Abstract
HR is not only about people — it’s about laws, compliance, and ethics. Mistakes in contracts, discrimination, or payroll compliance can result in lawsuits, penalties, and brand damage.
This blog provides a comprehensive guide to legal and ethical frameworks in HR, covering mandatory laws, real case examples, and Curiosity Tech’s practices in ensuring both compliance and fairness.
1. Introduction – Why Compliance Matters
In 2024, a major IT firm in Bengaluru faced a ₹3.5 crore penalty for violating POSH (Prevention of Sexual Harassment) law due to inadequate internal committees. Similarly, a Pune-based startup faced lawsuits for misclassifying employees as “contractors,” evading PF contributions.
These are not isolated incidents. In India, HR managers must navigate a dense legal landscape — from labour codes to ethical codes. Curiosity Tech, headquartered in Nagpur, built a compliance-first HR culture, ensuring they meet both legal obligations and employee rights.
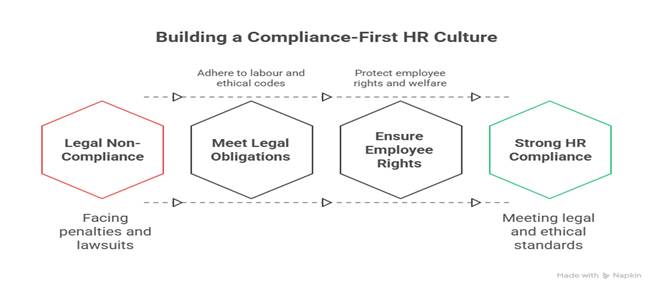
2. Mandatory Legal Frameworks for HR in India (2025)
a) Labour Codes (New Consolidation)
- Code on Wages (2019) – Covers minimum wages, equal pay, and timely payment.
- Industrial Relations Code (2020) – Rules for unions, disputes, and layoffs.
- Social Security Code (2020) – PF, ESI, maternity, gratuity benefits.
- Occupational Safety, Health & Working Conditions Code (2020) – Safety and health measures.
b) Employment Laws
- Contract Act (1872) – Ensures valid employment contracts.
- Shops and Establishment Acts (State-specific).
c) Anti-Discrimination & Equality
- Equal Remuneration Act.
- Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016.
d) POSH Act (2013)
- Mandatory Internal Complaints Committee (ICC).
- Training sessions for awareness.
e) Data Protection & Privacy
- Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023 (DPDPA).
- HR must protect employee data like medical records, Aadhaar, PAN, etc.
3. Ethical Principles in HR
- Transparency – No hidden clauses in contracts.
- Fairness – Equal treatment in promotions & pay.
- Confidentiality – Protecting employee personal and medical data.
- Accountability – Managers accountable for their actions.
- Integrity – HR decisions must prioritize ethics over cost-cutting.
4. Case Law Insights
| Case | Issue | Judgment | HR Lesson |
| Vishaka vs State of Rajasthan (1997) | Sexual harassment at workplace | Supreme Court guidelines → POSH Act | Mandatory ICC, gender sensitization |
| Air India vs Nergesh Meerza (1981) | Gender bias in service rules | Termination based on marital status struck down | No discrimination on marriage/pregnancy |
| Infosys BPO Sexual Harassment Case (2014) | Failure to follow ICC process | Company fined & reputation hit | HR must follow due POSH procedures |
| XYZ Startup vs Employees (2023, Pune) | Misclassification of employees | Labour court ruled in favor of employees | Ensure proper contracts & benefits |

5. Curiosity Tech’s Compliance Model
Curiosity Tech follows a 5C Model for HR Compliance:
| C | Practice |
| Contracts | Standardized, lawyer-vetted employment contracts. |
| Committees | Active POSH ICC + employee grievance redressal. |
| Compliance | Regular audits for PF, ESI, Gratuity. |
| Confidentiality | Strict data handling under DPDPA. |
| Culture | Training sessions on ethics, inclusivity, anti-harassment. |
Result: Zero compliance penalties in 2024–2025 and high trust among employees.
6. Practical Checklist for HR Managers
Maintain updated employee contract templates.
Set up ICC under POSH Act with external member.
Conduct annual compliance audits.
Implement data privacy protocols.
Document all disciplinary actions transparently.
Provide legal awareness training to employees & managers.
7. Ethical Dilemmas in HR – Real Scenarios
Scenario 1: Termination for Poor Performance
- Legal: Follow due process, notice period, and documentation.
- Ethical: Offer reskilling or performance improvement plans first.
Scenario 2: Gender Pay Gap
- Legal: Equal pay law applies.
- Ethical: Regular audits and publishing pay transparency reports.
- Scenario 3: Employee Data Breach
- Legal: Liability under DPDPA.
Ethical: Proactive communication and compensation for affected employees.
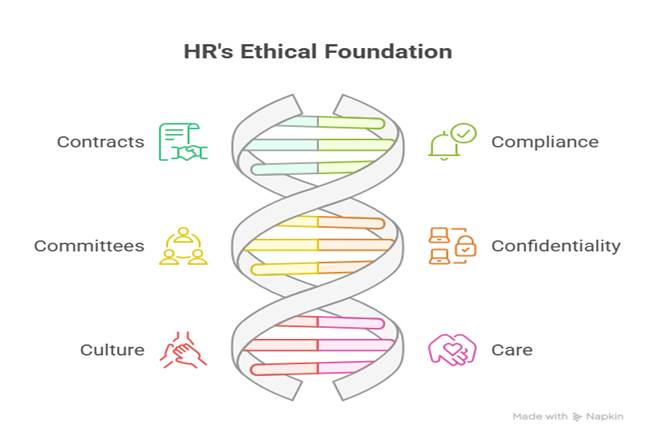
8. Infographic Description – HR Legal-Ethical Wheel
Visualize a wheel with 6 spokes:
- Contracts
- Compliance
- Committees
- Confidentiality
- Culture
- Care (well-being ethics)
The wheel symbolizes that if one spoke breaks, the entire HR system collapses.
9. Global Best Practices
EU GDPR Influence – Even Indian firms working with EU clients must ensure GDPR compliance.
US FMLA (Family Medical Leave Act) – Inspires better leave policies in India.
Japan’s Work-Life Laws – Restrict overtime → Indian firms adopting wellness laws.
Conclusion
Legal and ethical HR is not about fear of lawsuits, but about building trust. Organizations that balance compliance + culture not only avoid penalties but also build strong employer brands.
Curiosity Tech demonstrates that with the 5C Compliance Model, even mid-sized IT firms can ensure global-level HR standards.