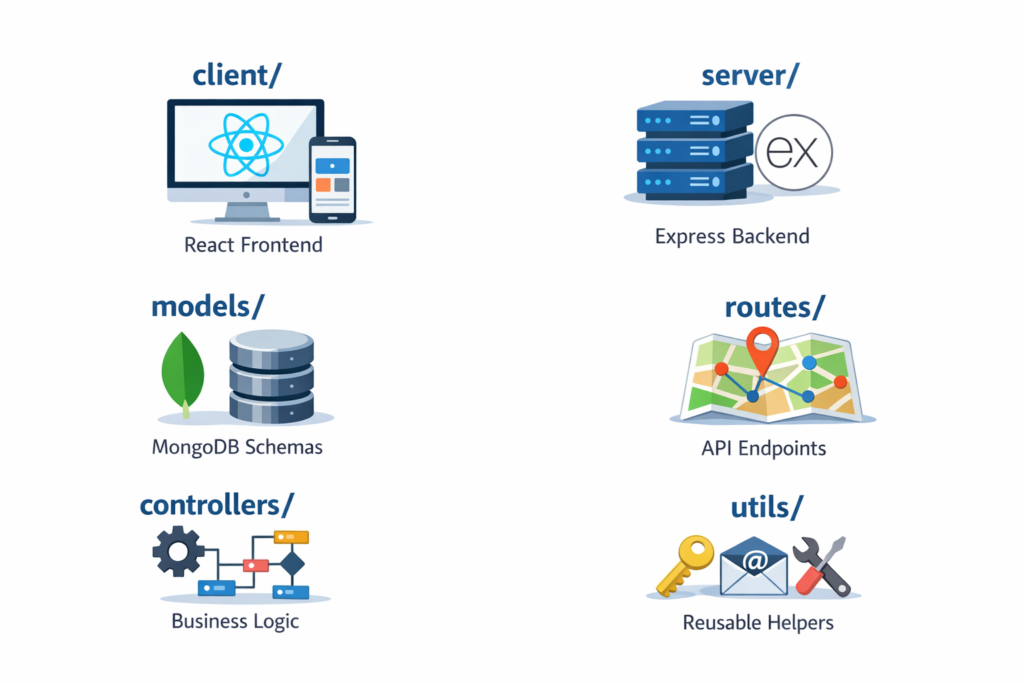
28. Explain the MERN stack folder structure best practices.
Ans :- Separate concerns:
- client/ → React frontend
- server/ → Express backend
- models/ → MongoDB schemas
- routes/ → API endpoints
- controllers/ → Business logic
- utils/ → Reusable helpers “
29. How do you implement search functionality?
Ans :- MongoDB supports text indexes, regex, or aggregation pipelines for search. Backend endpoints handle queries and filter results efficiently for frontend rendering.
30. How do you test MERN applications?
Ans :- Frontend: Jest + React Testing Library
Backend: Mocha, Chai, Supertest
Integration: Test APIs, authentication flows, and database interactions for reliability and robustness.
31. Explain aggregation in MongoDB.
Ans :- Aggregation pipelines allow data transformation and complex queries like filtering, grouping, sorting, and computing totals. It’s efficient for analytics and reporting in MERN apps.
32. How do you handle environment variables?
Ans :- Use .env files in development and platform-specific configuration for production (Heroku Config Vars, AWS Secrets Manager). Never commit secrets to Git.
33. Difference between MongoDB find() and findOne()?
Ans :- find() returns multiple documents in an array, while findOne() returns a single document. Both support filtering and projection but differ in result structure.
34. How do you implement pagination?
Ans :- Backend calculates skip and limit based on page number. Frontend sends requests with page and size parameters, ensuring efficient data retrieval for large datasets.
35. How do you secure REST APIs?
Ans :- Use authentication, authorization, rate limiting, input validation, HTTPS, and proper headers. Additionally, monitor and log requests to detect anomalies.
36. Explain difference between PUT and PATCH.
Ans :- PUT updates entire resource, replacing existing data. PATCH updates partial fields, modifying only what is necessary.
37. How do you optimize MongoDB queries?
Ans :-
- Create indexes on frequently queried fields
- Use projection to fetch only required fields
- Avoid $regex on large collections without indexes
- Use aggregation pipelines efficiently
38. Explain event-driven programming in Node.js.
Ans :- Node.js uses an event loop where events trigger callbacks asynchronously, allowing multiple operations to run without blocking, crucial for real-time apps and concurrency.
39. Difference between class and functional components in React.
Ans :- Class components have state and lifecycle methods, while functional components use hooks to manage state and side effects. Functional components are simpler, more readable, and preferred in modern React.
40. How do you manage CORS in MERN apps?
Ans :- Use the cors middleware in Express and configure allowed origins, methods, and headers. Ensures secure cross-domain communication.
41. Explain the difference between controlled and uncontrolled components.
Ans :- Controlled components have React state as the single source of truth, while uncontrolled components use the DOM directly. Controlled components allow better validation and consistency.
42. How do you implement search and filter in React?
Ans :- Use state for query input, filter data arrays in frontend, or send search queries to backend APIs for large datasets.
43. How do you prevent memory leaks in React?
Ans :-
- Cancel subscriptions and async operations in useEffect cleanup
- Avoid unnecessary component re-renders
- Use memoization for heavy computations
44. How do you implement role-based authorization?
Ans :- Assign roles in user models, check roles in middleware before granting access, and ensure endpoints are secured accordingly.
45. Difference between Node.js cluster and PM2.
Ans :- Node.js cluster module allows multi-core utilization, while PM2 provides process management, monitoring, and auto-restart features, making it suitable for production deployments.
46. How do you handle file uploads securely?
Ans :- Validate file type and size, store in secure directories or cloud, sanitize filenames, and prevent arbitrary path access.
47. Explain MERN app performance optimization techniques.
Ans :- Frontend: Lazy loading, virtual DOM, caching
Backend: Async operations, DB indexing, query optimization
Network: CDN, compression, HTTP/2
Monitoring: Logs, APM tools
48. How do you implement social login?
Ans :- Use OAuth2 with providers like Google, Facebook, or GitHub. Integrate passport.js strategies in Express and manage JWT tokens for session management.
49. How do you handle error reporting in MERN apps?
Ans :- Centralized error middleware in Express, logging to Sentry, Winston, or LogRocket, and returning user-friendly messages to frontend.
50. How do you become an expert MERN developer?
Ans :- Combine theoretical understanding with hands-on projects. Focus on end-to-end applications, adopt modern trends (Next.js, TypeScript, GraphQL), optimize performance and security, and deploy real-world apps. Continuous learning, collaboration, and code review are key to mastery.
Interview Preparation Tips
- Master core concepts: React, Node.js, Express, MongoDB, REST/GraphQL.
- Build real-world projects: Showcase problem-solving and end-to-end skills.
- Practice coding challenges: Algorithms, data structures, and JS fundamentals.
- Prepare scenario-based questions: Authentication, file uploads, real-time communication.
- Read official documentation: React, Node.js, MongoDB, and Express best practices.
- Mock interviews: Improve articulation and confidence.
Becoming Interview-Ready
- Create a portfolio with live deployed MERN apps.
- Maintain GitHub with clean, well-documented code.
- Prepare answers for common technical questions, MERN stack nuances, and problem-solving scenarios.
- Demonstrate knowledge of modern trends (Next.js, TypeScript, GraphQL).
- Show soft skills: communication, teamwork, and adaptability.
CuriosityTech.in provides guided MERN interview preparation, helping learners gain confidence, practice real-world scenarios, and secure their desired developer roles.



