Introduction
Cloud deployment is crucial for scalable, resilient, and globally accessible applications. FullStack .NET developers can leverage Azure and AWS to host ASP.NET Core backend, SQL databases, and frontend applications, ensuring professional-grade deployment and maintenance.
At CuriosityTech, learners gain hands-on experience deploying real-world FullStack projects in the cloud with best practices for security, scalability, and reliability.
1. Why Deploy to the Cloud?
| Benefit | Description |
| Scalability | Auto-scale based on demand |
| High Availability | Redundant servers ensure uptime |
| Global Access | Users can access apps worldwide |
| Cost Efficiency | Pay-as-you-go pricing models |
| Integration | Native integration with CI/CD pipelines |
2. Azure Deployment for .NET Apps
Step 1: Create Azure App Service
- Go to Azure Portal → App Services → Create
- Select ASP.NET Core runtime, subscription, and region
- Configure resource group and plan
Step 2: Publish from Visual Studio
- Right-click project → Publish → Azure → App Service → Select
- Click Publish
Step 3: Configure Database
- Use Azure SQL Database
- Update appsettings.json with connection string:
“ConnectionStrings” :- { “DefaultConnection” : “Server=tcp:<server>.database.windows.net,1433; Initial Catalog=<db>; Persist Security Info=False; User ID=<user>; Password=<password>; MultipleActiveResultSets=False; Encrypt=True; TrustServerCertificate=False; Connection Timeout=30;” }
Step 4: CI/CD Integration
- Connect Azure DevOps pipeline to App Service deployment task
- Automate build → test → deploy
3. AWS Deployment for .NET Apps
Step 1: Use AWS Elastic Beanstalk
- Create Elastic Beanstalk environment → .NET Core on Windows Server
- Upload publish folder from dotnet publish
Step 2: Configure Database
- Use Amazon RDS (SQL Server)
- Update connection string in appsettings.json
Step 3: CI/CD Deployment
- Use AWS CodePipeline or GitHub Actions
- Automate deployment: commit code → build → test → deploy
Architecture Diagram:
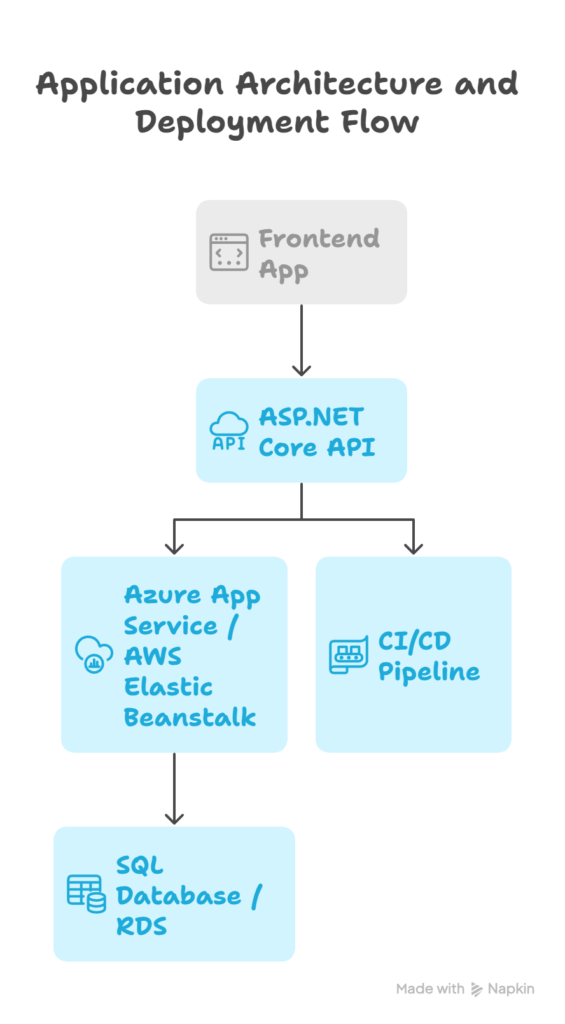
4. Real-World Project: CuriosityTech FullStack Portal
Scenario: Deploy Course Portal on Azure and AWS
- Backend: ASP.NET Core Web API
- Frontend: React Application
- Database: SQL Server / RDS
- CI/CD: Automated pipelines
- Benefits:
- Users access portal globally.
- Easy scaling during high traffic.
- Secure and reliable deployment.
5. Best Practices for Cloud Deployment
- Use environment-specific configurations
- Enable HTTPS & SSL certificates
- Monitor performance using Azure Monitor or AWS CloudWatch
- Implement auto-scaling policies
- Use secrets management (Azure Key Vault / AWS Secrets Manager)
6. CuriosityTech.in Mentorship Insights
- Step-by-step guidance to deploy FullStack .NET applications in Azure and AWS
- Real-world practice with CI/CD pipelines, database integration, and scaling
- Prepares learners for enterprise cloud deployment scenarios
Conclusion
Cloud deployment ensures that Full Stack .NET applications are scalable, reliable, and accessible globally. Leveraging Azure and AWS, developers can automate deployments, manage resources efficiently, and deliver professional-grade applications. At CuriosityTech learners gain hands-on expertise in deploying production-ready Full Stack projects.
The next step is Day 20 – Case Study: Building a Job Portal with .NET Full Stack, where we apply all learned concepts in a real-world Full Stack project



